Rh blood type and complications during pregnancy & Fertilization
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 10/30/2021
Tags: Rh blood type and complications during pregnancy Fertilization Rh- woman negative blood type women maternal bloodstream antibodies immune system maternal antibodies fetal red blood cells ovulation secondary oocyte noncellular zona pellucida remnants of the follicle oocyte zona pellucida oocyte's cytoplasm meiosis mature ovum sperm nucleus and egg nucleus fuse diploid zygote
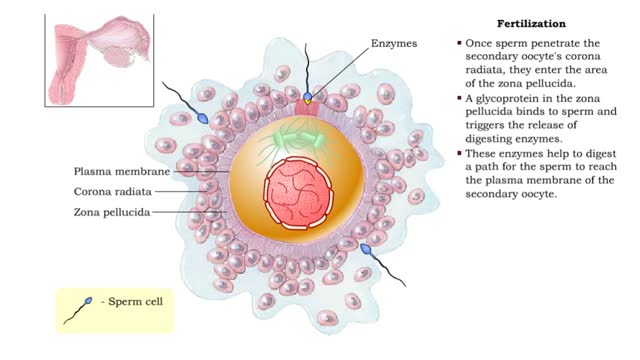
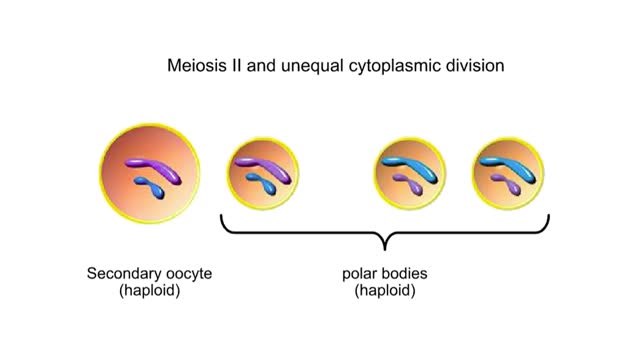
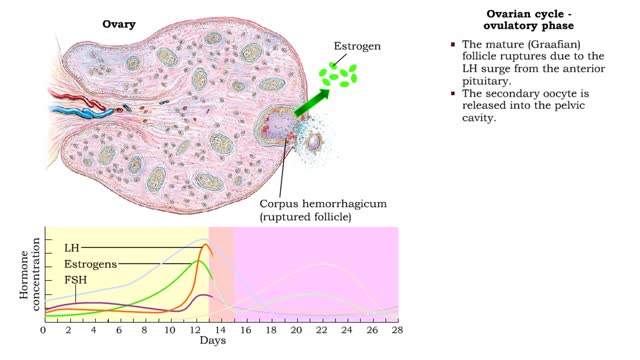
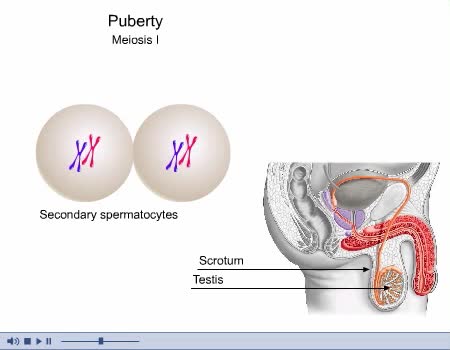
Complications can arise if an Rh- woman is impregnated by an Rh+ man. The fetus maybe Rh+. During childbirth, some of the fetal Rh+ cells may leak into the maternal bloodstream. The woman's immune system views the Rh+ as foreign and makes antibodies against it. If the woman becomes pregnant again, and the fetus is Rh+, her circulating antibodies will act against it. The attack of maternal antibodies against the fetal red blood cells can be fatal. Recall that ovulation released a secondary oocyte and first polar body enclosed within a noncellular zona pellucida and remnants of the follicle. If sperm meet up with such an oocyte, they surround it and release digestive enzymes that clear a path through the zona pellucida. Although many sperm get this far, usually only one penetrates the secondary oocyte. Inside the oocyte's cytoplasm, the sperm degenerates until only its nucleus and centrioles remain. Penetration induces the secondary oocyte to finish meiosis. There are now three polar bodies and a mature ovum, or egg. The sperm nucleus and egg nucleus fuse. At fusion, fertilization is over. The diploid zygote has formed and development will begin.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.