Search Results
Results for: 'ANS'
By: Administrator, Views: 14999
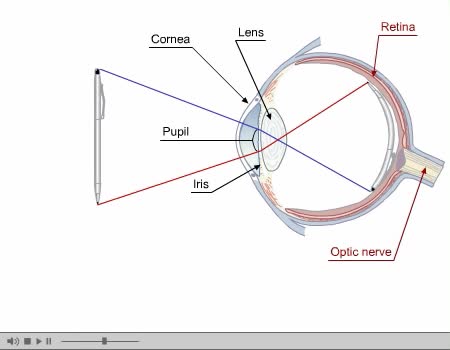
Eye Composed of special anatomical structures that work together to facilitate sight: Cornea Pupil Lens Vitreous body Light stimulates sensory receptors (rods and cones) in the retina or innermost layer of the eye. Vision is made possible through the coordinated actions of nerves that co...
By: Administrator, Views: 14735
Anatomic: Body erect, head facing forward, arms by the sides with palms to the front; used as a standard anatomical position of reference Dorsal recumbent: On back with lower extremities flexed and rotated outward; used in application of obstetric forceps, vaginal and rectal examination, and ...
By: Administrator, Views: 15823
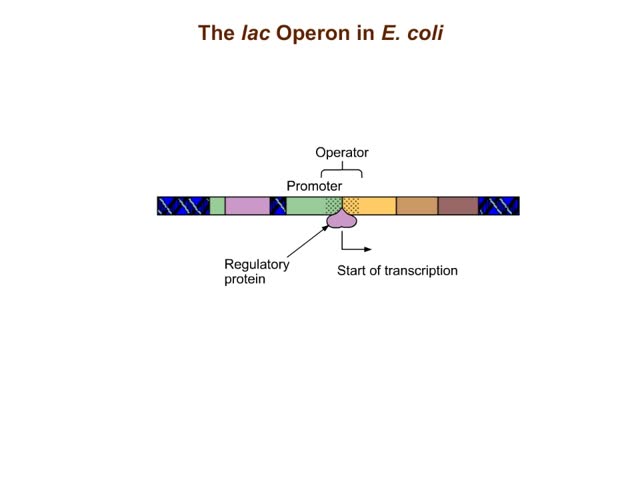
The lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is no...
Embryonic development - Week 3
By: HWC, Views: 11770
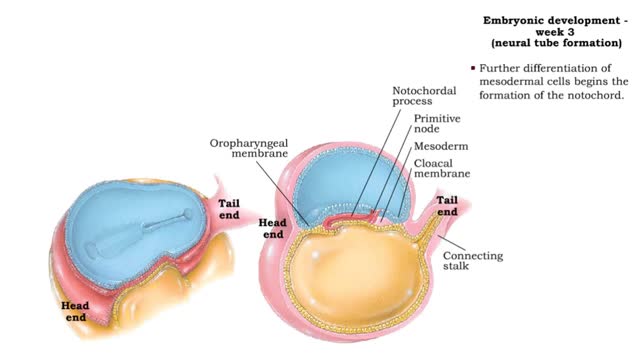
Week 3 (gastrulation) • Three primary germ layers are formed which provide cells for organ formation in the following months. • These germ cell layers are formed by a process known as gastrulation, which involves rearranging epiblast cells. • As cells from the epiblast migrate, a fain...
