Search Results
Results for: 'homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC active processes passive processes Vesicular transport Active transport Simple diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis concentration gradient bilayer'
Molecules, Membrane Permeability and Structure
By: HWC, Views: 10355
Organisms are not isolated system at equilibrium and need to intake nutrients and electrolytes as remove wastes. Similarly Cells within an organism must also exchange compound by passing them through membrane. The permeability of a membrane is the rate of passive diffusion of molecules th...
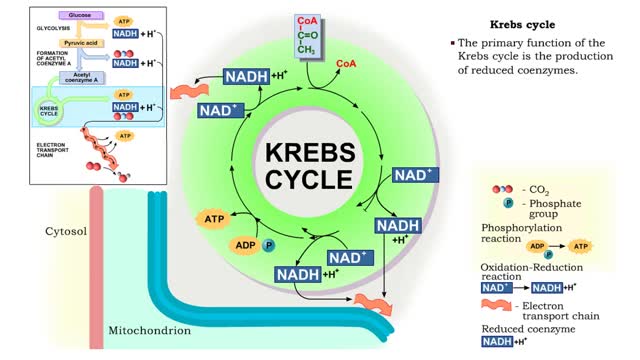
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11080
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
By: HWC, Views: 10025
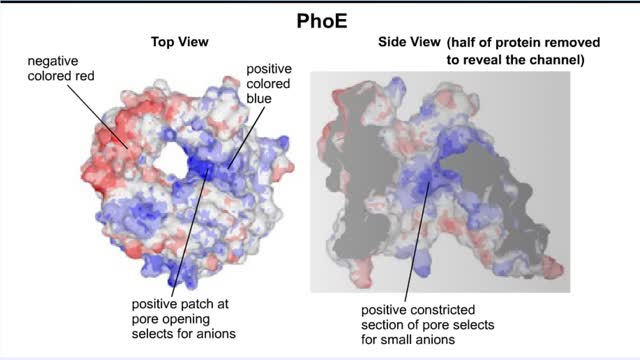
Transmembrane channels, also called membrane channels, are pores within a lipid bilayer. The channels can be formed by protein complexes that run across the membrane or by peptides. They may cross the cell membrane, connecting the cytosol, or cytoplasm, to the extracellular matrix. Membrane po...
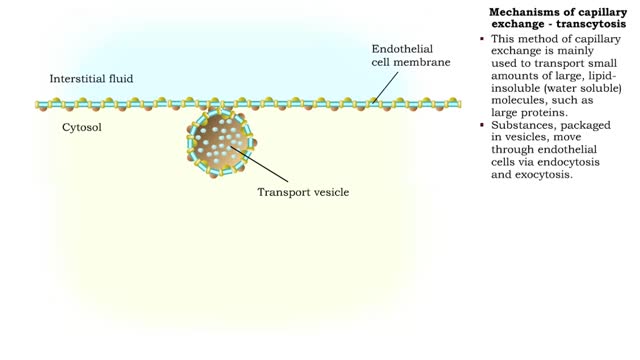
Mechanisms of capillary exchange
By: HWC, Views: 11077
■ The primary role of capillaries is to permit the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells (via interstitial fluid). ■ Oxygen and nutrients move from the blood to the cells. ■ Carbon dioxide and other wastes move from the cells to the blood. The three ba...
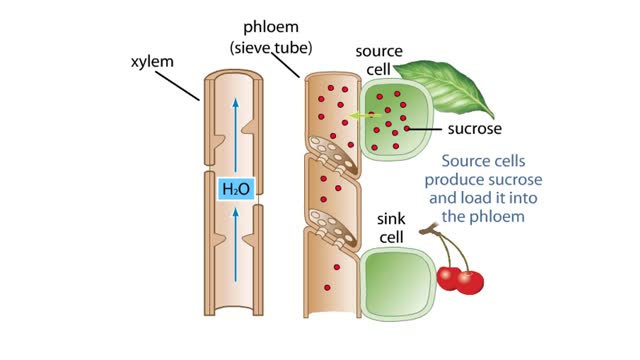
The Pressure Flow Model in a Plant
By: HWC, Views: 10257
The vascular system of plants has two transport tissues, called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports a variety of dissolved substances, including sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. Water in the xylem always moves up, in the direction from th...
