Search Results
Results for: 'Reproductive System'
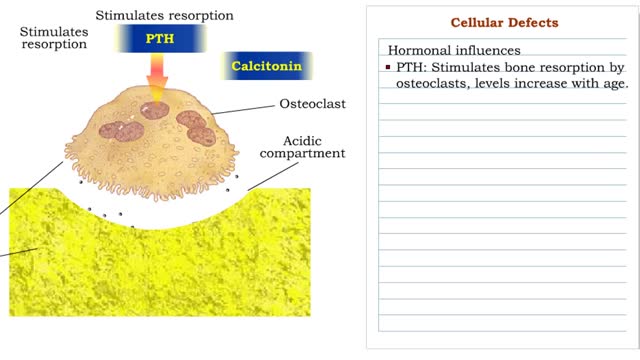
Cellular Defects - Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts and Osteocytes
By: HWC, Views: 10606
■ Metabolically active bone-building cells that secrete astroid. ■ Cover surfaces of newly formed bone and respond to growth stimuli ■ Less responsive to growth factors as the body ages. ■ Contribute to hone loss once their reproductive and biosynthetic potential lessens....
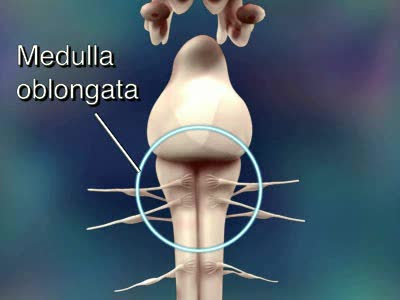
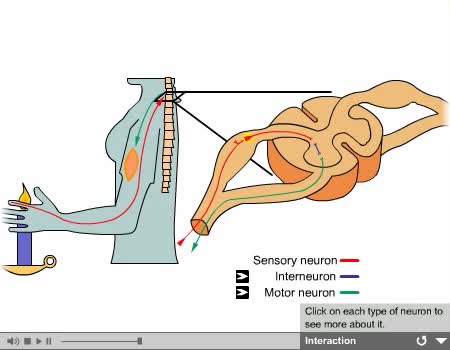
Central Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14089
Consists of the brain and spinal cord. CNS receives impulses from throughout the body processes the information responds with an appropriate action Brain and spinal cord can be divided into: gray matter (unsheathed cell bodies and true dendrites) white matter (myelinated nerve fibers) ...
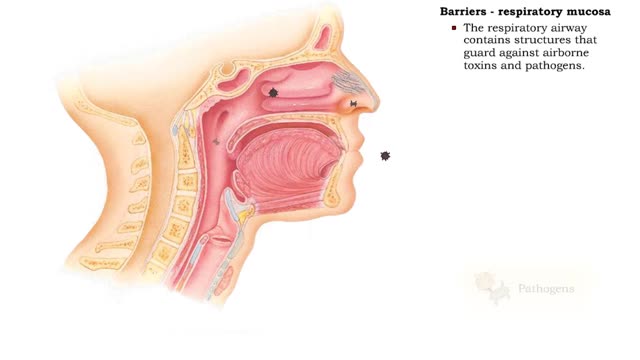
Barriers - eye structures, digestive mucosa, respiratory mucosa & genitourinary mucosa
By: HWC, Views: 11237
• Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and conjunctiva serve to trap microbes preventing their invasion. • Tearing (lacrimation) is a protective mechanism that washes away microbes that attempt to enter the eyes. • Salts, mucus, and lysozymes in tears neutralize substances and bacteria. �...
