Search Results
Results for: 'protein kinase'
By: HWC, Views: 10703
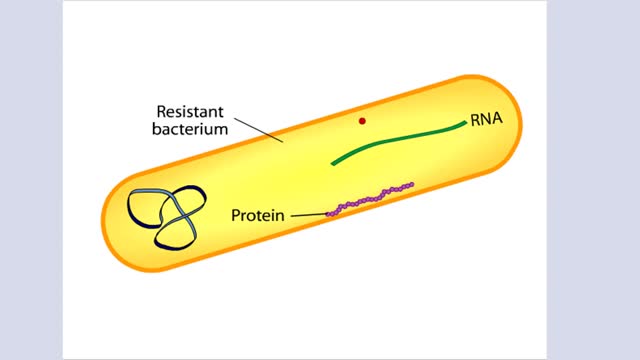
The Crisis in Antibiotic Resistance More than 70 years ago, Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin. A few decades later, when this antibiotic was used in World War II, Fleming's discovery had revolutionized medicine. No longer did people have to die from something as trivial as an infected cut.Y...
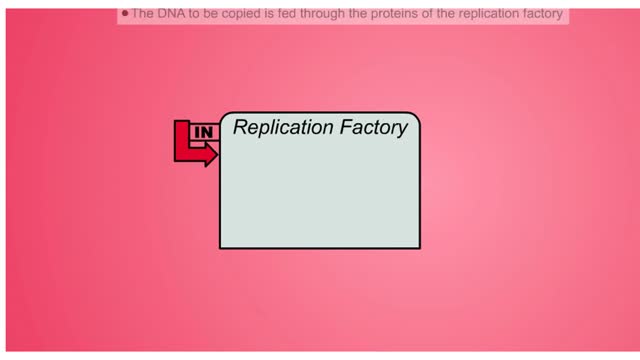
DNA Replication Factory and Protein
By: HWC, Views: 10631
DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) carries all the genetic information needed to re-create itself and to pass on the characteristics of the organism. The “factory” model of DNA replication hypothesizes a specific nuclear structure in which the molecular machinery for replication forks are brou...
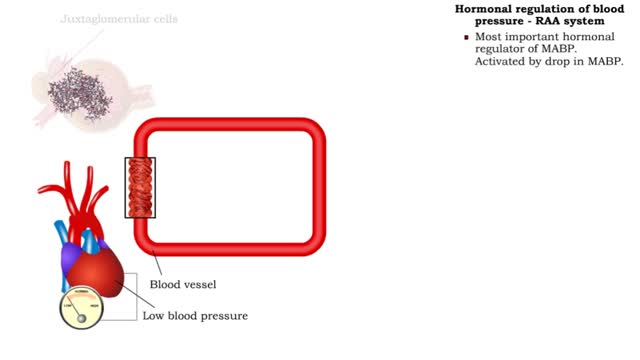
Hormonal regulation of blood pressure - RAA system
By: HWC, Views: 11534
■ Long-term regulation of MABP is under hormonal control. • Hormones that affect blood pressure and volume: the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) system, antidiuretic hormone (ADM), and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP). ■ Most important hormonal regulator of MABP. Activated by drop in...
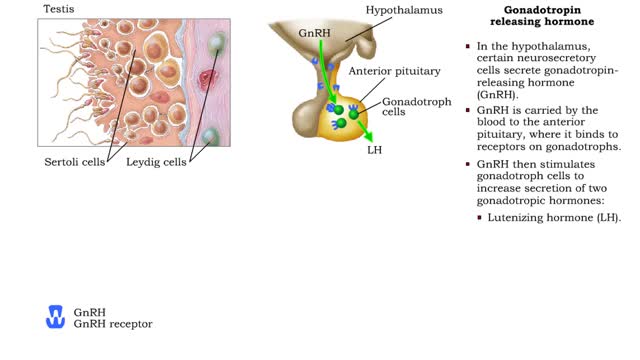
Male Reproductive System - The gonadotropin releasing hormone
By: HWC, Views: 11833
• Hormonal mechanisms that influence male reproductive function involve endocrine tissues contained in the: • Hypothalamus of the brain. • Anterior pituitary. • Testes. • In the hypothalamus, certain neurosecretory cells secrete gonadotropin- releasing hormone (GnRH). • GnRH ...