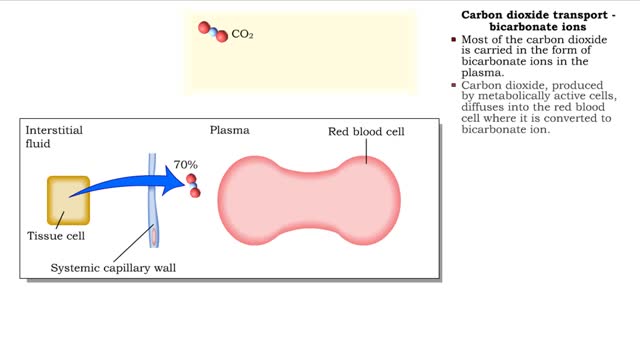
Methods of carbon dioxide transport - carbaminohemoglobin and bicarbonate ions
By: HWC, Views: 10919
• Carbon dioxide is transported three ways: • As bicarbonate ions in the plasma. • Bound to hemoglobin. • As a dissolved gas in the plasma. • A small percent of carbon dioxide is transported as a dissolved gas. • Some of the carbon dioxide is bound to hemoglobin, in the fo...
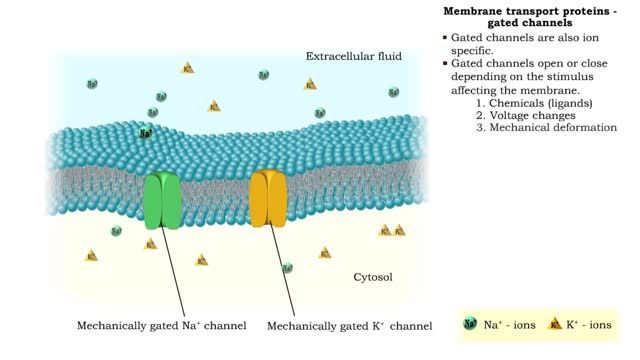
Membrane transport proteins - pores, gated channels and pumps
By: HWC, Views: 11033
• a Three different types of membrane ion transport proteins are required to produce and carry electrical signals: • Pores • Gated channels • Na+/ K+ pump • Pores are always open and allow the diffusion of Na+ and K+ ions across the membrane, down their concentration gradients...
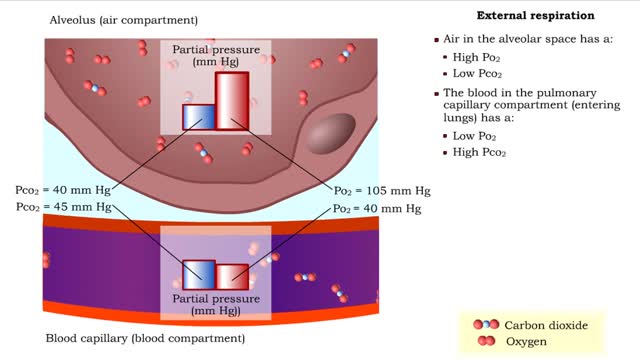
Gas exchange - partial pressure, locations, external and internal respiration
By: HWC, Views: 11051
▪ In a mixture, each individual gas exerts a pressure that is proportional to the concentration of that gas within the mixture. • This part of the total pressure is called a "partial pressure". • A gas moves along the part of the pressure gradient determined by its own concentration. ...
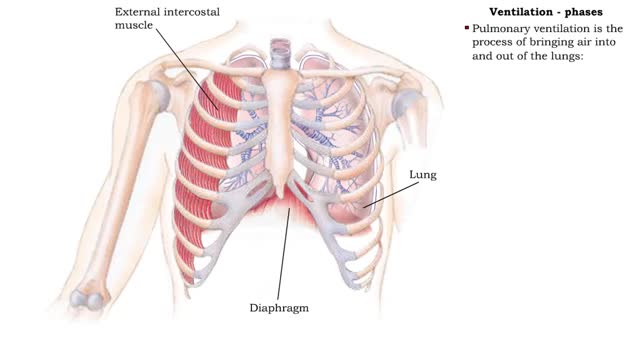
Ventilation - phases and driving forces
By: HWC, Views: 11022
Respiration is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells The combination of 3 processes is required for respiration to occur Ventilation (breathing) External (pulmonary) respiration Internal (tissue) respiration The cardiovascular system assists the respiratory system b...
Advertisement