Search Results
Results for: 'ED'
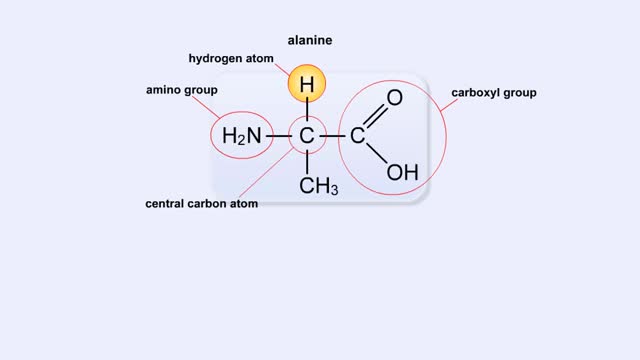
Structure of Amino Acid, Peptide Bonds & Polypeptides
By: HWC, Views: 10518
Here are the molecular formulas of three different amino acids. All amino acids share this backbone. The main difference between every amino acid is the side groups seen here, and these side groups give each of the amino acids their different characteristics. But before we get into that, let's ...
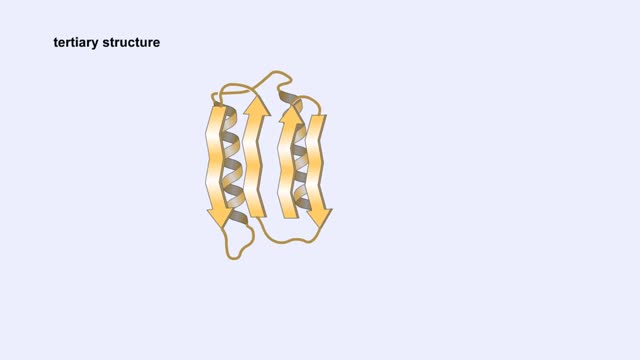
Protein Structure - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
By: HWC, Views: 10808
A protein's first order structure, or primary structure, begins with the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain. The 20 different amino acids can be arranged in an infinite number of sequences. For example, the hormone insulin, which regulates the uptake of glucose from the blood into ce...
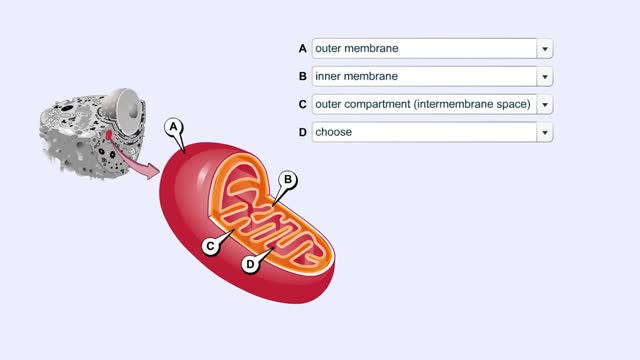
Mitochondrial Structure & ETC Protein Complexes (Protein Complexes and Electron Transport)
By: HWC, Views: 10501
The energy carrying molecules, NADH and FADH2, that were generated in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, now are processed in the mitochondria where their high energy electrons are deposited in an electron chain complex located in the inner mitochondrial membranes. These high-energy electrons now dr...
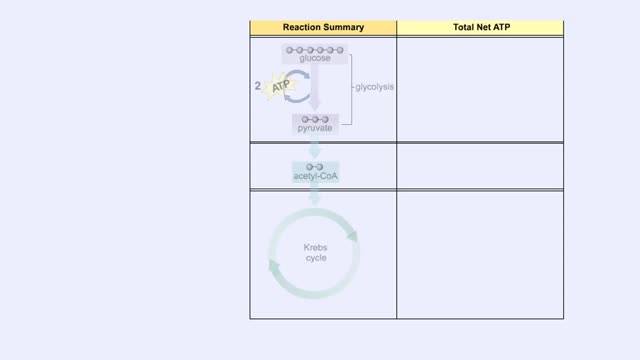
ETC Protein Complexes & Chemiosmosis (Total ATP Production and ATP Synthase)
By: HWC, Views: 10602
You will notice that FADH2 donates two electrons further downstream than NADH. This results in only two protons being pumped across the inner membrane. The final electron acceptor for these transported electrons is oxygen. Oxygen receives these electrons, plus protons from the aqueous matrix. ...
