Search Results
Results for: 'strong acid'
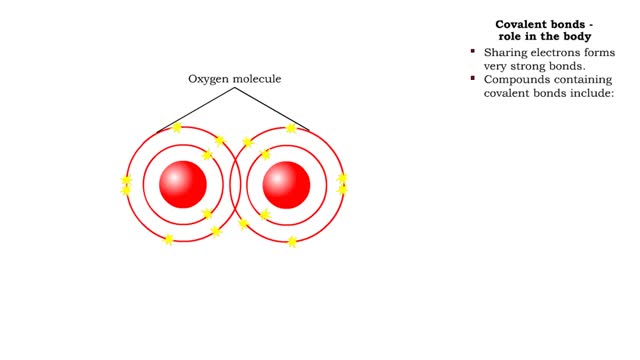
Covalent bonds - role in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11675
A covalent bond is formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This is opposed to an ionic bond, where electrons are actually transferred from one atom to another. Formation • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by sharing electrons. • Two oxygen atoms sharing electrons form on...
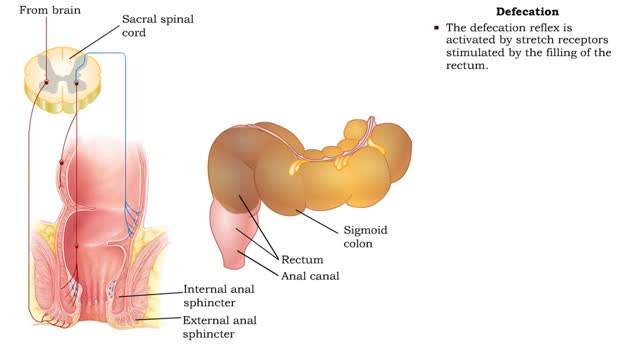
Haustral churning, Gastrocolic reflex and mass peristalsis & Defecation
By: HWC, Views: 12089
• As the cecum becomes filled and distends, a local reflex causes: • Closure of the ileocecal valve. • Activation of haustral churning. • Haustral churning mixes the chyme, which helps absorption of water, salts, and vitamins. • Haustral churning propels the contents of the colo...
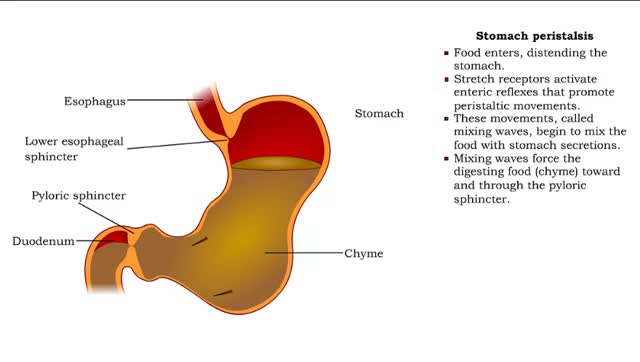
Stomach peristalsis - Movement of Food Through the Small Intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11756
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that moves food to different processing stations in the digestive tract. The process of peristalsis begins in the esophagus when a bolus of food is swallowed. The strong wave-like motions of the smooth muscle in the esophagus carry the food...
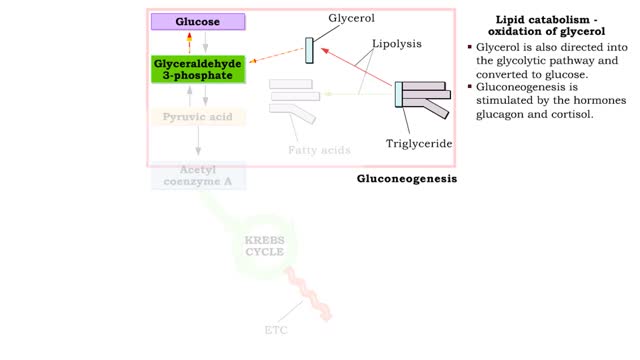
Lipid catabolism ( ketogenesis and oxidation of glycerol) and Lipid anabolism (lipogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 12068
• During excessive beta oxidation, the two-carbon fatty acid fragments are converted into acidic ketone bodies. • Ketosis, the overproduction of ketone bodies, can lead to acidosis (ketoacidosis) of the blood. • After lipolysis, glycerol is converted to pyruvic acid. • Pyruvic aci...
