Search Results
Results for: 'osmosis pressure real life examples'
By: HWC, Views: 12302
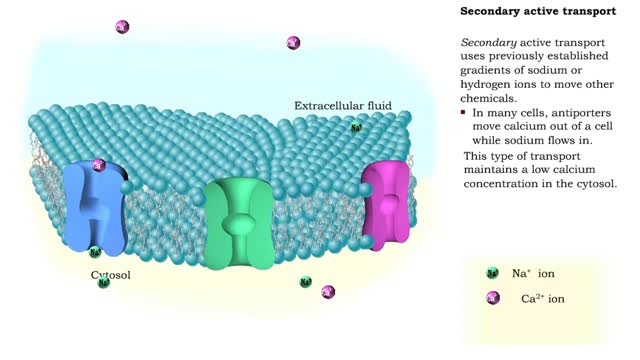
Energy stored (in a hydrogen or sodium concentration gradient) is used to drive other substances against their own concentration gradients Secondary active transport, is transport of molecules across the cell membrane utilizing energy in other forms than ATP. In many cells, antiporters mov...
By: Administrator, Views: 14782
Cardiac dysrhythmias are a problem with the rate or rhythm of your heartbeat caused by changes in your heart’s normal sequence of electrical impulses. Your heart may beat too quickly, called tachycardia; too slowly, bradycardia; or with an irregular pattern. Dysrhythmias can range from complete...
ADH and the arterioles, kidneys, sweat glands and the Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
By: HWC, Views: 11817
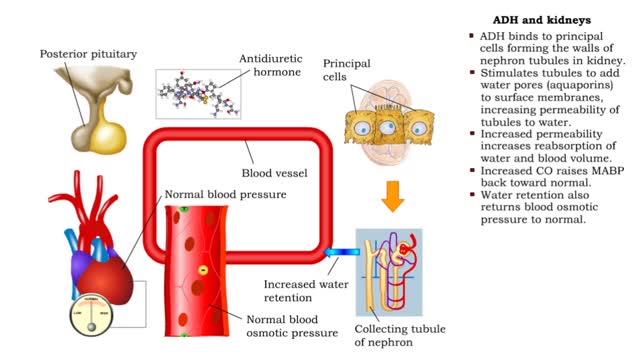
• ADH is also known as vasopressin. • Produced by hypothalmus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in posterior pituitary gland. • Responds to high blood osmotic pressure representing low amounts of water in the blood. • Binds to smooth muscle cells in walls of arterioles, stimulate...
By: HWC, Views: 12075
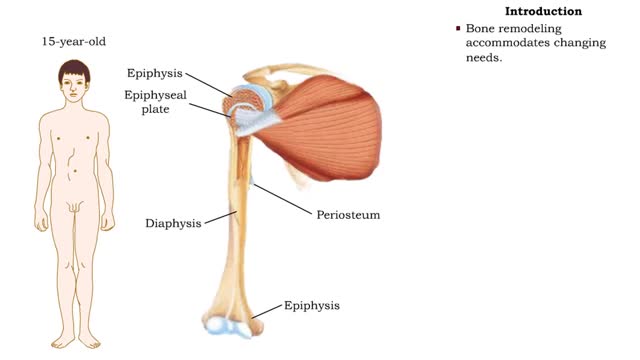
• After birth, bones grow in thickness and length. • Bones grow in diameter via appositional growth at the periosteum. • Epiphyseal plates enable lengthwise growth of long bones, such as the humerus, by interstitial growth. • Bone remodeling accommodates changing needs. • While th...
