Search Results
Results for: 'cycle of cellular respiration'
Energy inputs and release in glycolysis Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5581
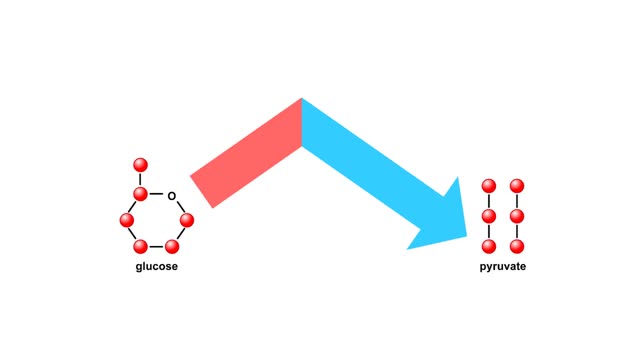
Glycolysis breaks the six-carbon sugar glucose into two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate. The first steps of glycolysis require an energy input in the form of two phosphate-group transfers from ATP. These phosphorylations raise the energy level of glucose enough to allow the energy-releas...
ETC Protein Complexes & Chemiosmosis (Total ATP Production and ATP Synthase)
By: HWC, Views: 11417
You will notice that FADH2 donates two electrons further downstream than NADH. This results in only two protons being pumped across the inner membrane. The final electron acceptor for these transported electrons is oxygen. Oxygen receives these electrons, plus protons from the aqueous matrix. ...
Non-specific disease resistance mechanisms & Skin's defense barriers
By: HWC, Views: 11735
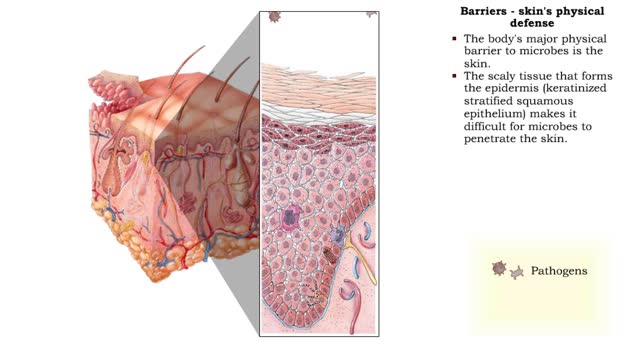
• Non-specific disease resistance acts quickly to fight a wide variety of invaders. • Mechanisms include: • Barriers • Antimicrobial substances • Cellular defenses • Inflammation • Fever Barriers - types • Physical and chemical bathers prevent invasion by micro...
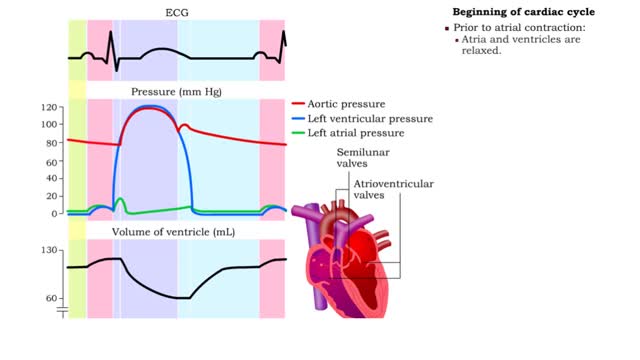
Five phases of cardiac cycle & Atrial contraction
By: HWC, Views: 11771
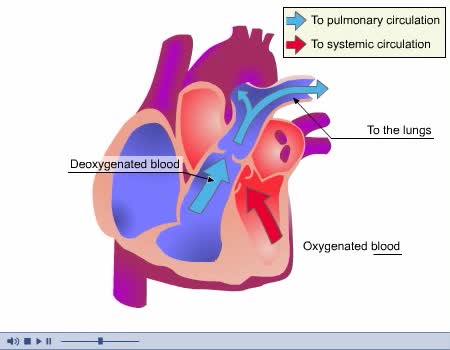
1. Atrial contraction (atrial systole). 2. Isovolumetric (ventricular) contraction. 3. Ventricular ejection. 4. Isovolumetric (ventricular) relaxation. 5. Passive ventricular filling. Beginning of cardiac cycle • Prior to atrial contraction: • Atria and ventricles are relaxed....
