What is Reverse Osmosis?
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 11/17/2021
Tags: What is Reverse Osmosis? How Does Reverse Osmosis Work Compare Osmosis with Reverse Osmosis Reverse Osmosis Industries Wine Industry and Reverse Osmosis Dairy Industry Ethanol Reverse Osmosis Animation Dasani Water Reverse Osmosis Is reverse osmosis water healthy osmosis vs reverse osmosis osmosis pressure real life examples osmosis and diffusion difference hypertonic solution reverse osmosis examples reverse osmosis explained التناضح العكسي أو الأسموزية المعاكسة
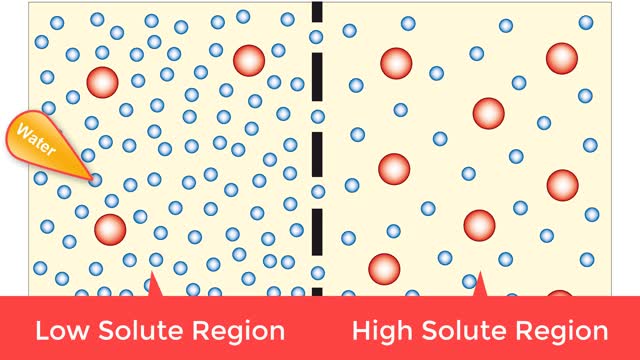
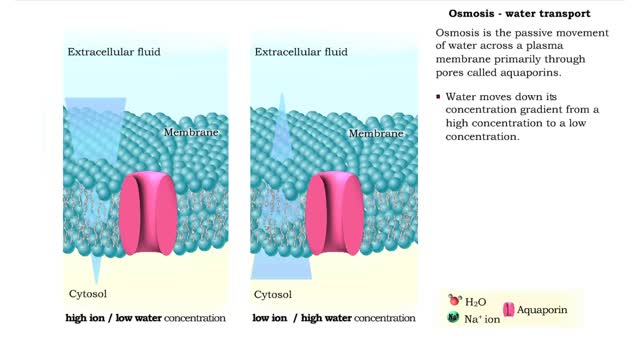
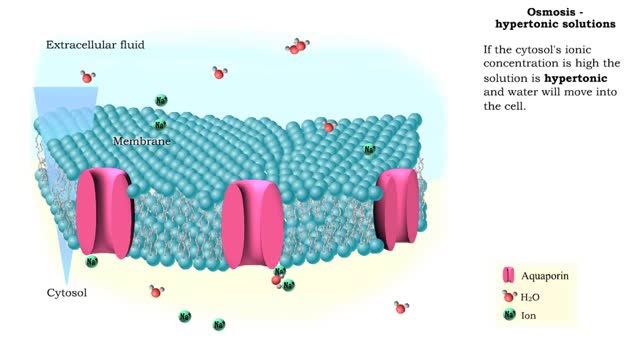
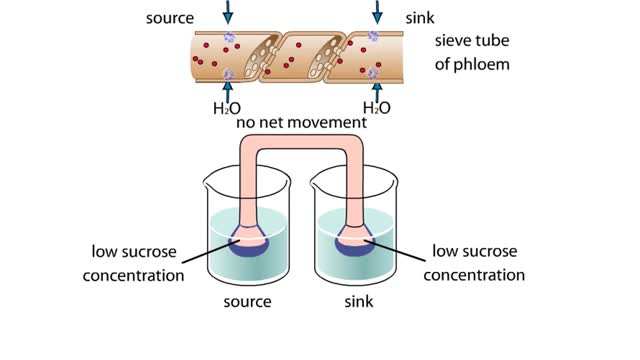
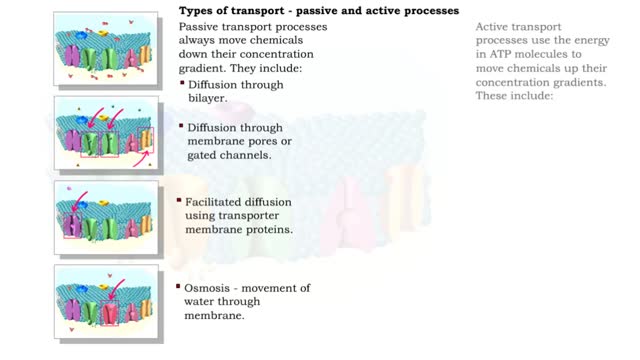
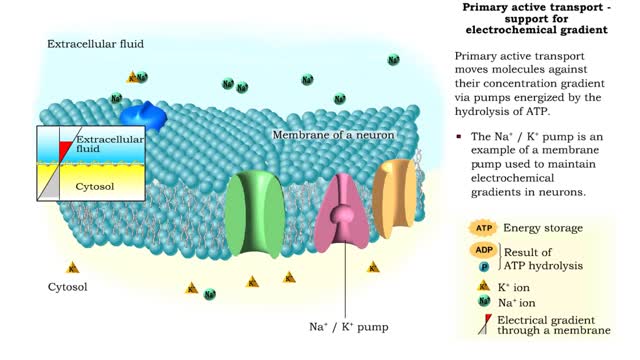
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs across a semipermeable membrane that allows only water to pass. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. An animal cell placed in a hypertonic solution (high solute concentration) will cause the cell to shrivel up, whereas a hypotonic solution (low solute concentration) will cause it to bloat. Placing raisins in a cup of water will cause them to puff up Reverse osmosis applies high hydrostatic pressure (external pressure) to a solution across a semipermeable membrane to prepare a purified solvent. Because the hydrostatic pressure is greater than the osmotic pressure (the pressure that happens as the molecules move), the direction of water flow through the membrane can be reversed.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.