Neurotransmission at chemical synapses & Excitory and inhibitory potentials
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 11/15/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Neurotransmission at chemical synapses chemical synapses presynaptic membrane depolarization phase cytosol exocytosis synaptic cleft ligand gated hyperpolarization postsynaptic cell membrane Excitory and inhibitory potentials IPSP inhibitory postsynaptic membrane potentials EPSP
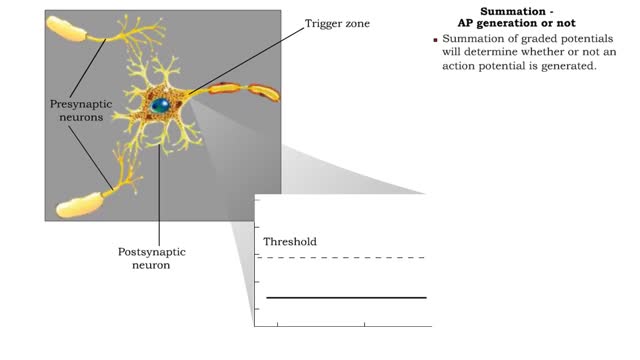
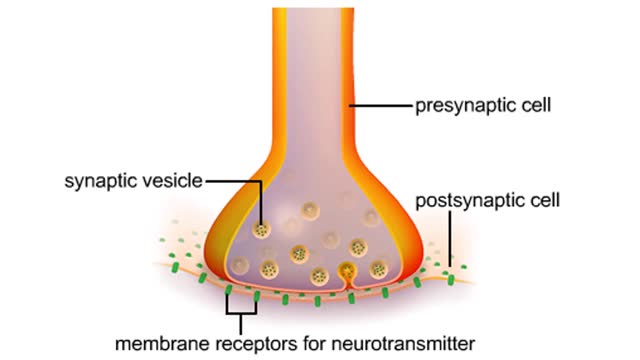
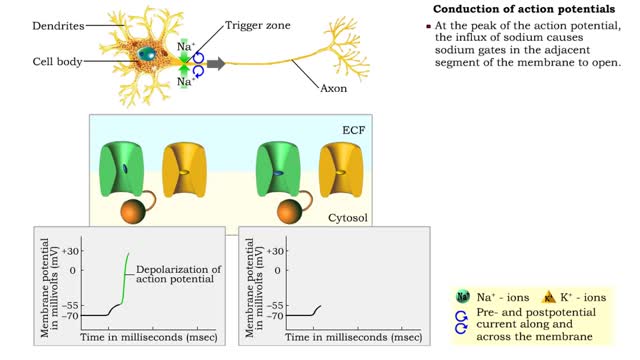
• A series of events occur at chemical synapses in order to communicate with the adjacent cell. • The action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane. • The depolarization phase of the action potential opens voltage gated Ca+ channels. • increased inflow of Ca+' into the cytosol triggers exocytosis of vesicles carrying neurotransmitter chemicals. • Released into the synaptic cleft, neurotransmitters diffuse across the cleft and bind to receptors (often, ligand gated ion channels). • gated channels open allowing ions to flow according to their concentration gradient. • Sodium flows into the cell making its interior slightly more positive. • Potassium flows out of the cell making its interior slightly less positive. • The ionic flow through the channels will cause either a graded depolarization or hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic cell membrane. • Large graded depolarizations tend to generate action potentials. Excitory and inhibitory potentials - EPSP • The ionic flow made possible because of the opening of the ligand gated channels in the postsynaptic membrane determines whether a graded depolarization or hyperpolarization occurs. • If Na+ gates open, the depolarization of the membrane charge will move closer to threshold and the ability to generate an action potential. • These depolarizations are called excitatory postsynaptic membrane potentials (EPSP). Excitory and inhibitory potentials - IPSP • If Cl- or K+ gates open, this creates hyperpolarizations which will inhibit the generation of an action potential. • These hyperpolarizations are called inhibitory postsynaptic membrane potentials (IPSP). Excitory and inhibitory potentials - role • The sum of all IPSPs and EPSPs, from all synapses, determines whether an action potential will be generated at a neuron's trigger zone.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.