Search Results
Results for: 'interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure (IFHP)'
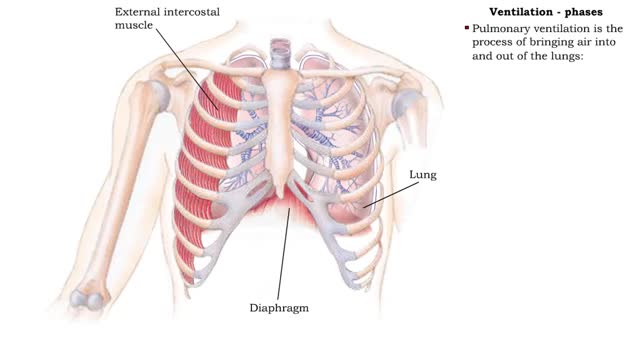
Ventilation - phases and driving forces
By: HWC, Views: 11200
Respiration is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells The combination of 3 processes is required for respiration to occur Ventilation (breathing) External (pulmonary) respiration Internal (tissue) respiration The cardiovascular system assists the respiratory system b...
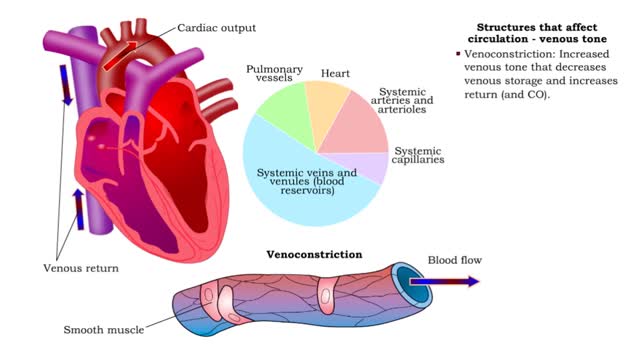
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys and blood volume and skeletal muscle pumping
By: HWC, Views: 11749
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption Increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
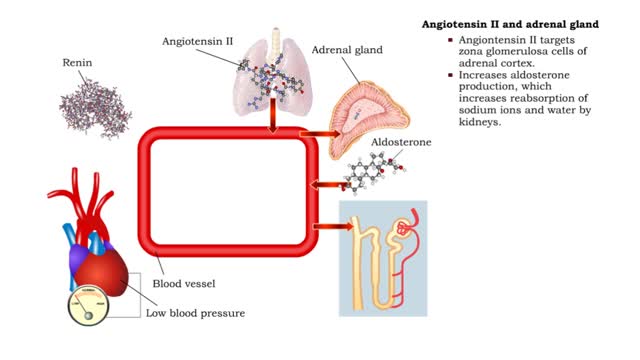
Angiotensin II - kidneys, adrenal glands and dehydration
By: HWC, Views: 11146
• Angiontensin II targets cells in the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. ■ The reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- ions sets up an osmotic gradient favoring the retention of water. • Decreases urine production and increases blood volume and pressure. • Angiontensin II targets zon...
By: Administrator, Views: 14270
Carpal tunnel syndrome is numbness, tingling, weakness, and other problems in your hand because of pressure on the median nerve in your wrist. The median nerve and several tendons run from your forearm to your hand through a small space in your wrist called the carpal tunnel.
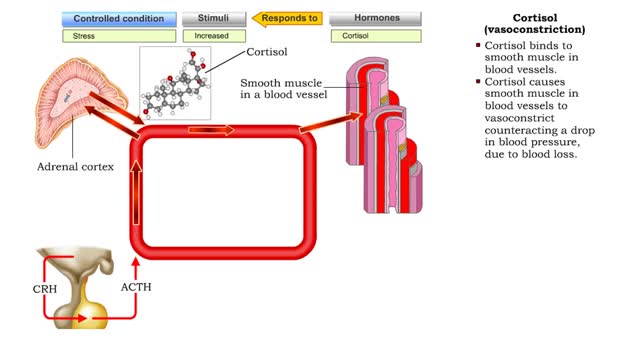
Cortisol (protein catabolism, gluconeogenesis, vasoconstriction & anti-inflammation)
By: HWC, Views: 10784
• Stressors stimulate production of hypothalamic releasing hormones, corticotropin releasing hormone, hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulate. • These hormones promote increased production of 1 cortisol from the zona fasciculata cells of the adrenal cortex. • Cort...
