Search Results
Results for: 'hydrophobic amino acids'
By: HWC, Views: 11871
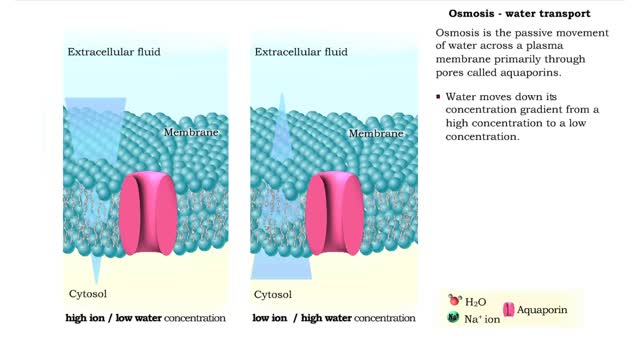
Osmosis is the flow of water down its concentration gradient, across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis is an example of diffusion, which is when molecules tend to distribute themselves evenly in a space. what is a semi-permeable membrane? It is a membrane or barrier that allows some molec...
Lipid digestion - mouth, stomach and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11852
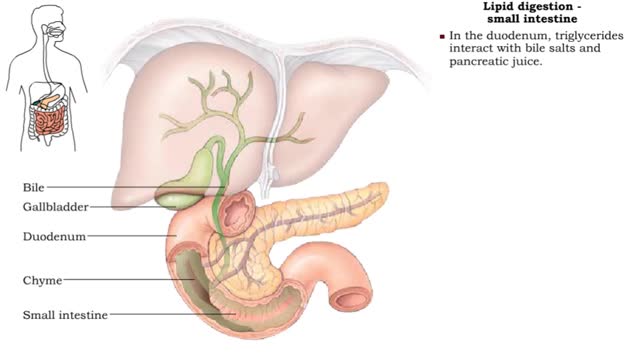
• Lipid digestion takes place primarily in the small intestine; some occurs in the mouth and stomach. • Lipases are enzymes that break down triglycerides and phospholipids. • Lingual and gastric lipases hydrolyze a small amount of triglycerides. • End products are fatty acids and...
Mechanisms of capillary exchange
By: HWC, Views: 11879
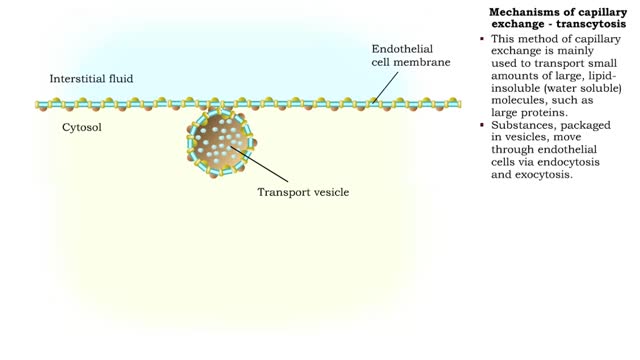
■ The primary role of capillaries is to permit the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells (via interstitial fluid). ■ Oxygen and nutrients move from the blood to the cells. ■ Carbon dioxide and other wastes move from the cells to the blood. The three ba...
Insulin (glucose uptake by body cells), glycogenesis and lipogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 11922
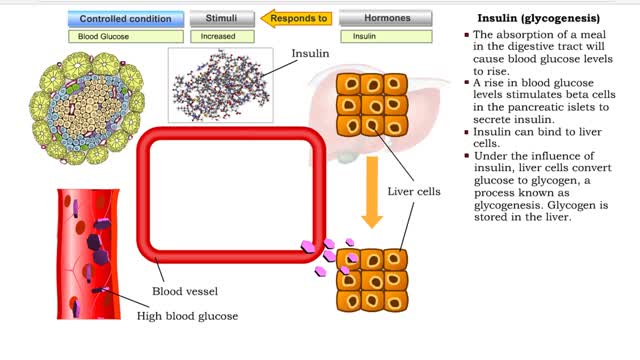
Insulin is the regulator that allows the sugar from the foods we eat (be it a piece of cake or a stick of celery) to enter our tissues and become part of the metabolic process. Insulin is made by the Islets of Langerhans, which are found in the pancreas of every person. As we previously mentio...
