Search Results
Results for: 'osmosis pressure real life examples'
By: Administrator, Views: 14643
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
By: HWC, Views: 6067
Life cycle of Porphyra. The most conspicuous part of this algal life cycle is the haploid gametophyte. This sheetlike form is collected and dried for use as nori, the wrapping for sushi. Gametes form in packets interspersed between vegetative cells near the sheet margins. The gamet...
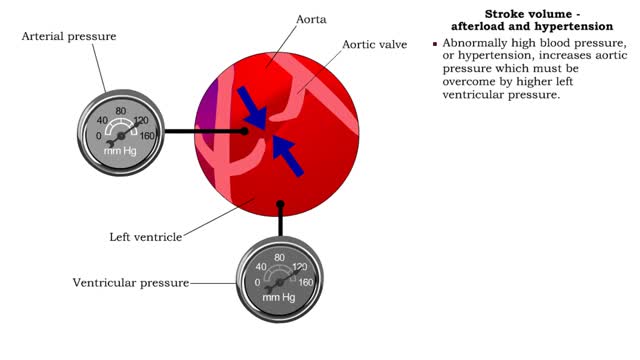
Stroke volume - afterload definition & hypertension
By: HWC, Views: 11094
• Pressure (or other resisting force) that ventricles must overcome to push open semilunar valves and eject blood. ▪ Normally, the left ventricle blood pressure must overcome arterial pressure in the aorta. ▪ Abnormally high blood pressure, or hypertension, increases aortic pressure w...
By: HWC, Views: 11709
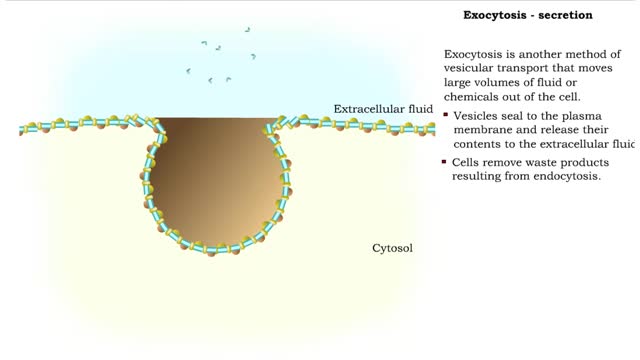
Exocytosis is another method of vesicular transport that moves large volumes Of fluid or chemicals out of the cell. It is a process by which a cell transports secretory products through the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. A examples of cellular secretory products: 1. Secreted protein - enzym...
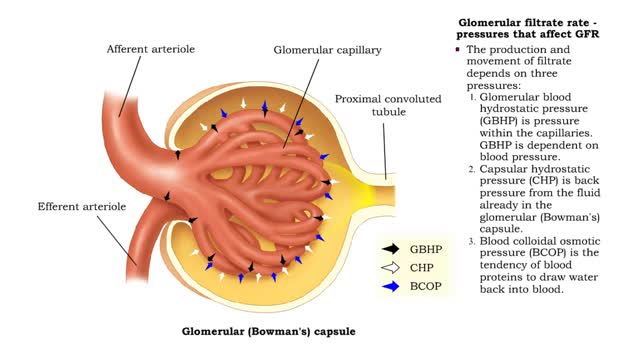
Glomerular filtrate rate: pressures that affect GFR, NFP & GFR and blood composition
By: HWC, Views: 12220
• The glomerular filtration rate is the amount of filtrate formed per minute within the renal corpuscle. • Once the filtrate is formed it moves down the tubule. • The production and movement of filtrate depends on three pressures: I. Glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP) is ...
By: HWC, Views: 11812
• Dissociation of the chemical substances in the body fluids can result in the production of free hydrogen ions. • The pH scale is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. • Normal blood pH values vary around 7.4. • When hydrogen ion concentration increases, t...
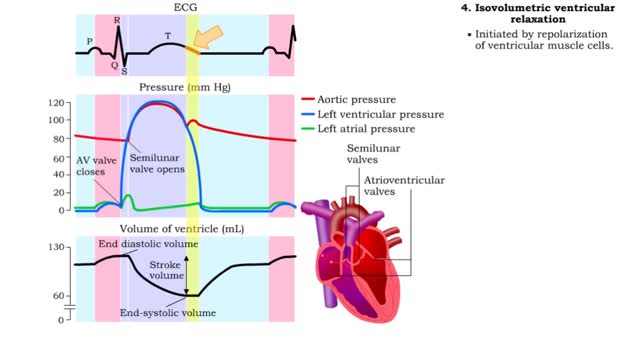
Isovolumetric VC, Ventricular ejection, Isovolumetric & Passive ventricular filling
By: HWC, Views: 11656
• Isovolumetric means that blood volume does not change. • Ventricular blood volume and cell length remain constant. • With valves closed and contraction continuing, ventricular pressure continues to rise. • Ventricular pressure rises above arterial pressure. • Increased ventr...
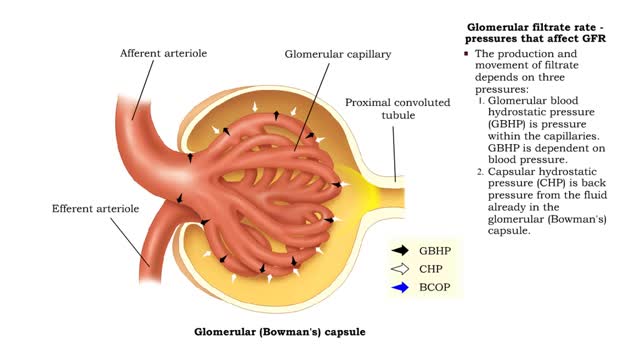
Glomerubular filtrate rate -pressures that affect GFR and net filtration pressure
By: HWC, Views: 12089
• The glomerular filtration rate is the amount of filtrate formed per minute within the renal corpuscle. • Once the filtrate is formed it moves down the tubule. • The production and movement of filtrate depends on three pressures: I. Glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP) is pre...
By: HWC, Views: 11462
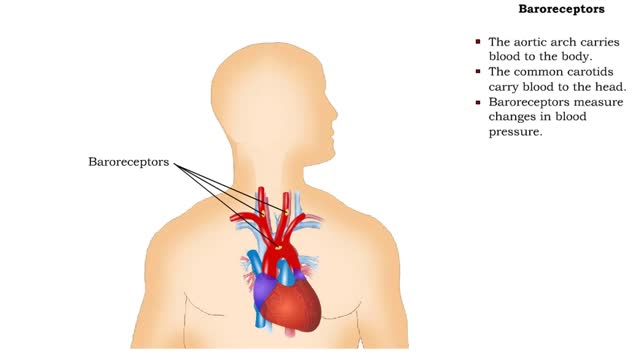
A baroreceptor is a specialized nerve ending that allows your brain to sense blood flow and blood pressure in the major blood vessels of your circulatory system. • The aortic arch carries blood to the body. • The common carotids carry blood to the head. • Baroreceptors measure chang...
Advertisement