Search Results
Results for: 'Chemical control of heart rate'
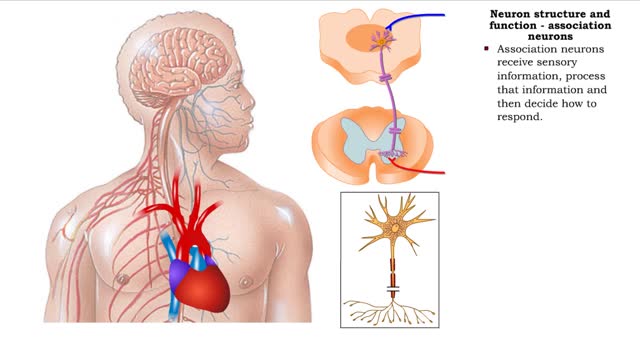
Neuron structure and function - sensory neurons, association neurons & motor neurons
By: HWC, Views: 11203
• The primary function of the nervous system is to provide rapid communication within the body to maintain homeostasis. • This function underlies behaviors, thinking and control of organ functions. • The basic functions of the nervous system are provided by: • Sensory neurons • ...
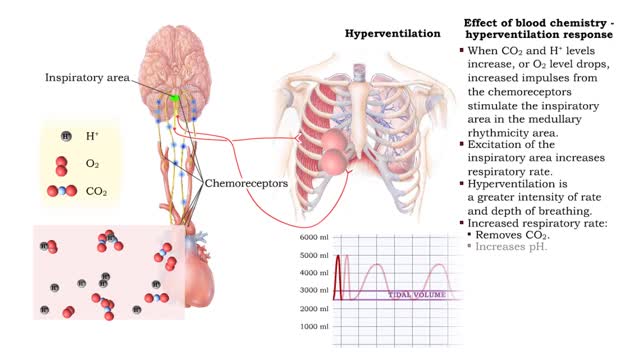
Effect of blood chemistry - stimuli, hyperventilation response and hypoventilation response
By: HWC, Views: 10883
• Respiratory rate is effected by changes in: • Blood pH. • Blood Pco2. • Blood P02. • Chemoreceptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems closely monitor the Fr, CO2 and 02 levels in blood. • Changes in frequency of impulses from Chemoreceptors affect respiratory r...
Labor and Delivery - Infant Cord Apgar
By: Administrator, Views: 468
As soon as your baby is born, a delivery nurse will set one timer for one minute and another for five minutes. When each of these time periods is up, a nurse or physician will give your baby her first "tests," called Apgars. This scoring system (named after its creator, Virginia Apgar) helps t...
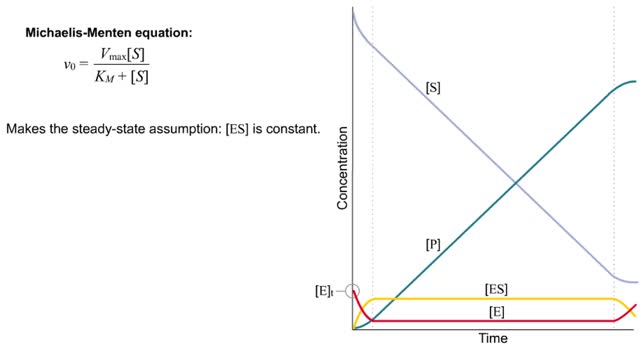
Michaelis–Menten equation & Kinetic parameters
By: HWC, Views: 11063
The Michaelis–Menten equation is the rate equation for a one-substrate enzyme-catalyzed reaction. This equation relates the initial reaction rate (v0), the maximum reaction rate (Vmax), and the initial substrate concentration [S] through the Michaelis constant KM—a measure of the substrat...
