Search Results
Results for: 'endothelial cell membranes'
By: HWC, Views: 11203
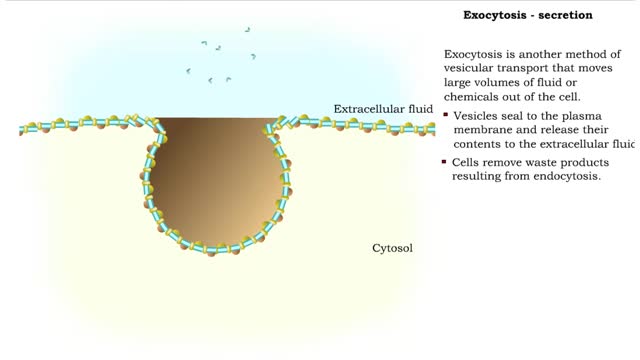
Exocytosis is another method of vesicular transport that moves large volumes Of fluid or chemicals out of the cell. It is a process by which a cell transports secretory products through the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. A examples of cellular secretory products: 1. Secreted protein - enzym...
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 10872
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
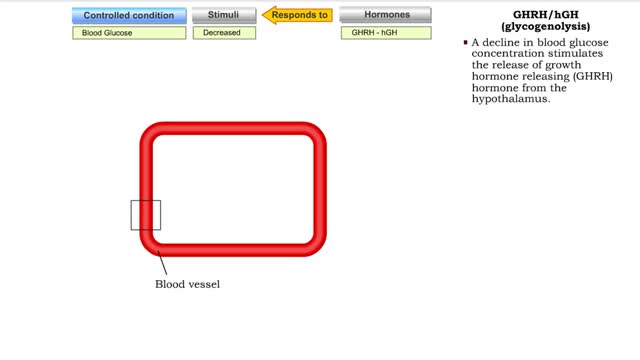
Hormonal feedback loop components & Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10991
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after ...
By: HWC, Views: 9423
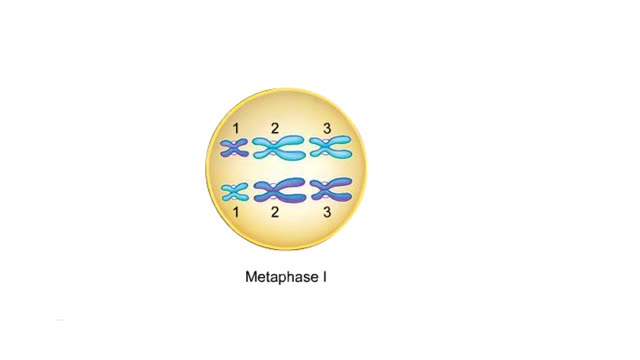
This is a cell during metaphase I. For each pair of chromosomes, any gamete produced by this cell could contain either the maternal chromosome or the paternal chromosome. How many different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes are possible in the gametes produced by a cell with th...
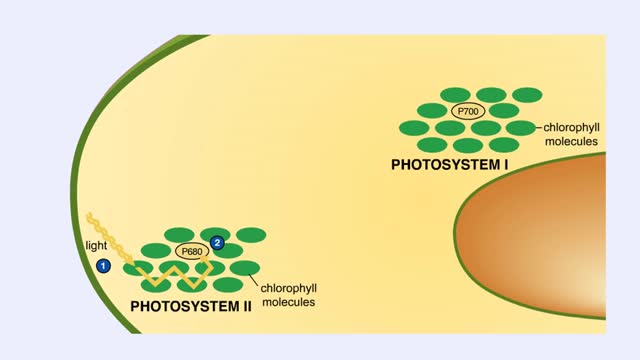
Chloroplast Structure & Light Dependent Reactions (Photosystem 1 and 2 Cyclic Electron Flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10757
The leaf is the principle photosynthetic organ of the plant. This is a cross section of a leaf. The rectangular-shaped cells are part of the photosynthetic tissue called the palisade mesophyll. Each photosynthetic cell can contain several hundred organelles known as chloroplasts. The chlorop...
Neurotransmission at chemical synapses & Excitory and inhibitory potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11172
• A series of events occur at chemical synapses in order to communicate with the adjacent cell. • The action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane. • The depolarization phase of the action potential opens voltage gated Ca+ channels. • increased inflow of Ca+' into the cyto...
By: Administrator, Views: 14098
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply to the target organ, excessive amount of apoptosis of c...
HIV replication/ Replication cycle of HIV
By: HWC, Views: 8406
Replication cycle of HIV, one of the retroviruses. The HIV virus is surrounded by a lipid envelope with embedded proteins. A coat of viral proteins surrounds two strands of RNA and the enzymes used during replication. The virus attaches to and enters the host cell. Viral reverse trans...
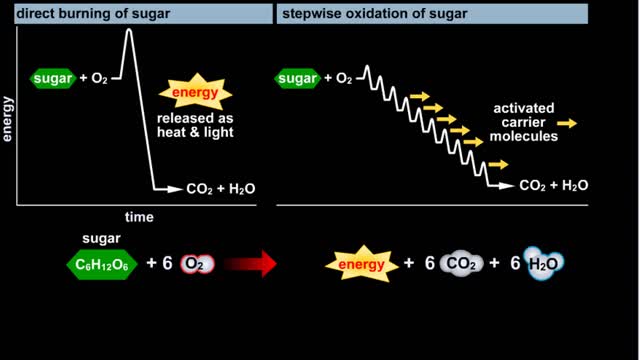
Glycolysis - Introduction to ATP and the burning of sugar
By: HWC, Views: 11435
Do you use sugar with your coffee or tea? Or do you occasionally drink a sport or soft drink? As millions of people do each day, they obtain energy from the sugar added or contained in these drinks. How can we understand this concept of energy within a sugar molecule? Let's take a tablespoon ...
Advertisement