By: HWC, Views: 9067
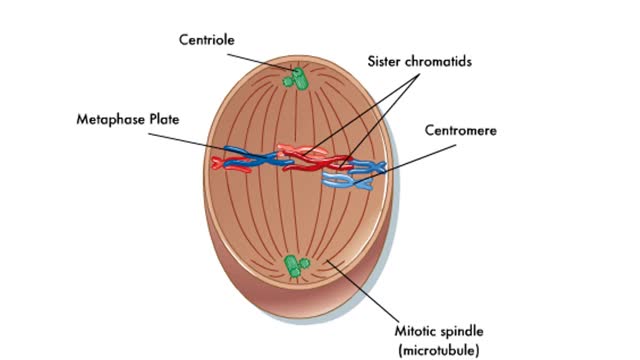
Prophase is the first step in the mitotic process. During prophase, the chromosomes condense. The centrosomes begin to form a spindle and move into position on opposite sides of the cell. Sister chromatids are held together by a protein called cohesin at the centromere. Prometaphase is the sec...
By: HWC, Views: 8440
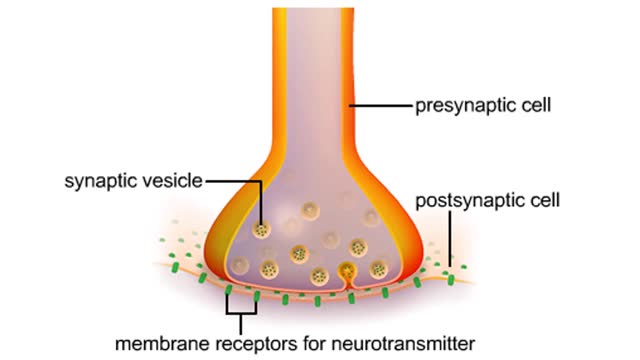
A neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between the axon endings of a motor neuron and a muscle cell. A narrow synaptic cleft separates the presynaptic cell (the motor neuron) from the postsynaptic cell (the muscle cell). The presynaptic cell contains vesicles filled with neurotransmitt...
By: HWC, Views: 10184
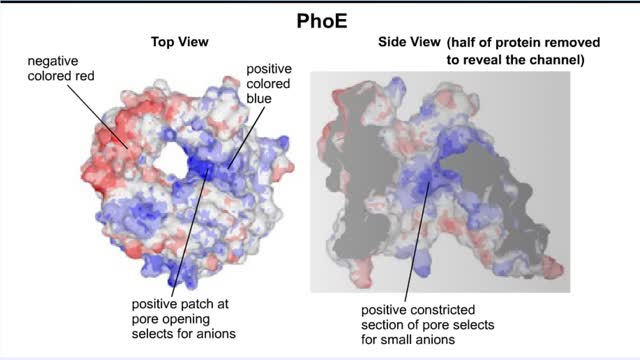
Transmembrane channels, also called membrane channels, are pores within a lipid bilayer. The channels can be formed by protein complexes that run across the membrane or by peptides. They may cross the cell membrane, connecting the cytosol, or cytoplasm, to the extracellular matrix. Membrane po...
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 10784
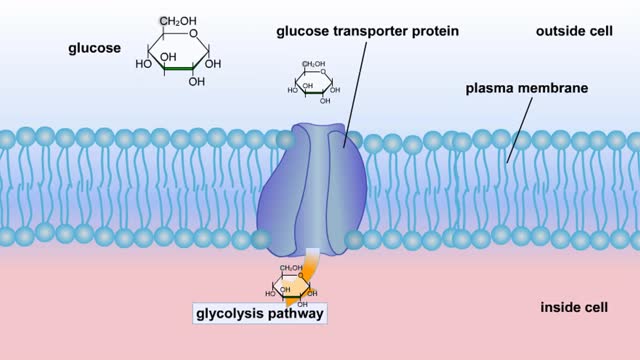
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
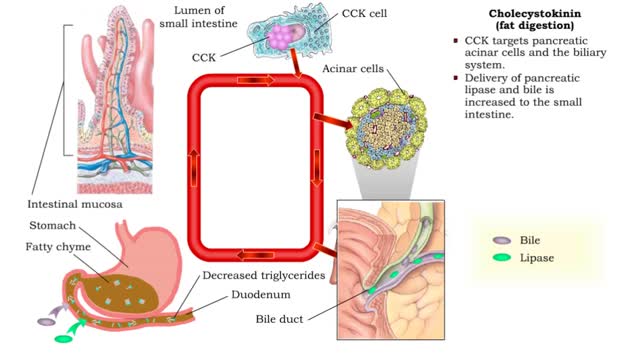
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 10892
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
Advertisement