Glucose anabolism reactions: Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 10/23/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Glucose anabolism Glycogenolysis Gluconeogenesis egulate blood glucose glycogen hormones epinephrine and glucagon Glucose anabolism reaction types insulin Glycogen anabolism gluconeogenesis hormones glucagon and cortisol ماهو الجليكوجين
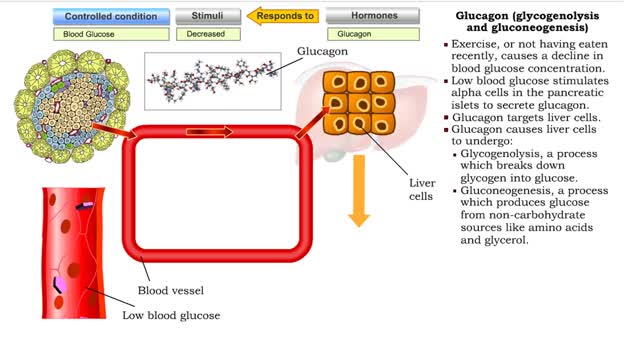
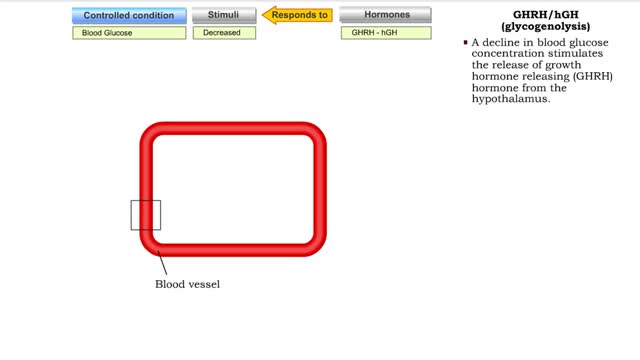
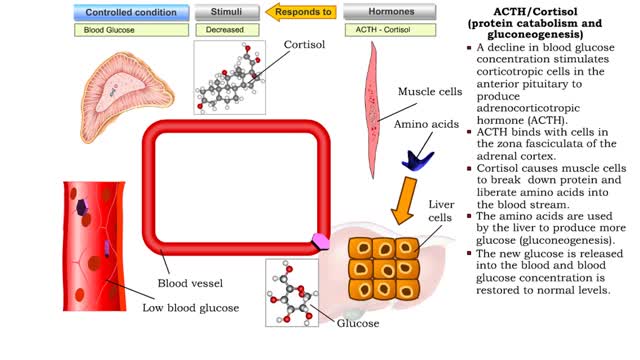
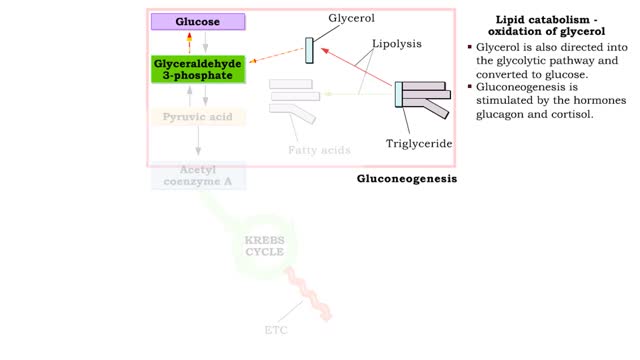
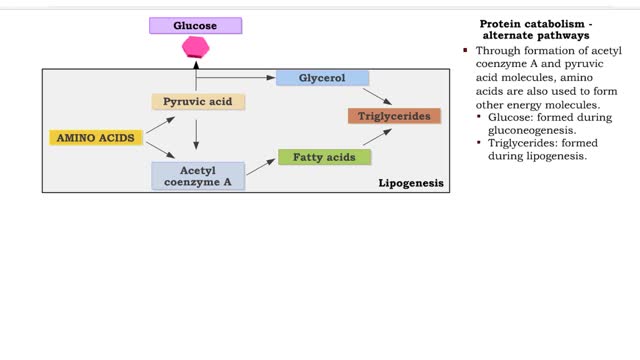
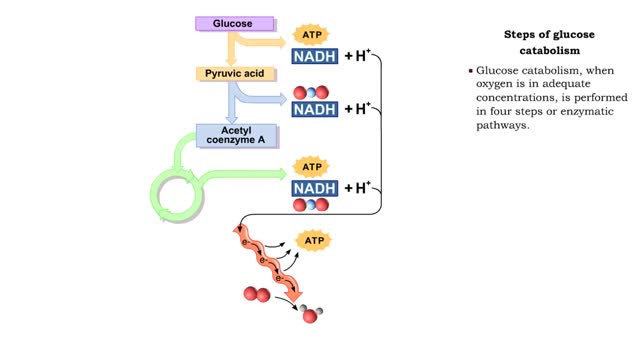
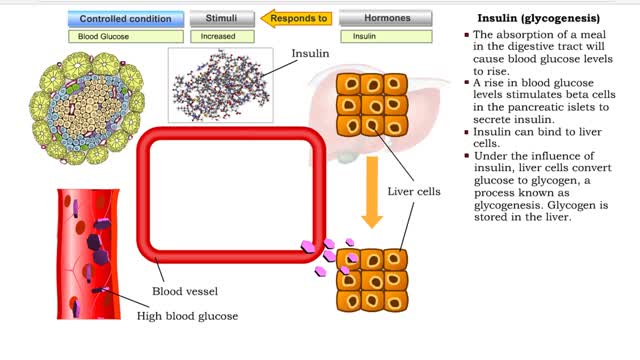
• Glucose not needed immediately is stored as glycogen. The process that creates it is glycogenesis. • When ATP is needed for body activities, stored glycogen is broken down by a process called glycogenolysis. • Glucose can be formed through two different anabolic reactions: • Glycogenolysis • Gluconeogenesis • These reactions help regulate blood glucose. • Glucose may be formed from proteins as well as the glycerol portion of triglycerides, lactic acid and certain amino acids. The process is known as gluconeogenesis. • Cortisol, glucagon and thyroid hormones stimulate gluconeogenesis. • Glycogenolysis breaks up glycogen. • It occurs in the liver or skeletal muscle cells. • It is stimulated by the hormones epinephrine and glucagon. • Blood glucose increases as glycogen is hydrolyzed. • The process of glycogenesis coverts excessive blood glucose back to glycogen for storage in liver and muscle cells. • The hormone insulin stimulates glycogenesis. • Blood glucose decreases as glycogen is synthesized. • If your blood glucose level rises, your body springs into action to sweep out the excess sugar. It does this by promoting a process called glycogenesis, which is