Search Results
Results for: 'Secondary and Tertiary Levels of Protein Structures'
By: HWC, Views: 10335
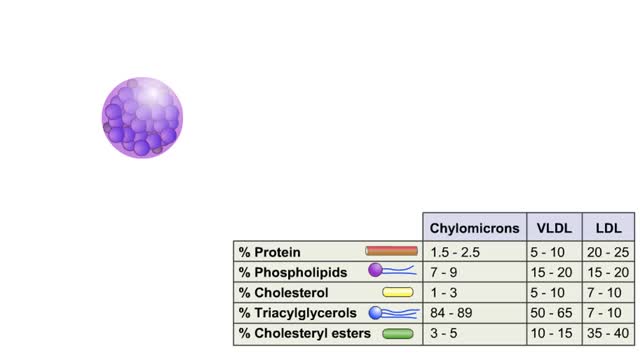
LDL comprises 60–70% of total blood lipoproteins and is responsible for carrying cholesterol particles throughout your body. Having a lot of cholesterol carried by LDL lipoproteins is associated with an increased risk of heart disease. In fact, the higher the level, the greater the risk. ...
Peptide Bond Formation Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4837
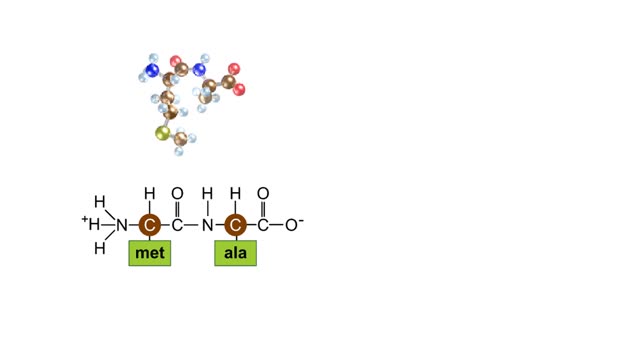
During protein synthesis, peptide bonds link amino acids together in the order specified by DNA instructions. In this case, the first two amino acids in the protein are methionine and alanine. Here are ball-and-stick models of these amino acids. Peptide bond formation is a type of condensatio...
Parathyroid hormone (bone resorption) & Calcitonin (bone deposition)
By: HWC, Views: 10910
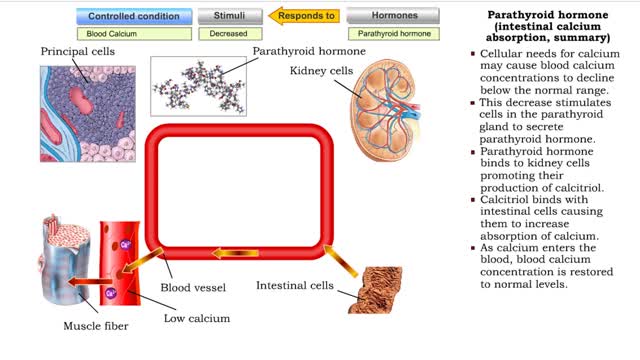
• Cellular needs for calcium may cause blood calcium concentrations to decline below the normal range. • This decrease stimulates cells in the parathyroid gland to secrete parathyroid hormone. • Binding of parathyroid hormone to osteoclasts in bone tissue promotes bone resorption and th...
How do the different types of chromatography work? (No Audio)
By: HWC, Views: 10500
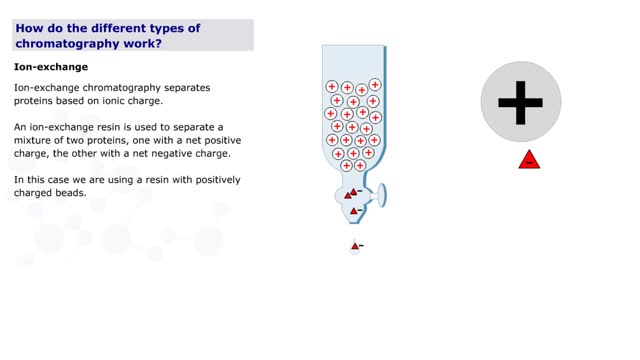
Chromatography is a term for a variety of techniques in which a mixture of dissolved components is fractionated as it moves through some type of porous matrix. A glass column is filled with beads of an inert matrix. The mixture of proteins to be purified is dissolved in a solution and passed ...
