Energy sources - types
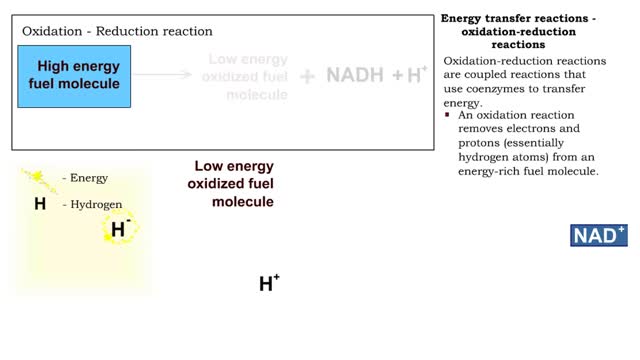
• The amount of ATP stored in a skeletal muscle cell can only provide muscular activity for two to three seconds. • Muscle cells must be able to generate additional molecules of ATP to continue contracting. • Muscle cells can generate ATP from several processes: • Phosphogen system • Anaerobic cellular respiration • Aerobic cellular respiration • The duration of muscular activity determines which energy process is used. Energy sources - creatine phosphate • Through a direct phosphorylation reaction unique to muscle cells, ATP molecules are rapidly generated from creatine phosphate and ADP. • One creatine phosphate molecule generates one ATP molecule. • The phosphogen system can sustain maximum muscle contraction for about 15 seconds. • When the muscle is inactive, creatine is restored to creatine phosphate. Energy sources - anaerobic cellular respiration • Muscle cells use glucose as an source during longer periods of activity. • Glucose can be supplied to muscle cells by the breakdown of glycogen. • Glycolysis: Glucose is broken down into pyruvic acid. • One glucose molecule can yield a net gain of two ATP molecules. • The pyruvic acid is commonly oxidized to generate large amounts Of ATP in the mitochondria during aerobic respiration. • When there is a lack of oxygen in the muscle, pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid. Energy sources - anaerobic cellular respiration • Anaerobic cellular respiration Can produce enough ATP to sustain maximum muscle activity for 30-40 seconds. Energy sources - aerobic cellular respiration • Extended muscle activity requires a continuous supply of ATP. • A series of reactions known as aerobic cellular respiration utilizes oxygen and available nutrients to produce large amounts of ATP. • Nutrient sources include: • Carbohydrates (pyruvic acid) • Proteins (amino acids) • Lipids (fatty acids) • One glucose molecule can generate a net yield of thirty-six ATP molecules. • Aerobic cellular respiration is able to produce enough ATP to sustain maximum muscular activity for minutes and hours.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



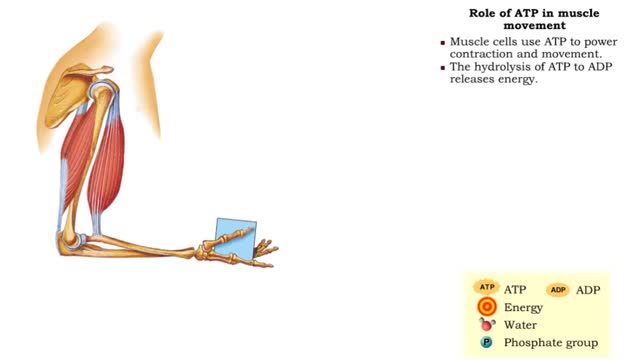
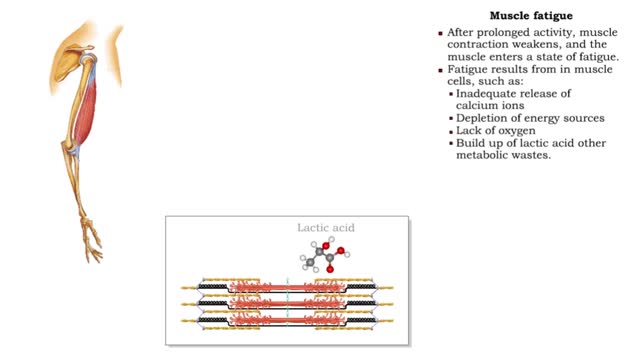
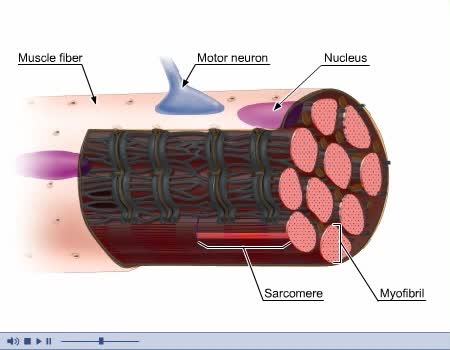


Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.