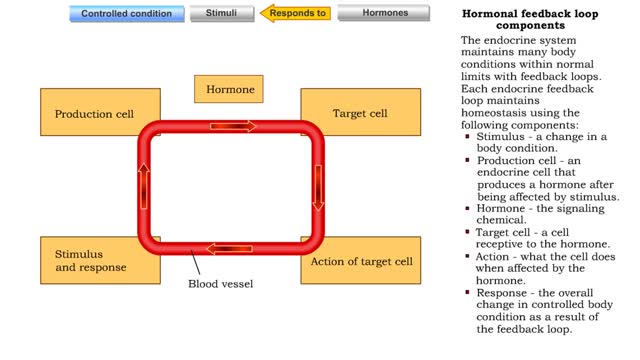
Hormonal feedback loop components
By: HWC, Views: 11094
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: ■ Stimulus - a change in a body condition. ■ Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after b...
By: HWC, Views: 11067
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after b...
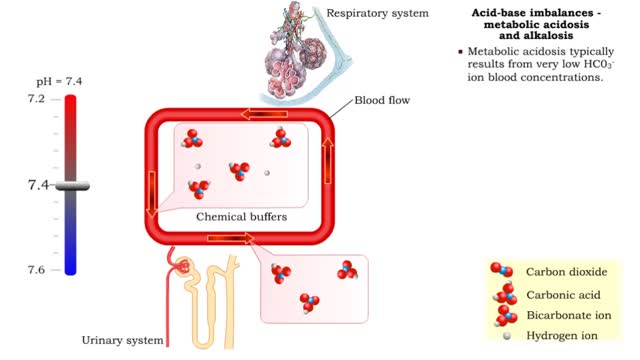
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11163
• When one pH balancing system is affected then the other balancing system attempts to correct, or compensate for, the pH imbalance. - Respiratory acidosis: • Excessive CO2 is present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased secretion of H+ into urine and reabsorption ...
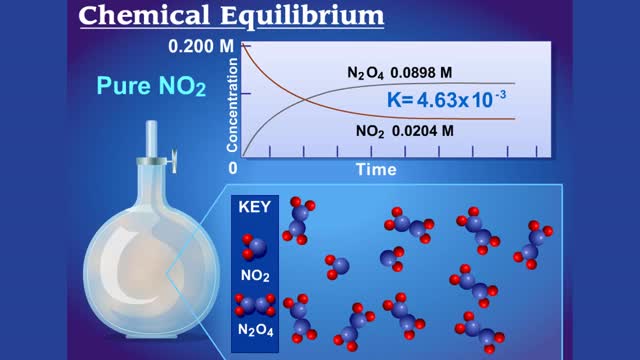
Chemical Equilibrium between N2O4 (colorless gas) and NO2 (brown gas)
By: HWC, Views: 10151
For a system at equilibrium: ◆ both forward and reverse reactions are occurring simultaneously ◆ rate of forward reaction must equal rate of reverse reaction OR Rate forward = Rate reverse ◆ concentrations of reactants and products remain constant with time the equilibrium positio...
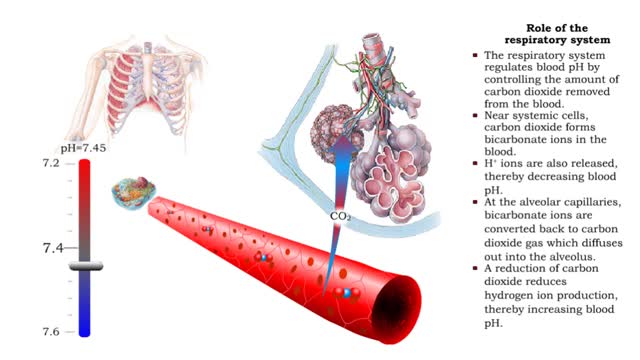
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 11533
• The respiratory system regulates blood pH by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide removed from the blood. • Near systemic cells, carbon dioxide forms bicarbonate ions in the blood. H+ ions are also released, thereby decreasing blood pH. • At the alveolar capillaries, bicarbonate io...
By: Administrator, Views: 14036
Interneurons: - Are called central or associative neurons. - Located entirely within the central nervous system. - They function to mediate impulses between sensory and motor neurons.
Advertisement