Calvin Cycle Explained!
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 10/10/2020
Tags: Calvin Cycle Explained! clavin cycle animation rubisco ribulose bisphosphate PGA ATP NADPH
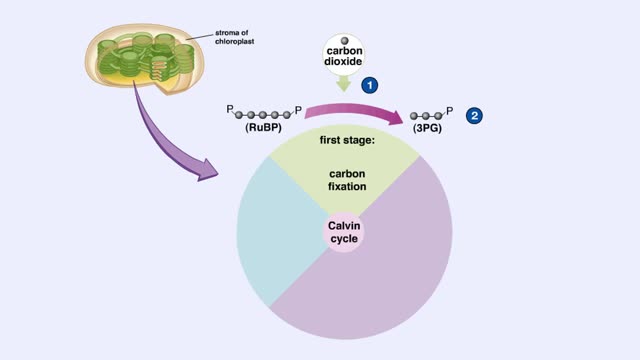
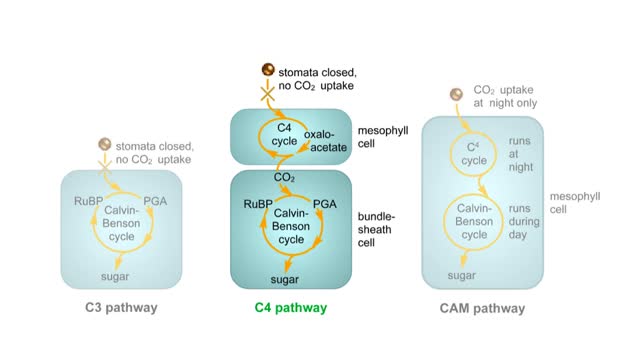
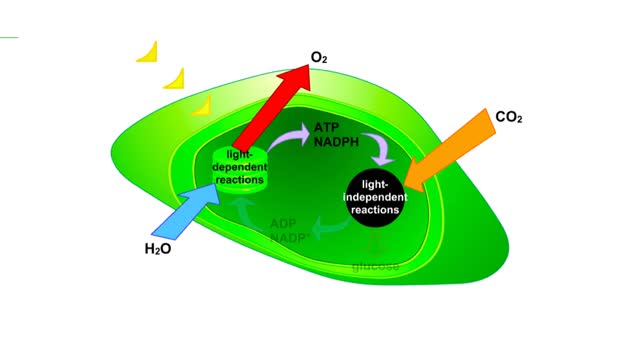
he light-independent reactions make sugars by way of a cyclic pathway called the Calvin cycle. The cycle begins when rubisco attaches a carbon from carbon dioxide to ribulose bisphosphate. The molecule that forms splits into two molecules of PGA. Each PGA gets a phosphate group from ATP and electrons from NADPH. The resulting intermediate, PGAL, is primed for a reaction. After six molecules of carbon dioxide have been fixed, 12 PGAL form. Two of the PGAL molecules combine to form the six-carbon sugar glucose. The glucose will enter other reactions that form carbohydrates. The remaining 10 PGAL get phosphate groups from ATP. This primes them for the reactions that regenerate RuBP, thus completing the cycle.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.