Search Results
Results for: 'Major Elements in Biological Molecules'
The pH scale - Strong acids and Weak acids
By: HWC, Views: 11238
The pH scale • Expresses concentration of H+. • range: 0-14. • 7 is neutral. • Less 7 is acid. • greater 7 is basic (alkaline). Strong acids - role in the body ■ In strong acids all molecules dissociate. ■ HC1 is highly acidic and found only in the stomach. • H...
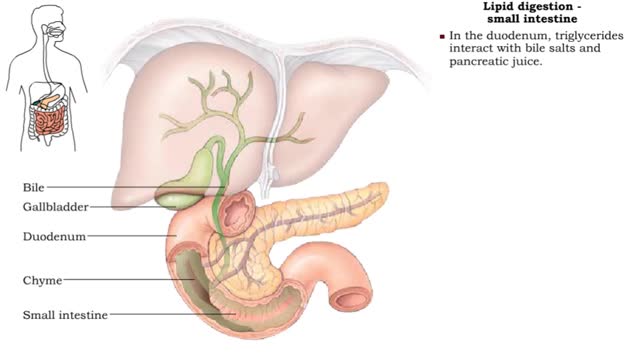
Lipid digestion - mouth, stomach and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11276
• Lipid digestion takes place primarily in the small intestine; some occurs in the mouth and stomach. • Lipases are enzymes that break down triglycerides and phospholipids. • Lingual and gastric lipases hydrolyze a small amount of triglycerides. • End products are fatty acids and...
By: HWC, Views: 10325
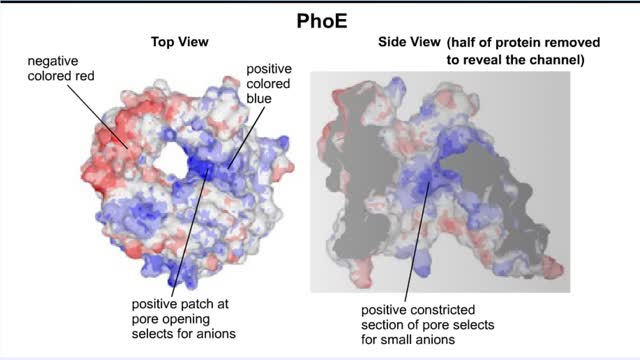
Transmembrane channels, also called membrane channels, are pores within a lipid bilayer. The channels can be formed by protein complexes that run across the membrane or by peptides. They may cross the cell membrane, connecting the cytosol, or cytoplasm, to the extracellular matrix. Membrane po...
By: Administrator, Views: 14513
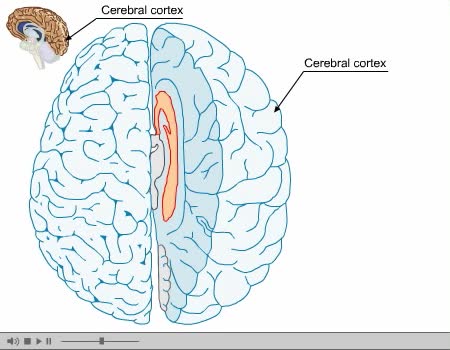
The cerebral cortex (plural cortices), also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain, in humans and other mammals. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemisp...
By: HWC, Views: 10766
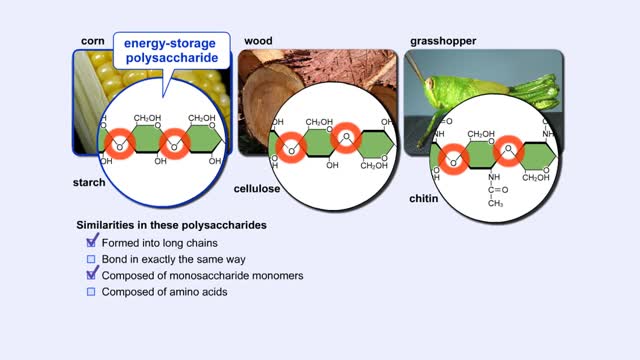
More complex sugars are called polysaccharides (from "poly" meaning "many" and "saccharum" meaning "sugar"). Many things in nature are made of polysaccharides. Here we show one of the polysaccharides in corn, another in wood, and another in the exoskeletons of insects like grasshoppers. How are a...
Transferring genes into plants Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8571
Researchers extract DNA from an organism that has a trait they want to introduce into a plant. The genetic donor can be a bacterial cell, a plant cell. or even an animal cell. The desired gene will be transferred into a plasmid, a small circle of bacterial DNA. The gene is cut out of th...
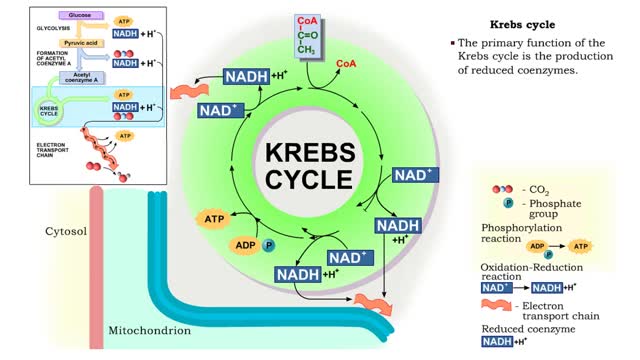
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11397
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
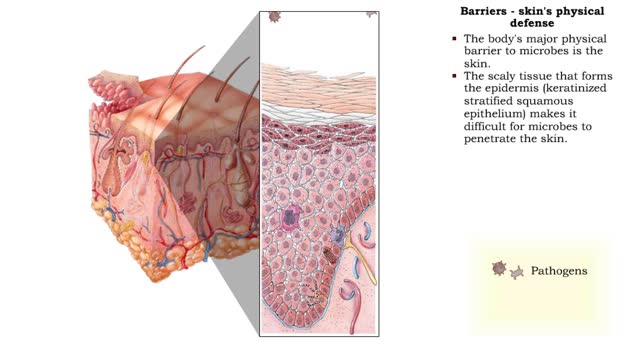
Non-specific disease resistance mechanisms & Skin's defense barriers
By: HWC, Views: 11192
• Non-specific disease resistance acts quickly to fight a wide variety of invaders. • Mechanisms include: • Barriers • Antimicrobial substances • Cellular defenses • Inflammation • Fever Barriers - types • Physical and chemical bathers prevent invasion by micro...
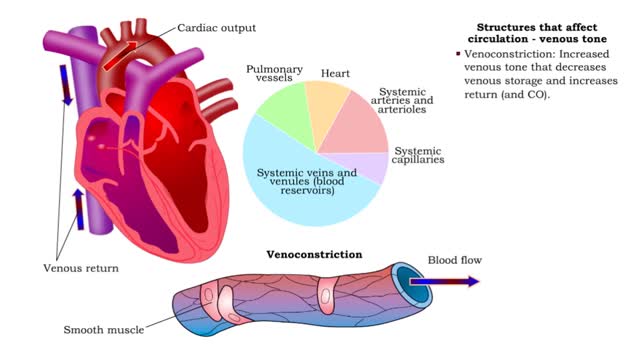
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys and blood volume and skeletal muscle pumping
By: HWC, Views: 11832
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption Increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
Advertisement