Nerve Type Animation (Part 1)
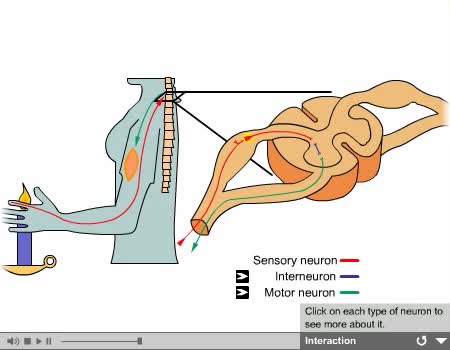
Used to describe neuronal processes conducting impulses from one location to another. Nerve fibers: - Nerve fibers of the PNS are wrapped by protective membranes called sheaths. - Myelinated fibers have an inner sheath of myelin, a thick fatty substance, and an outer sheath or neurilemma composed of Schwann cells. - Unmyelinated fibers lack myelin and are sheathed only by the neurilemma. Nerve fibers: - Nerve fibers of the CNS do not contain Schwann cells. - Damage to fibers of the CNS is permanent. - Damage to a peripheral nerve can be reversible. Nerves: - A nerve is a collection of nerve fibers, outside the CNS. - Afferent: Sensory nerves that conduct to the CNS. - Efferent: Motor nerves that conduct away from the CNS to muscles, organs, and glands. Tracts: - Groups of nerve fibers within the CNS that have the same origin, function, and termination. - Spinal cord contains afferent sensory tracts ascending to the brain, and efferent motor tracts descending from the brain. - Brain itself contains numerous tracts; largest is the corpus callosum joining the left and right hemispheres.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.