Search Results
Results for: 'Enzyme structure'
By: HWC, Views: 10177
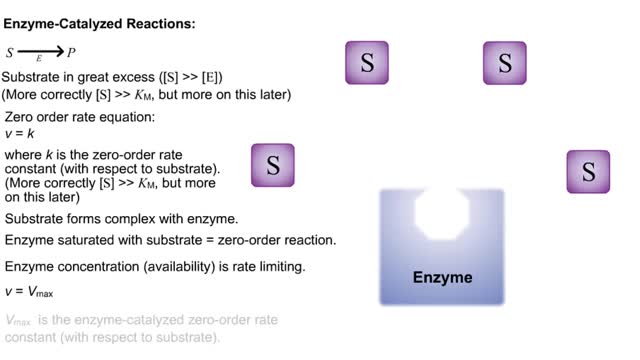
S P Substrate in great excess ([S] -- [E]) (More correctly [S] -- KM, but more on this later) Zero order rate equation: v = k where k is the zero-order rate constant (with respect to substrate). (More correctly [S] -- KM, but more on this later) Substrate forms complex with enzyme. ...
By: HWC, Views: 9700
Living things must accomplish a great number of tasks just to get through a day, and these tasks are accomplished by a diverse range of biological molecules. In the range of tasks that molecules accomplish, however, proteins reign supreme. Almost every chemical reaction that takes place in living...
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 10665
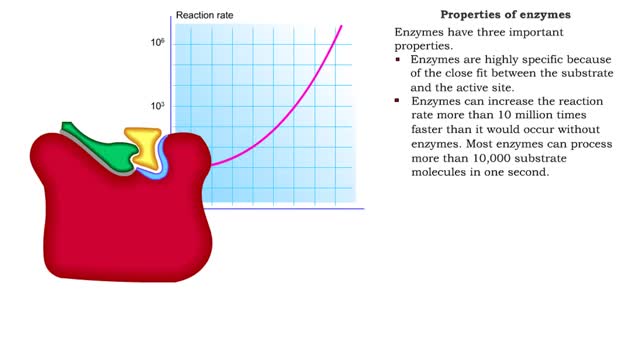
■ Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. ■ Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. ■ Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. ■ Coenzymes often come from vitamins. ■ Cofactors affect the shape of...
By: HWC, Views: 7586
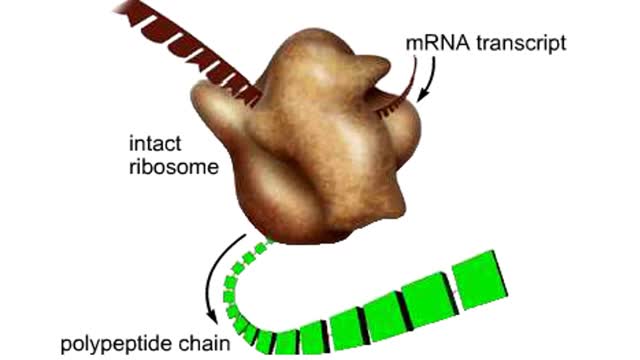
The structure and function of the mammalian ribosome. The mammalian ribosome consists of two subunits, one small and one large. Each subunit is assembled in the nucleus from rRNA and structural proteins. Once assembled, the ribosomal subunits are shipped separately to the cytoplasm. ...
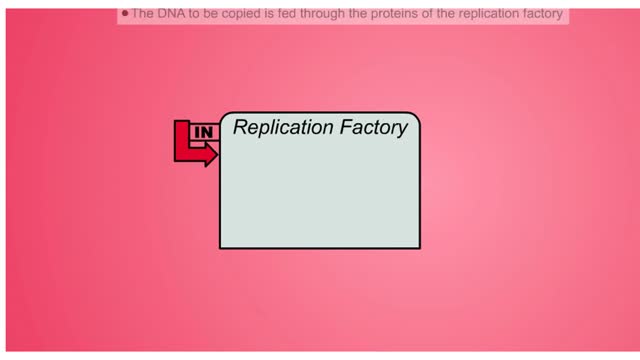
DNA Replication Factory and Protein
By: HWC, Views: 10304
DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) carries all the genetic information needed to re-create itself and to pass on the characteristics of the organism. The “factory” model of DNA replication hypothesizes a specific nuclear structure in which the molecular machinery for replication forks are brou...
