Search Results
Results for: 'cycle of cellular respiration'
By: HWC, Views: 11691
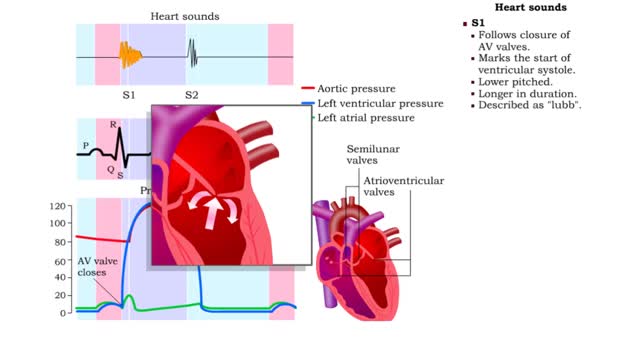
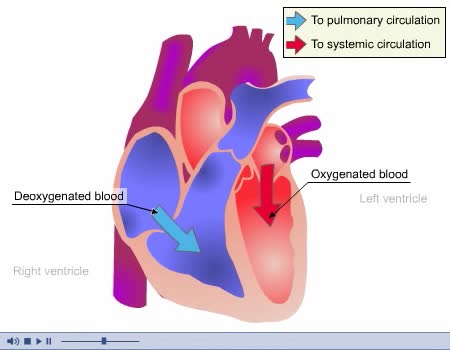
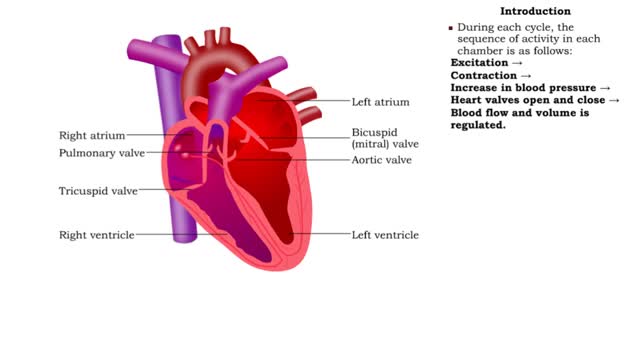
During a normal, healthy heartbeat, or what we call a cardiac cycle, the top two chambers of the heart, called the atria, contract simultaneously. Then, as they relax, the bottom two chambers, called the ventricles, contract. This explains what happens during a cardiac cycle, but what it doesn't ...
Fermentation - When Oxygen Is Absent, Pyruvate to Lactate & Pyruvate to Ethanol
By: HWC, Views: 11203
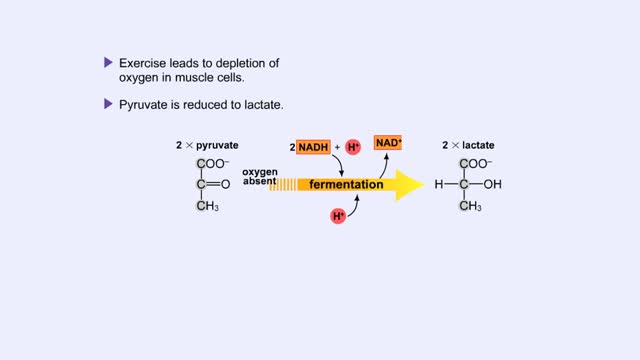
Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis. If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion where further energy yielding reactions of the Krebs cycle will take place. However, if oxygen is not present, pyruvate will enter a pathway called fermentation. This pathway regenerates NAD+ fro...
Lipid catabolism - lipolysis and beta oxidation and oxidation of fatty acids
By: HWC, Views: 12023
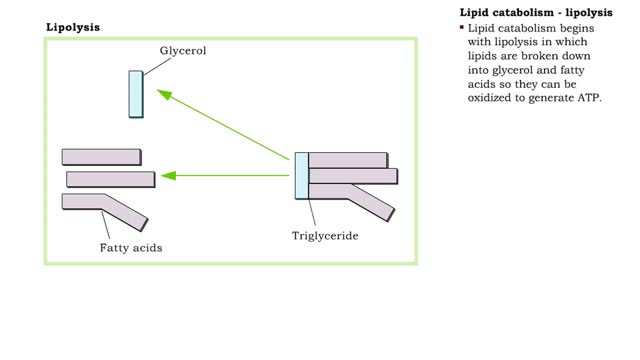
• Digestion hydrolyzes lipids into fatty acids and glycerol. • Fatty acids and glycerol are: • Oxidized to generate ATP. • Used to produce triglycerides that are stored as energy reserves in adipose tissue. • Lipid catabolism begins with lipolysis in which lipids are broken do...
