Search Results
Results for: 'active site'
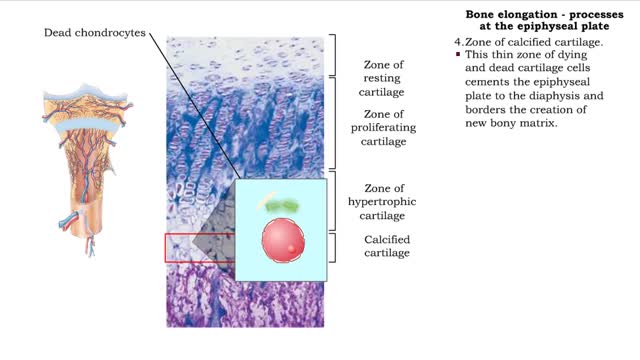
Bone elongation - processes at the epiphyseal plate
By: HWC, Views: 11580
• Interstitial lengthening occurs in only certain bones, primarily those of the appendages. • Such lengthening takes place at the epiphyseal plate, a layer of hyaline cartilage in the metaphysis of a growing bone. 1. Zone of resting cartilage. • Consisting of a hyaline cartilage pa...
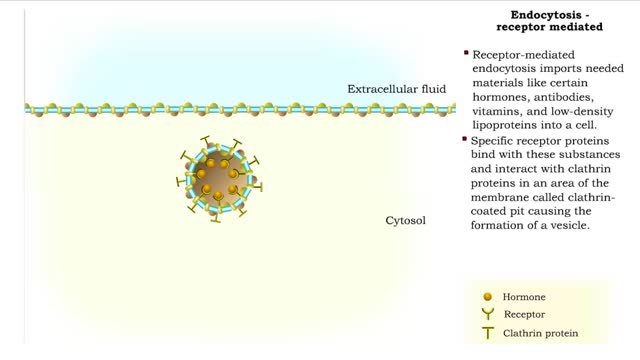
Endocytosis - pinocytosis, receptor mediated and Transcytosis
By: HWC, Views: 11288
Pinocytosis is the process in which a cell "drinks" a tiny droplet Of extracellular fluid, including its solutes. Pinocytosis (Cell Drinking) is the process by which the cell takes in fluids (as well as any small molecules dissolved in those fluids). • The plasma membrane folds inward to...
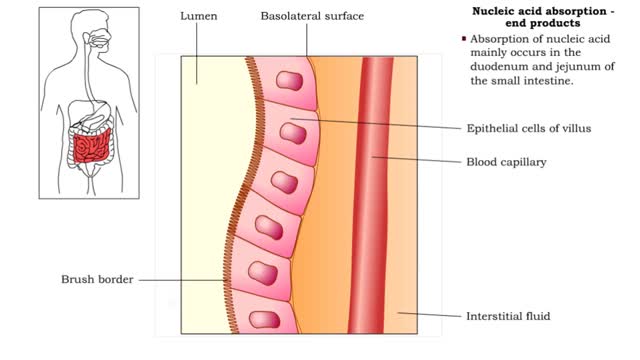
Nucleic acid digestion - brush border enzymes, end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 11208
• Further digestion occurs at the microvilli (brush border) of the epithelial cells of the villi in the small intestine. • Two brush border enzymes complete nucleic acid digestion: • Phosphatases, which catalyze the cleavage of a phosphate to form a nucleoside (nitrogenous base and pent...
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 11063
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
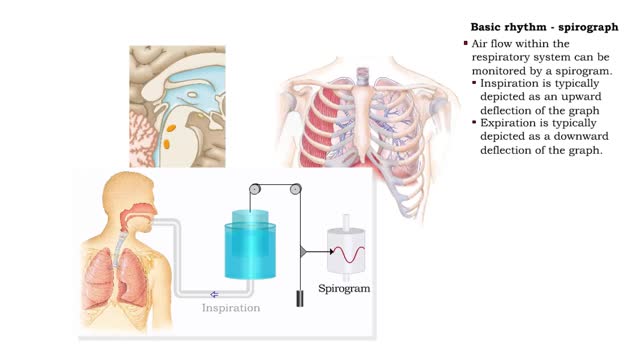
Basic rhythm - control centers in medulla oblongata, spirograph and normal tidal cycle
By: HWC, Views: 11261
• Normal ventilation is rhythmic and involves continuous cycles of inspiration and expiration. • Various regions of the brain closely regulate this rhythmic pattern of ventilation. • The rhythmicity area in the medulla regulates the basic rhythm of ventilation. • The medullary rhy...