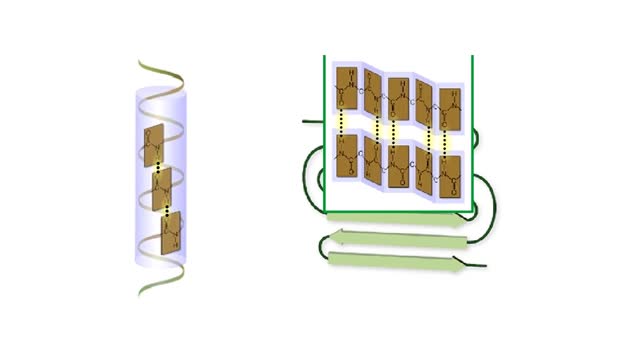
Secondary and tertiary levels of protein structure Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4577
Amino acid sequence dictates a protein's final shape. The presence of certain amino acids favors a pattern of hydrogen bonding that causes part of the polypeptide chain to coil and twist into an alpha helix. The presence of other amino acids enables hydrogen bonding between strand like re...
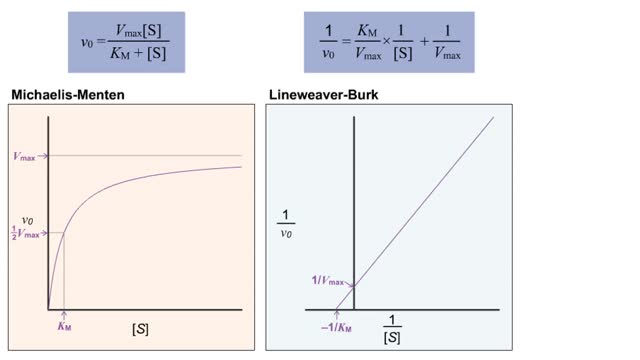
Virtual Enzyme Kinetics & Lineweaver Burk Plot
By: HWC, Views: 10270
• The double-reciprocal (also known as the Lineweaver-Burk) plot is created by plotting the inverse initial velocity (1/V0) as a function of the inverse of the substrate concentration (1/[S]). • This plot is a useful way to determined different inhibitors such as competitive, uncompetitive...
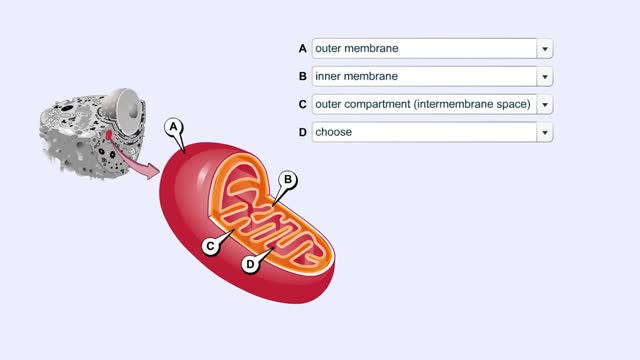
Mitochondrial Structure & ETC Protein Complexes (Protein Complexes and Electron Transport)
By: HWC, Views: 10290
The energy carrying molecules, NADH and FADH2, that were generated in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, now are processed in the mitochondria where their high energy electrons are deposited in an electron chain complex located in the inner mitochondrial membranes. These high-energy electrons now dr...
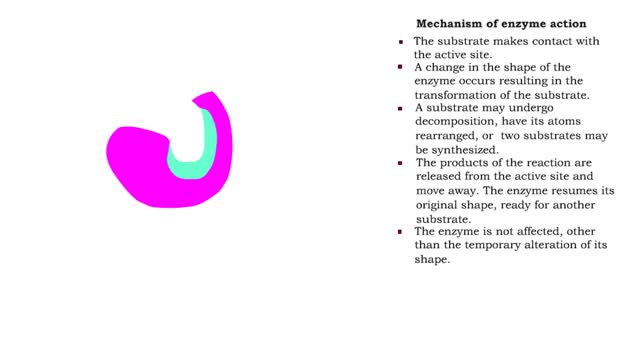
By: HWC, Views: 10504
■ The substrate makes contact with the active site. ■ A change in the shape of the enzyme occurs resulting in the transformation of the substrate. ■ A substrate may undergo decomposition, have its atoms rearranged, or two substrates may be synthesized. ■ The products of the reaction...
Advertisement