Search Results
Results for: 'Major Elements in Biological Molecules'
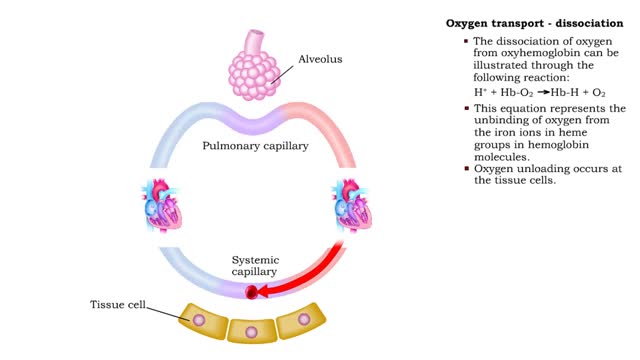
Oxygen transport: association and dissociation & Factors that affect hemoglobin's saturation with O2
By: HWC, Views: 11060
• The production of oxyhemoglobin can be illustrated through the following reaction: 02 + Hb-H --) Hb-02 + H+ • This equation represents the binding of oxygen to the iron ions in heme groups in hemoglobin molecules. • Oxygen binding or loading occurs at the lungs • The dissociatio...
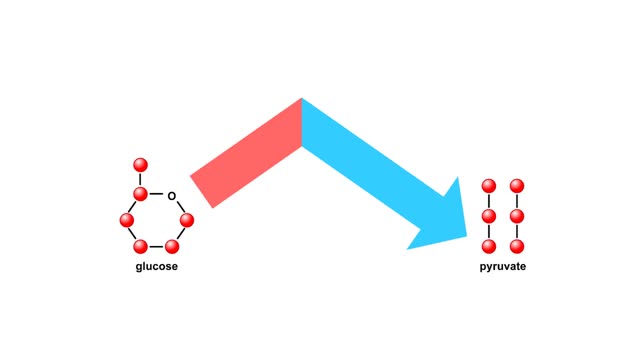
Energy inputs and release in glycolysis Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5046
Glycolysis breaks the six-carbon sugar glucose into two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate. The first steps of glycolysis require an energy input in the form of two phosphate-group transfers from ATP. These phosphorylations raise the energy level of glucose enough to allow the energy-releas...
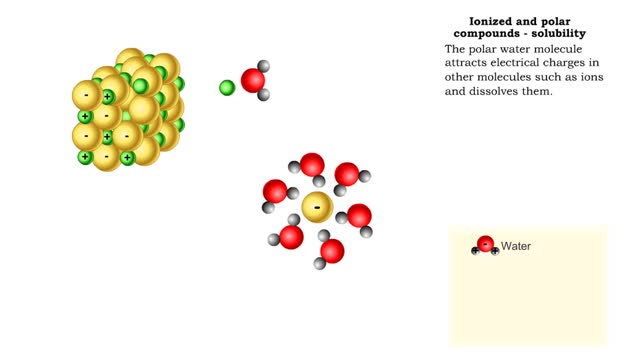
Properties of water -structure of water and polarity (Ionized and polar compounds)
By: HWC, Views: 11311
■ Water transports most of the molecules in the body. ■ The structure of a water molecule allows it to dissolve other molecules. ■ Shared electrons spend more time near the oxygen atom. ■ Oxygen end has a partial negative charge. ■ Hydrogen ends have a partial positive charge....
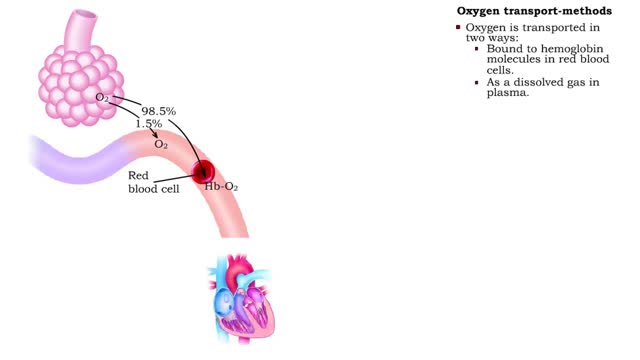
Oxygen transport - methods and oxyhemoglobin
By: HWC, Views: 11014
• The blood is the medium used for gas transport throughout the body. • Oxygen is only available in the lungs. Because the partial pressure of oxygen is higher in the alveoli than in the blood, oxygen diffuses into the blood and is transported to systemic cells. • At the tissues the par...