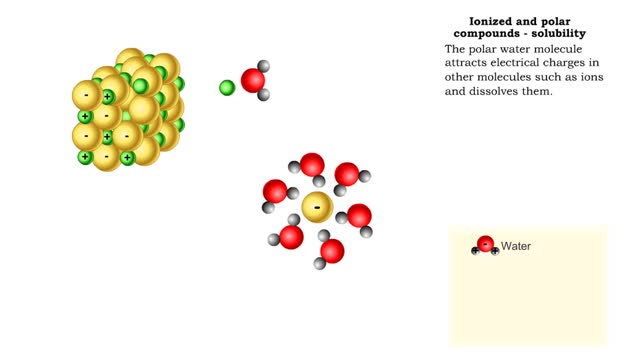
Properties of water -structure of water and polarity (Ionized and polar compounds)
By: HWC, Views: 11838
■ Water transports most of the molecules in the body. ■ The structure of a water molecule allows it to dissolve other molecules. ■ Shared electrons spend more time near the oxygen atom. ■ Oxygen end has a partial negative charge. ■ Hydrogen ends have a partial positive charge....
By: HWC, Views: 11223
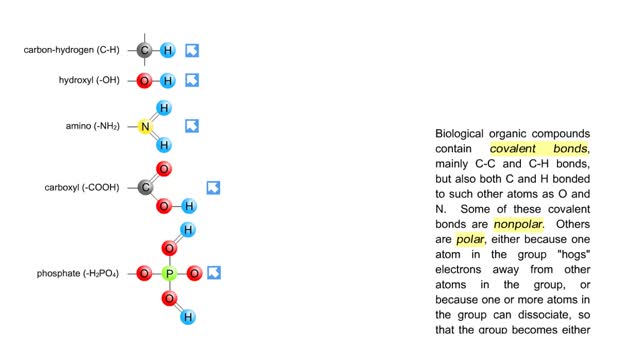
Biological organic compounds contain covalent bonds, mainly C-C and C-H bonds, but also both C and H bonded to such other atoms as O and N. Some of these covalent bonds are nonpolar. Others are polar, either because one atom in the group "hogs" electrons away from other atoms in the group, or...
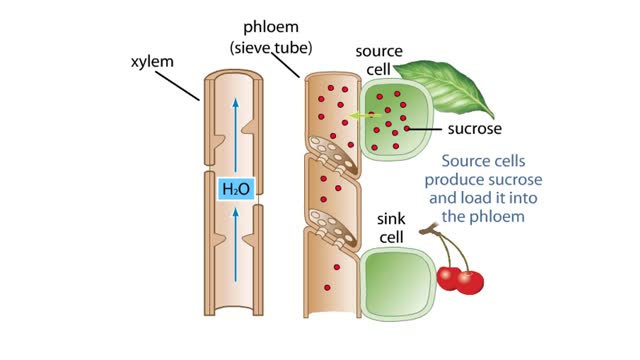
The Pressure Flow Model in a Plant
By: HWC, Views: 11096
The vascular system of plants has two transport tissues, called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports a variety of dissolved substances, including sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. Water in the xylem always moves up, in the direction from th...
By: HWC, Views: 8197
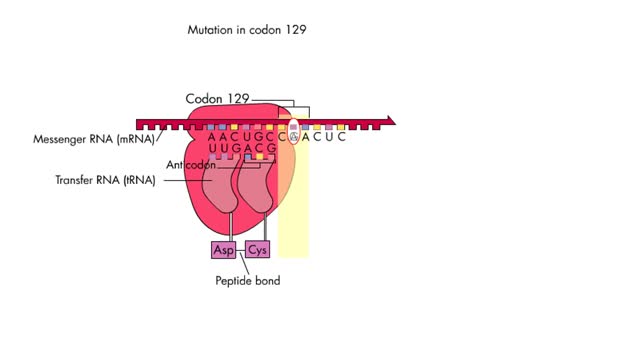
A mutation, which may arise during replication and/or recombination, is a permanent change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. Damaged DNA can be mutated either by substitution, deletion or insertion of base pairs. Mutations, for the most part, are harmless except when they lead to cell death or t...
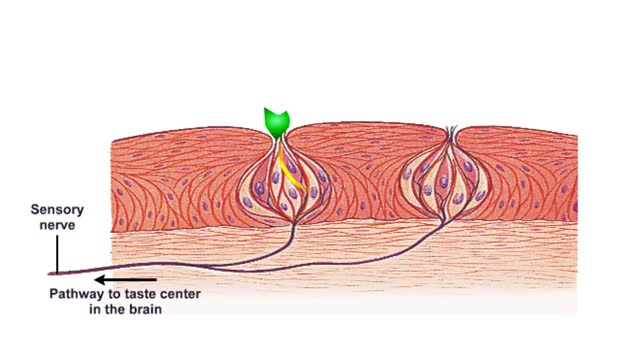
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8582
Do you ever wonder how you can taste the foods you eat? It all starts with taste receptors in your muscular tongue. Taste receptor neurons are found in your taste buds but you are not looking at the taste buds. The raised bumps on the surface of the tongue that you see are specialized epith...
Advertisement