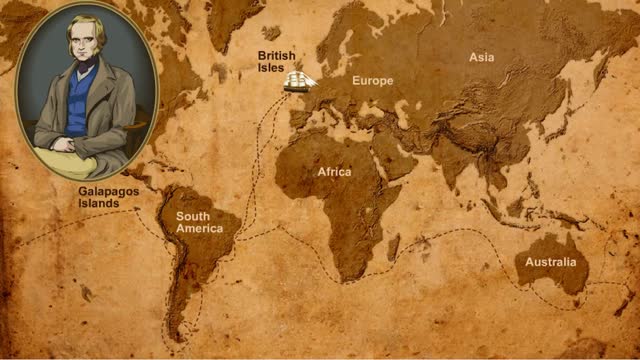
Diversity of Living Creatures - Charles Darwin & the Beagle's Voyage
By: HWC, Views: 10492
As we look around at the living creatures on Earth, we see a great amount of diversity. In some cases, the differences are quite noticeable, like the differences between plants and animals. Some differences are not as easy to see, like the differences between two species of lizard. How did all...
Darwin's Observation (Fossils, Galapagos Islands & Africa ) and Natural Selection (Adaptive Traits)
By: HWC, Views: 10756
Along Darwin's voyage, he made many observations. Each one added to his understanding of how organisms change over time. Darwin was already familiar with fossils and knew that many fossils were very different from living organisms. But, also there were some fossils that were very similar to li...
Natural Selection, Species Isolation and Real World Example
By: HWC, Views: 10318
`Natural selection' is the process in which organisms with adaptive traits survive and breed in greater number than organisms without such traits. Eventually, almost all of the individuals in the population will have the same adaptive trait. This was the concept presented by Charles Darwin in ...
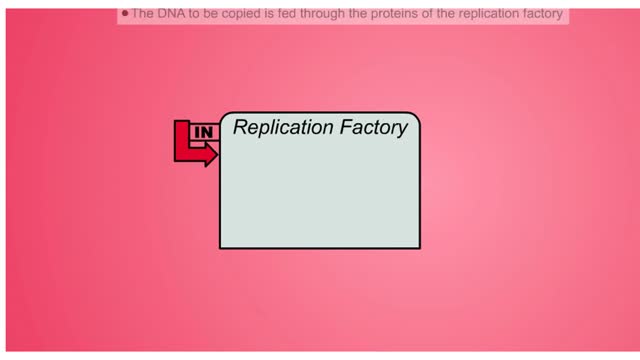
DNA Replication Factory and Protein
By: HWC, Views: 10493
DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) carries all the genetic information needed to re-create itself and to pass on the characteristics of the organism. The “factory” model of DNA replication hypothesizes a specific nuclear structure in which the molecular machinery for replication forks are brou...
By: HWC, Views: 10303
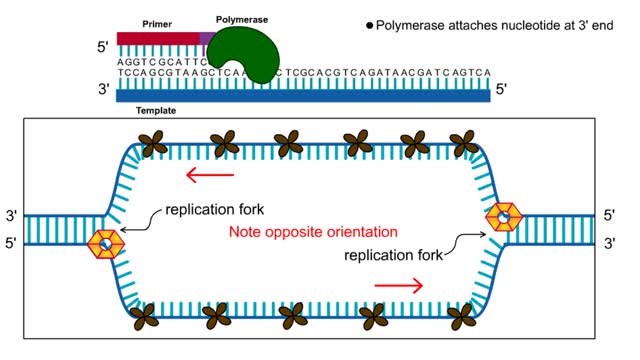
First step: strands are separated • Helicase unwinds the DNA double helix at the replication fork • SSBs coat the single strands to prevent reannealing • Polymerase attaches nucleotide at 3' end • Synthesis is in 5' to 3' direction DNA Polymerase: • Only extends nucleic ac...
Advertisement