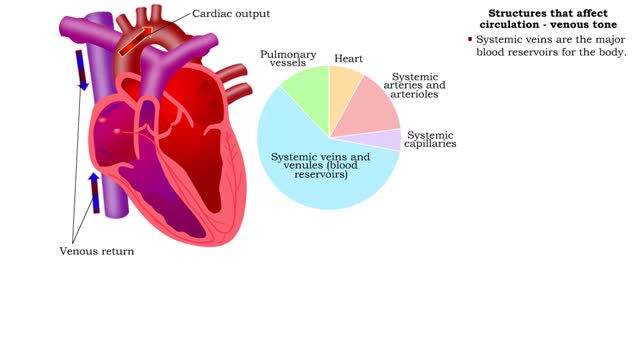
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys, blood volume and venous tone
By: HWC, Views: 11206
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
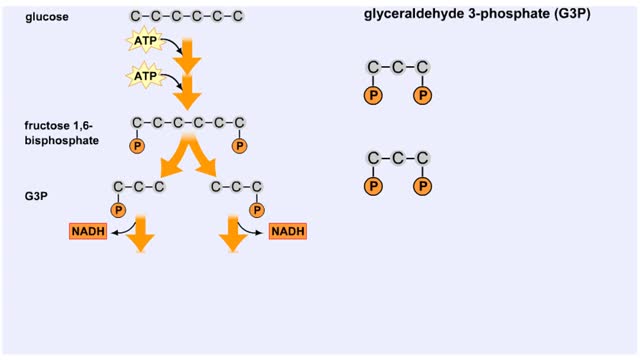
Splitting of Sugar, Oxidation/ Reduction & ATP Generation
By: HWC, Views: 10913
The next reaction shows us the meaning of "glycolysis" or the splitting of glucose. The fructose bisphosphate molecule is split into two molecules each containing 3 carbons as the backbone. FBP is split into two 3-carbon molecules called G3P, or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. Notice that the phos...
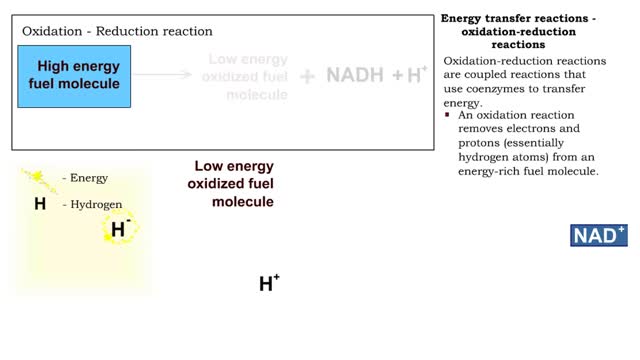
Types of energy transfer reactions: oxidation-reduction reactions and ATP generation reactions
By: HWC, Views: 11801
■ Metabolism balances anabolic and catabolic reactions. ■ Anabolism is energy transfer from ATP to simpler molecules in order to build them up into larger, more complex molecules. ■ Catabolism is breaking down larger, more complex molecules, usually to transfer energy from them in order...
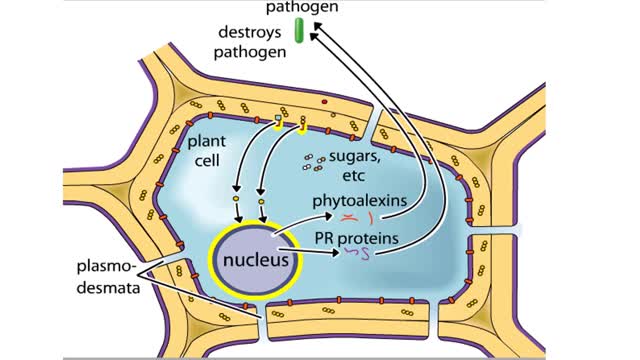
Plant Defense Mechanisms from Pathogens
By: HWC, Views: 10565
Plants and pathogens have coevolved such that pathogens can recognize plants by the sugars, or other molecules, they produce. Plants, in turn, can recognize pathogens by the molecules they produce. The ability to recognize pathogens allows plants to activate defense systems that can prevent wides...
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 10827
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
Advertisement