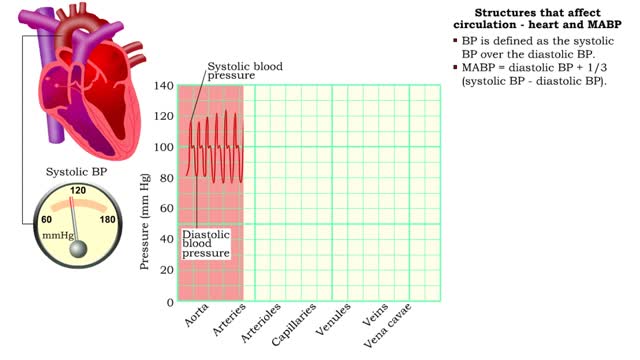
Structures that affect circulation - heart and MABP
By: HWC, Views: 10579
■ BP is defined as the systolic BP over the diastolic BP. ■ MABP = diastolic BP + 1/3 (systolic BP - diastolic BP). ■ MABP accounts for diastole lasting longer than systole; mean is not equidistant between the two pressures.
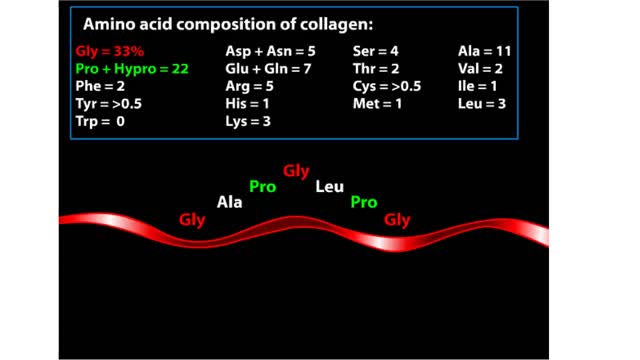
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Proteins
By: HWC, Views: 10556
Proteins are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. The 20 different amino acids used to make all proteins differ only in their side chains, and the properties of these side chains account for the great diversity of protein structure and function. Collagen is an example of how a prote...
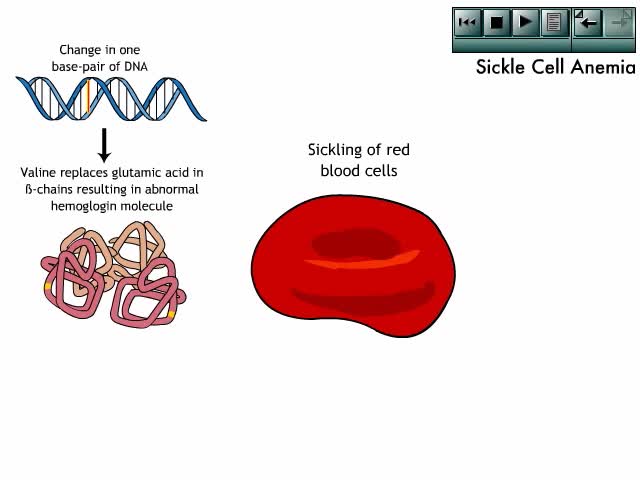
By: Administrator, Views: 14041
The clinical manifestations of sickle cell anemia result from pathologic changes to structures and systems throughout the body.
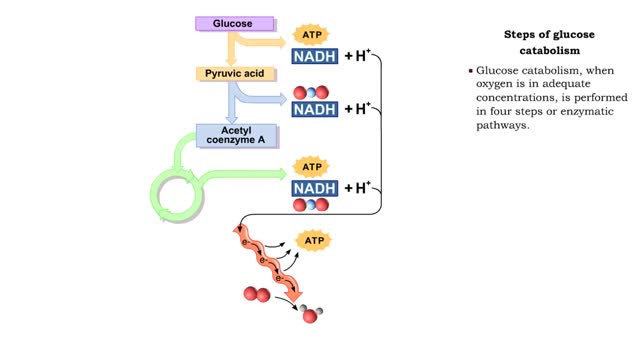
By: HWC, Views: 11273
• During digestion, complex carbohydrates are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides, primarily glucose. • The catabolism of glucose is the primary source of energy for cellular production of ATP. • The anabolism of glucose is important in regulating blood glucose levels. • Glucose cat...
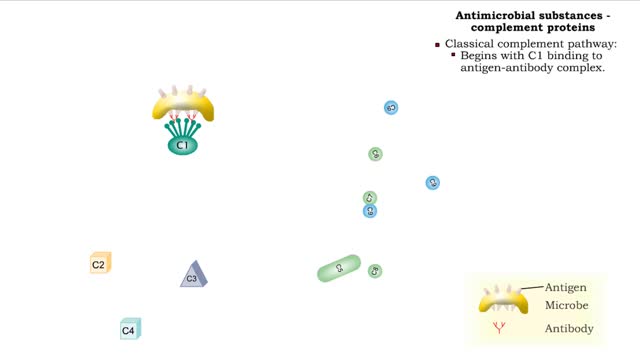
Types of antimicrobial substances (interferons & complement protein)
By: HWC, Views: 11122
• Found in blood and interstitial fluids. • Discourage microbial growth. • Include interferon and complement proteins. • Produced and released by virus-infected lymphocytes. • Enter new cells and inhibit viral replication. • Act against a large variety of viruses (non-speci...
Advertisement