Origin of organelles Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5398
Possible origins of the nucleus and other organelles. Some prokaryotic cells have infoldings of their plasma membrane. These infoldings may have served as channels from the cytoplasm to the cell surface. These membranous folds may have evolved into the endoplasmic reticulum and the nuclear e...
By: HWC, Views: 11240
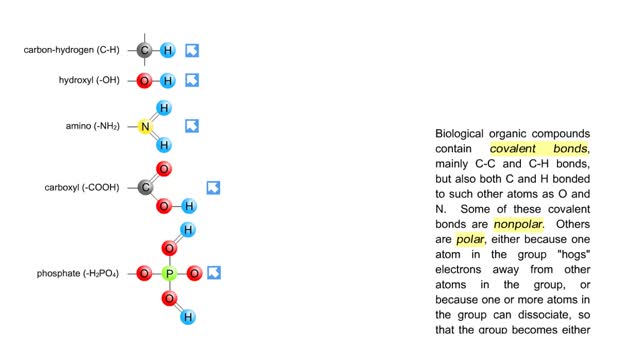
Biological organic compounds contain covalent bonds, mainly C-C and C-H bonds, but also both C and H bonded to such other atoms as O and N. Some of these covalent bonds are nonpolar. Others are polar, either because one atom in the group "hogs" electrons away from other atoms in the group, or...
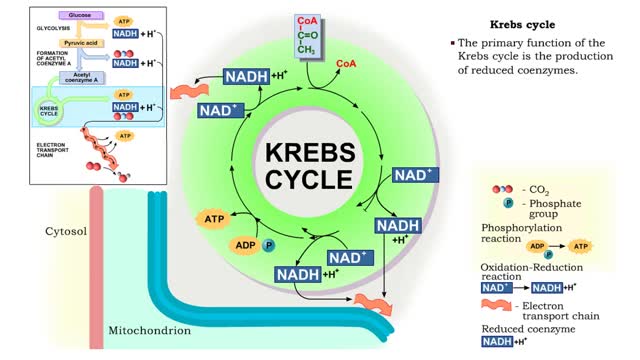
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11984
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
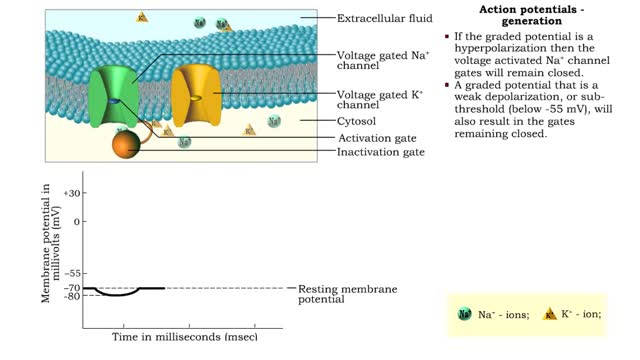
Action potentials - electrical characteristics and generation
By: HWC, Views: 11536
• An action potential is the nervous impulse or signal for long distance communication. Each action potential is generated at the cell's trigger zone. • Action potentials are considered an all-or-nothing phenomena because they are either generated or not. • The generation of an action...
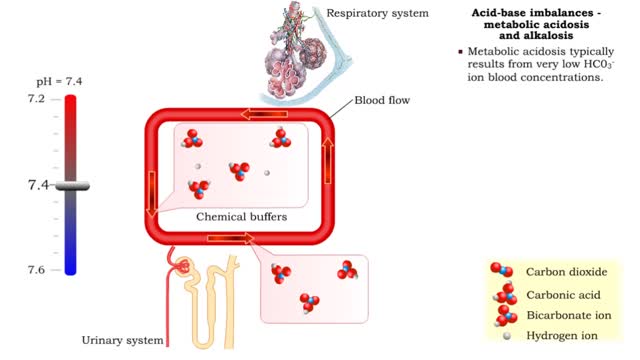
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11868
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
Advertisement