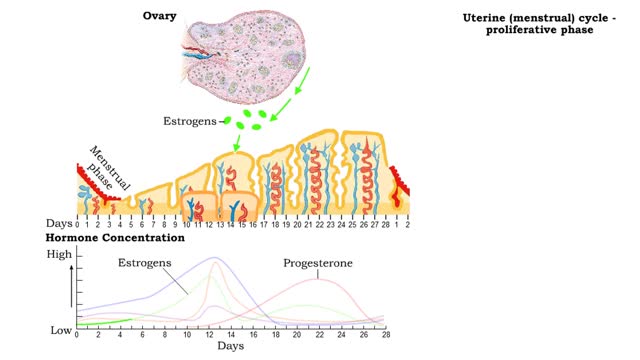
Uterine (menstrual) cycle - phases
By: HWC, Views: 11623
• The uterus goes through a cyclical developmental pattern to be ready for implantation and support of an embryo. • The uterine, or menstrual, cycle is under the control of ovarian horrnones. • The uterine cycle also has three phases: • Menstrual phase • Proliferative phase �...
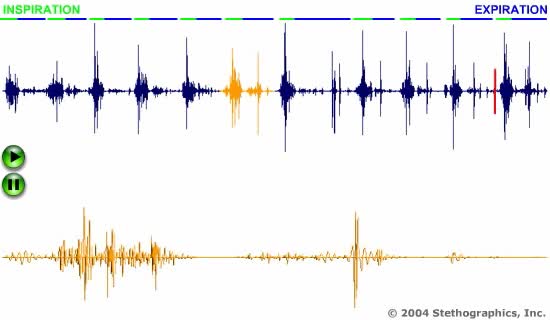
Lung Sounds Animation (2 of 5)
By: Administrator, Views: 429
Respiratory rates for some different age groups: Newborn 30 – 80/min 1st year 20 – 40/min 5th year 20 – 25/min 15th year 15 – 20/min Adult 12 – 20/min
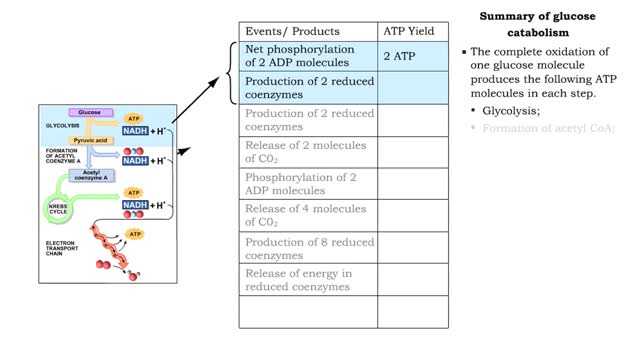
By: HWC, Views: 11956
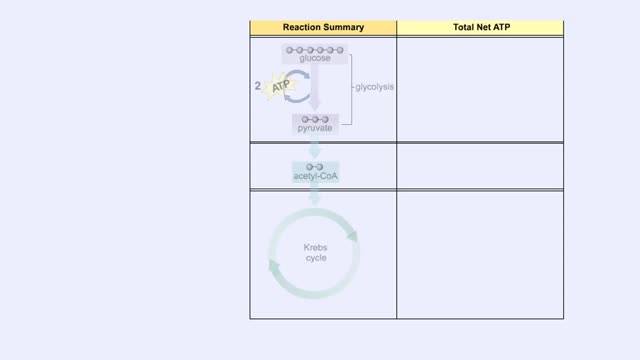
■ The complete oxidation of one glucose molecule produces the following ATP molecules in each step. • Glycolysis; • Formation of acetyl CoA; • Krebs cycle; • Electron transport chain. ■ In addition, glucose catabolism produces six CO2 molecules and water.
By: HWC, Views: 11392
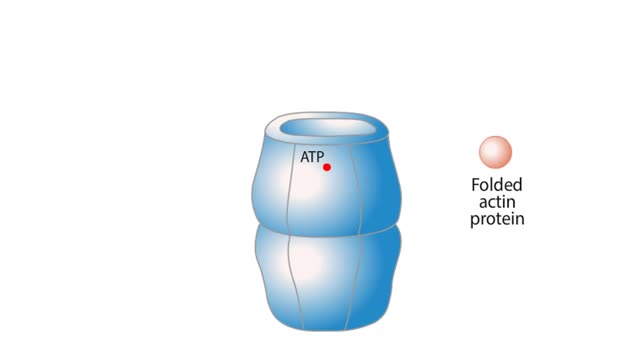
The life cycle of a typical protein begins with its synthesis on a ribosome. As the polypeptide chain grows, molecules of a chaperone protein bind along its length. This prevents misfolding of the nascent polypeptide. ATP binding causes chaperone release. For most proteins, the polypeptide th...
Advertisement