the creation and storage of glycogen. • This term is easy to remember if you recall the suffix 'genesis' means creation; so, glycogenesis is literally the creation of glycogen, which is the name we give to the stored form of glucose. You have glycogen storage in your liver and in your muscles, so you might want to think of these structures like a pantry, where you store bags of sugar to use later. Glycogen anabolism - gluconeogenesis • Gluconeogenesis converts non-carbohydrate molecules (lactic acids, amino acids and glycerol) into glucose. • It occurs in the liver 'This process is stimulated by the hormones glucagon and cortisol. • Blood glucose increases as glucose is synthesized. الجليكوجين هو عديد السكاريد القائم على الجلوكوز. هذه هي الكربوهيدرات المعقدة ، والتي هي فقط في الكائنات الحية ، وأنها تحتاج إلى احتياطي الطاقة. الجليكوجين يمكن مقارنته ببطارية يستخدمها الجسم في وضع مرهق حتى يتحرك. ويمكن أن يكون الجليكوجين بديلا عن الأحماض الدهنية ، وهو أمر مهم جدا للرياضيين. الفرق بين الأحماض الدهنية والجليكوجين هو أن الأخير هو السكر النقي ، ولكن حتى يطلبه الجسم ، فإنه يتم تحييده ولا يدخل إلى الدم. الأحماض الدهنية أكثر صعوبة - فهي تتكون من الكربوهيدرات وتنقل البروتينات التي تربط الجلوكوز وتتكثف إلى الحالة التي يكون من الصعب كسرها. هناك حاجة إلى الأحماض الدهنية من قبل الجسم لزيادة قيمة الطاقة من الدهون وتقليل احتمال انهيارها العرضي. يخزن الجسم الأحماض الدهنية لنقص السعرات الحرارية الحاد ، ويوفر الجليكوجين الطاقة حتى مع القليل من الإجهاد. تعتمد كمية الجلايكوجين في الجسم على حجم مستودع الجليكوجين. إذا لم يكن الشخص مشاركًا بشكل محدد ، فسيكون هذا الحجم صغيرًا. الرياضيون قادرون على زيادة "مستودع الجليكوجين" بمساعدة التدريب ، بينما يتلقون: التحمل عالية. زيادة النسيج العضلي. تغيرات ملحوظة في الوزن أثناء التمرين. ومع ذلك ، الجليكوجين ليس له أي تأثير تقريبا على الأداء الرياضي.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.