By: HWC, Views: 12186
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
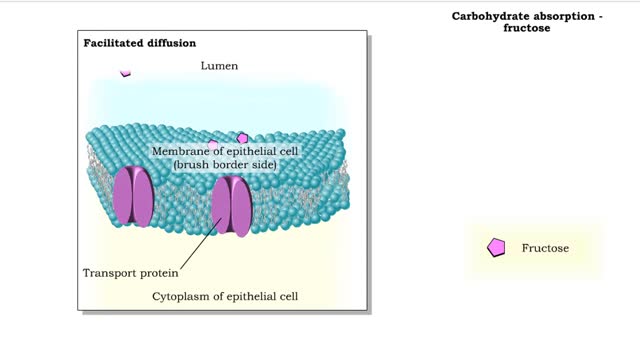
Carbohydrate digestion (brush border enzymes, end products) & Carb absorption (fructose, galactose)
By: HWC, Views: 11302
• Carbohydrate digestion concludes in microvilli of the small intestine, in brush border epithelial cells. Carbohydrate digestion -brush border enzymes • Four brush-border enzymes are involved: • Alpha-dextrinase breaks down alpha-dextrin chains by removing glucose units. • Sucras...
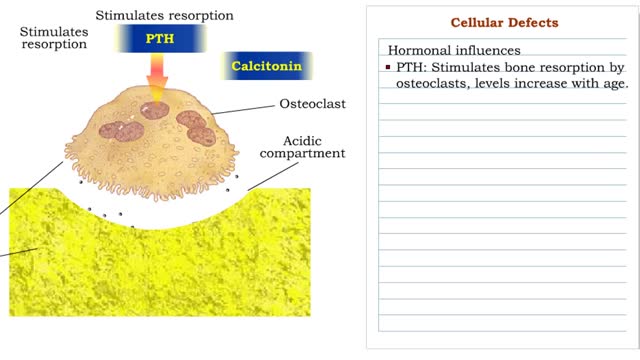
Cellular Defects - Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts and Osteocytes
By: HWC, Views: 11028
■ Metabolically active bone-building cells that secrete astroid. ■ Cover surfaces of newly formed bone and respond to growth stimuli ■ Less responsive to growth factors as the body ages. ■ Contribute to hone loss once their reproductive and biosynthetic potential lessens....
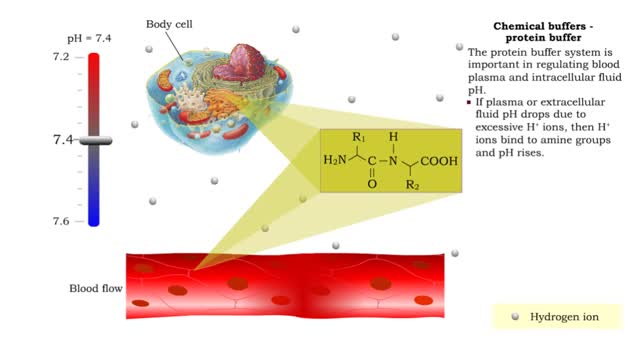
Chemical Buffers - protein buffer, phosphate buffer system and bicarbonate buffer system
By: HWC, Views: 11587
• There are a variety of chemicals in body fluids that prevent the fluids from undergoing large changes in. • These chemicals buffer or regulate fluctuations in H+ concentration. • Chemical buffers: • Bind to H+ ions when there are too many in a solution so pH remains normal. •...
Advertisement