By: Administrator, Views: 14699
Prior to atrial systole, blood has been flowing passively from the atrium into the ventricle through the open AV valve. During atrial systole the atrium contracts and tops off the volume in the ventricle with only a small amount of blood. Atrial contraction is complete before the ventricle begins...
Transcription—A molecular view
By: HWC, Views: 7393
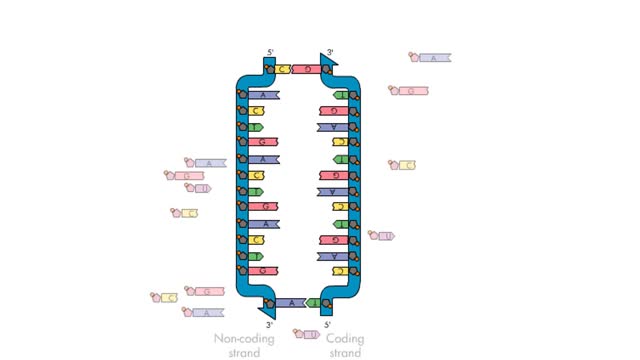
Transcription, as related to genomics, is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence. This copy, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the gene's protein information encoded in DNA. During transcription, a DNA molecule is copied into RNA molecules that are then used to translate...
By: HWC, Views: 10883
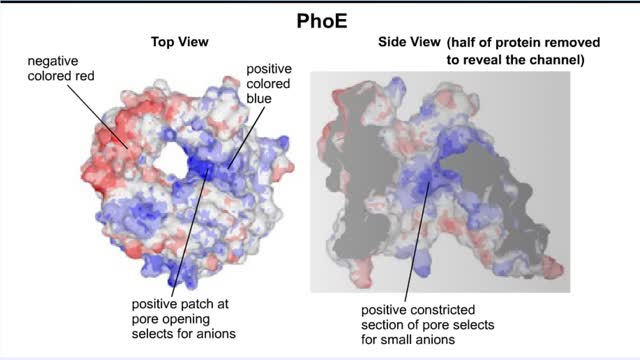
Transmembrane channels, also called membrane channels, are pores within a lipid bilayer. The channels can be formed by protein complexes that run across the membrane or by peptides. They may cross the cell membrane, connecting the cytosol, or cytoplasm, to the extracellular matrix. Membrane po...
By: HWC, Views: 11692
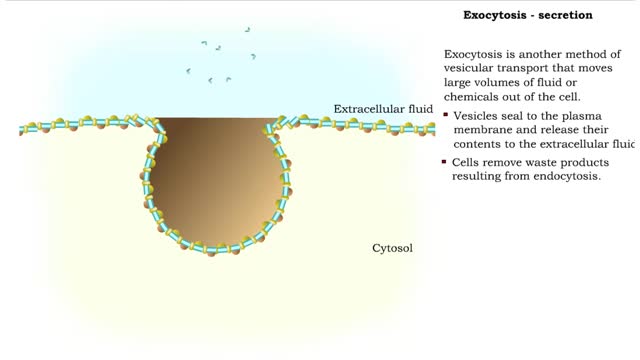
Exocytosis is another method of vesicular transport that moves large volumes Of fluid or chemicals out of the cell. It is a process by which a cell transports secretory products through the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. A examples of cellular secretory products: 1. Secreted protein - enzym...
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates
By: HWC, Views: 11262
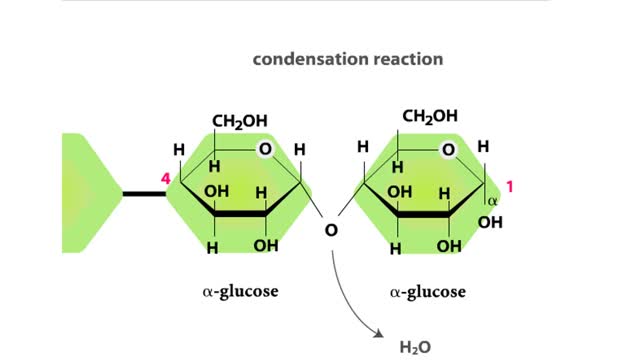
Carbohydrates include simple sugars (monosaccharides) as well as large polymers (polysaccharides). Glucose is a hexose, a sugar composed of six carbon atoms, usually found in ring form. A starch macromolecule is a polysaccharide composed of thousands of glucose units. Glucose molecules can be ...
Electrical changes in the heart
By: HWC, Views: 11535
• ECG: Graph of the voltage changes that occur during the cardiac cycle. • Readings are taken by electrodes placed on the surface of the body. • Electrodes detect voltage changes caused by the electrical activity of the heart. • P wave = atrial excitation (atrial depolarization). ...
Advertisement