Search Results
Results for: 'Henle'
Medullary osmotic gradient - influencing factors
By: HWC, Views: 12154
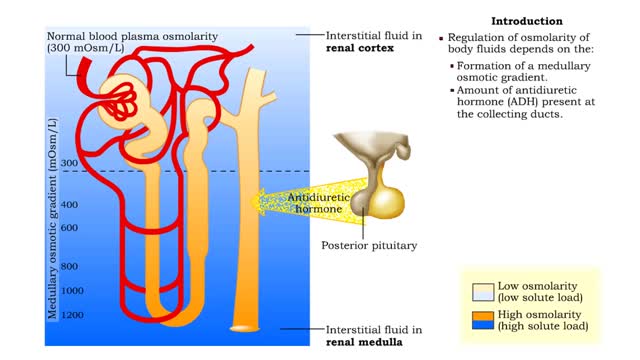
▪ Maintenance of fluid volume and composition, despite changes in water input and output, is crucial to a healthy life. ▪ Regulation of blood's osmolarity, or solute concentration, is a function of the nephron. • Normal osmolarity is maintained by the ability of the nephron to alter uri...
By: HWC, Views: 12513
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
Regulation of GFR: three methods, autoregulation & autoregulation via myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 12176
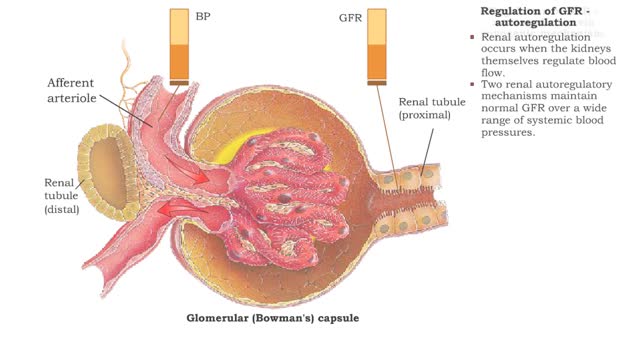
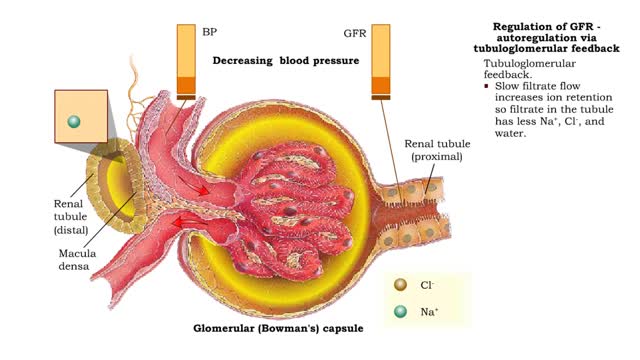
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Hormonal regulation. • Ren...
Forming urine ( influencing factors), Forming dilute urine & Forming concentrated urine
By: HWC, Views: 12203
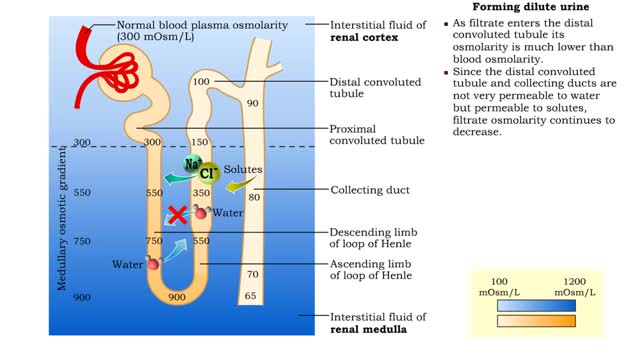
• The amount of urine produced by the nephron depends on : • Body fluid volume. • Body fluid composition. • Dilute urine is formed when the body is normally hydrated. • The medullary osmotic gradient determines the osmolarity of the filtrate. • Filtrate osmolarity increase...
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via myogenic mechanism Myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 13267
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Renal autoregulation occurs when...
Advertisement