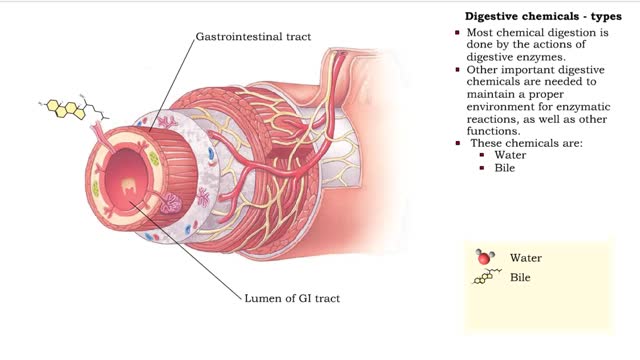
Digestive chemicals - types & enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11270
• Chemical digestion breaks down food as it moves through the digestive tract. • Using enzymes and other digestive chemicals, the process reduces food particles into nutrient molecules that can be absorbed. • Most chemical digestion is done by the actions of digestive enzymes. • O...
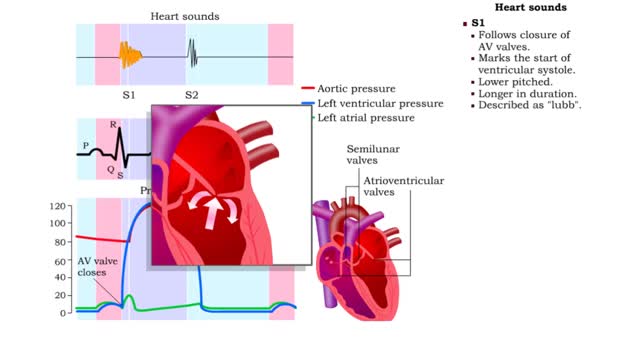
By: HWC, Views: 11230
During a normal, healthy heartbeat, or what we call a cardiac cycle, the top two chambers of the heart, called the atria, contract simultaneously. Then, as they relax, the bottom two chambers, called the ventricles, contract. This explains what happens during a cardiac cycle, but what it doesn't ...
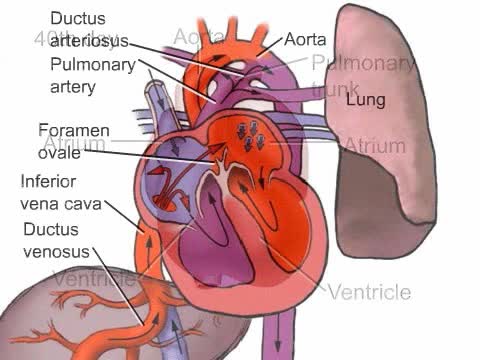
Fetal Development of the Cardiovascular System
By: Administrator, Views: 13944
How the heart develops in the uterus.
By: Administrator, Views: 14044
Pericarditis refers to inflammation of the pericardium, two thin layers of a sac-like tissue that surround the heart, hold it in place and help it work. A small amount of fluid keeps the layers separate so that there's no friction between them.
By: Administrator, Views: 479
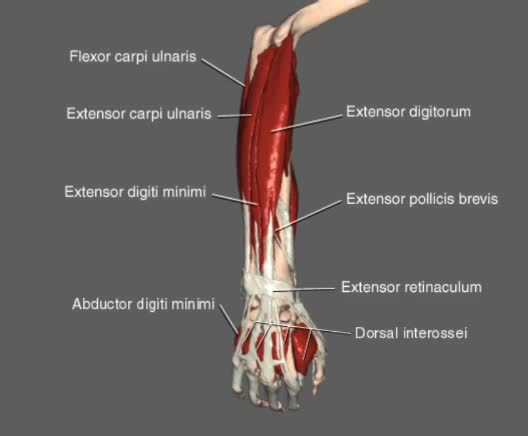
Muscles of both the upper arm and forearm control movement of the forearm. The biceps brachii flex the forearm and work with the supinator of the forearm to rotate it so the palm faces upward. The pronator teres and quadratus control pronation, or rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces do...
Advertisement