By: HWC, Views: 11811
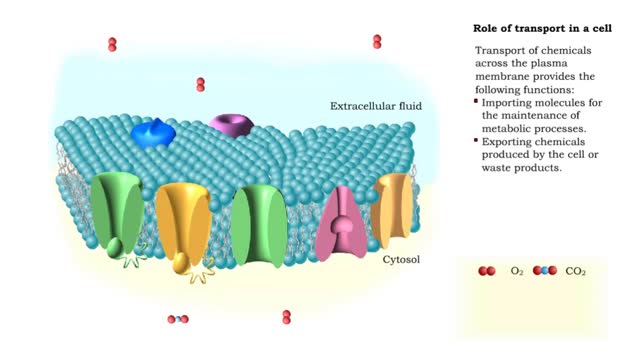
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
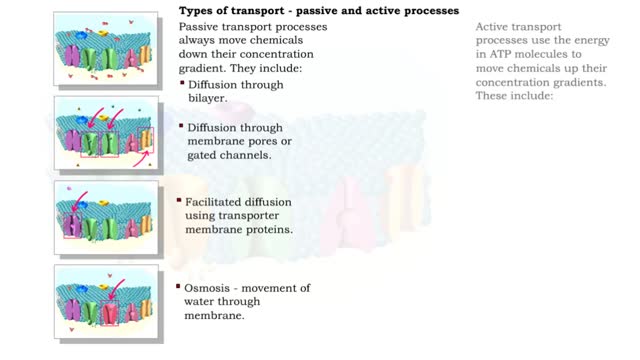
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 12005
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
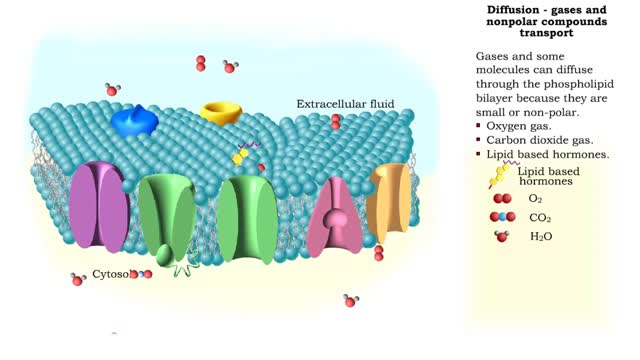
Simple Diffusion - gases and nonpolar compounds transport
By: HWC, Views: 12206
Gases and some molecules can diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer because they are small or non-polar. Oxygen gas. Carbon dioxide gas. Lipid based hormones. Plasma membranes are selectively permeable: The lipid bilayer is always permeable to small, nonpolar, uncharged molecules ...
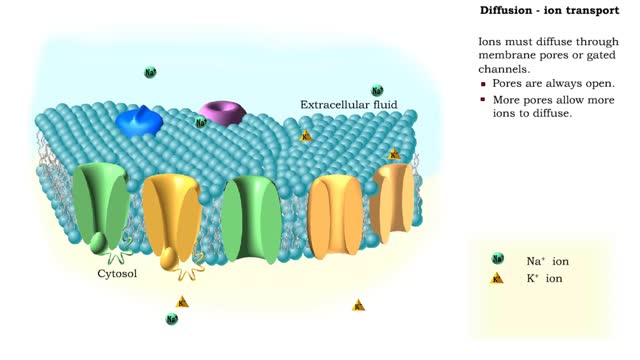
Simple Diffusion - Ion transport
By: HWC, Views: 11717
In the process of diffusion, a substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until its concentration becomes equal throughout a space. Ions must diffuse through membrane pores or gated channels. Pores are always open. More pores allow more ions...
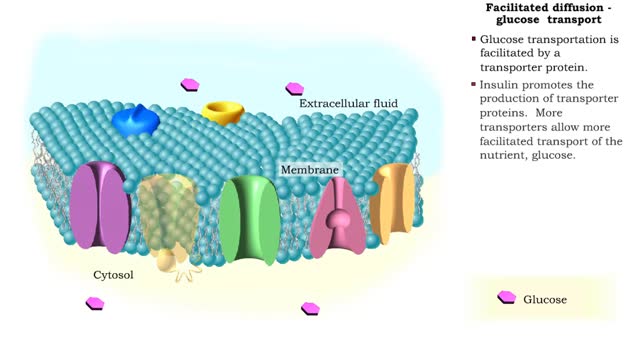
Facilitated Diffusion - Glucose transport
By: HWC, Views: 11939
Transmembrane proteins help solutes that are too polar or too highly charged move through the lipid bilayer The processes involved are: Channel mediated facilitated diffusion Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein i...
Advertisement