Five phases of cardiac cycle & Atrial contraction
By: HWC, Views: 11775
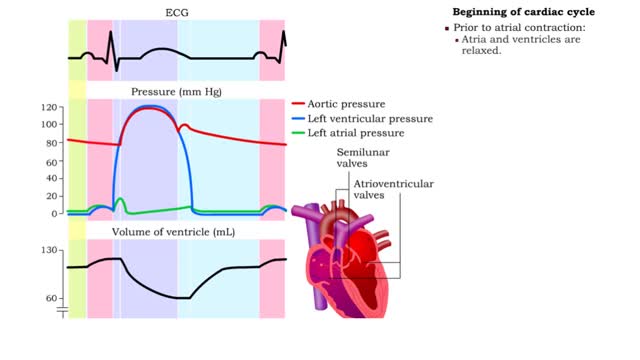
1. Atrial contraction (atrial systole). 2. Isovolumetric (ventricular) contraction. 3. Ventricular ejection. 4. Isovolumetric (ventricular) relaxation. 5. Passive ventricular filling. Beginning of cardiac cycle • Prior to atrial contraction: • Atria and ventricles are relaxed....
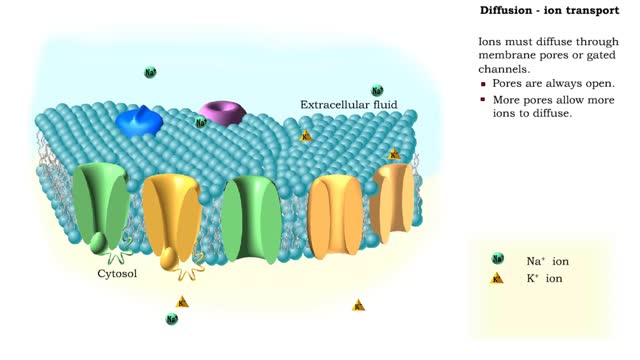
Simple Diffusion - Ion transport
By: HWC, Views: 11738
In the process of diffusion, a substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until its concentration becomes equal throughout a space. Ions must diffuse through membrane pores or gated channels. Pores are always open. More pores allow more ions...
Automated external defibrillator (AED)
By: Administrator, Views: 14862
An automated external defibrillator (AED) is a portable electronic device that automatically diagnoses the life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias of ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia, and is able to treat them through defibrillation, the application of electricity which...
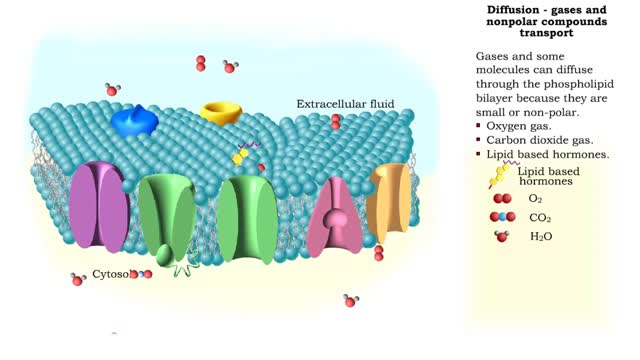
Simple Diffusion - gases and nonpolar compounds transport
By: HWC, Views: 12224
Gases and some molecules can diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer because they are small or non-polar. Oxygen gas. Carbon dioxide gas. Lipid based hormones. Plasma membranes are selectively permeable: The lipid bilayer is always permeable to small, nonpolar, uncharged molecules ...
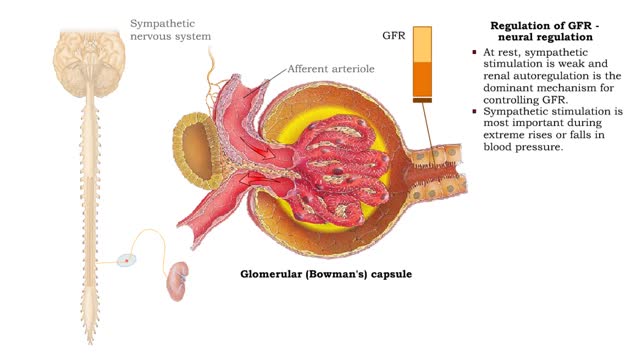
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 12762
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
Advertisement