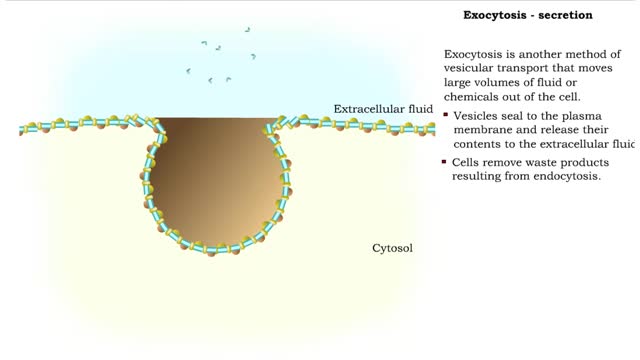
By: HWC, Views: 11061
Exocytosis is another method of vesicular transport that moves large volumes Of fluid or chemicals out of the cell. It is a process by which a cell transports secretory products through the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. A examples of cellular secretory products: 1. Secreted protein - enzym...
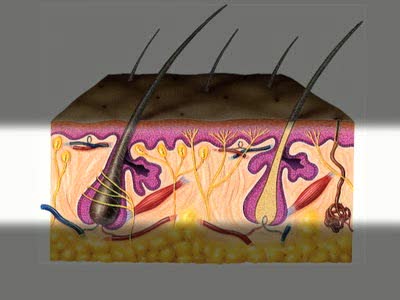
By: Administrator, Views: 14336
The integumentary system comprises the skin and its appendages acting to protect the body from various kinds of damage, such as loss of water or damages from outside. The integumentary system includes hair, scales, feathers, hooves, and nails. It has a variety of additional functions; it may serv...
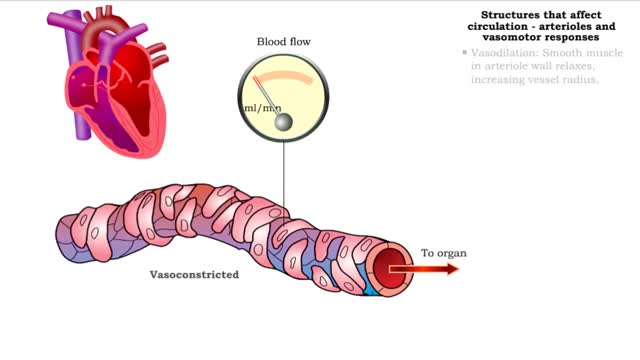
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses and venous return
By: HWC, Views: 11125
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. • Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. • Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
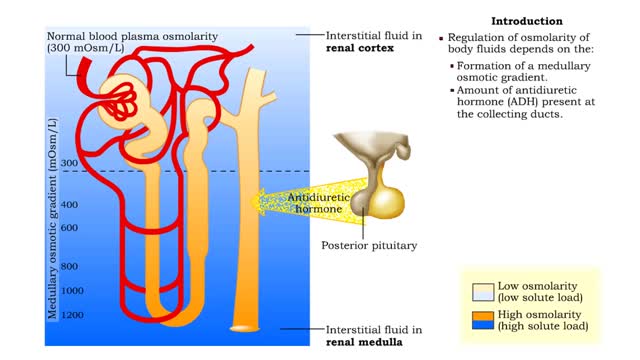
Medullary osmotic gradient - influencing factors
By: HWC, Views: 11524
▪ Maintenance of fluid volume and composition, despite changes in water input and output, is crucial to a healthy life. ▪ Regulation of blood's osmolarity, or solute concentration, is a function of the nephron. • Normal osmolarity is maintained by the ability of the nephron to alter uri...
Advertisement