Search Results
Results for: 'Properties of macromolecules'
Properties of macromolecules (Explained with No Audio)
By: HWC, Views: 10246
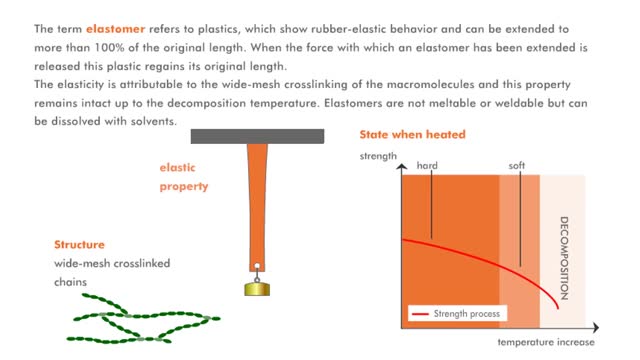
The term thermoplast refers to a plastic, which when heated is soft and deformable, but which rehardens when cooled. The molecular structure of the macromolecules is comparable to a cotton ball in which the individual fibers of the macromolecules are shown. The fibers of the cotton ball can s...
By: HWC, Views: 10825
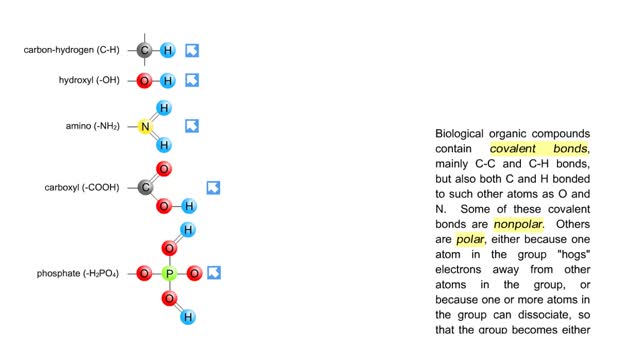
Biological organic compounds contain covalent bonds, mainly C-C and C-H bonds, but also both C and H bonded to such other atoms as O and N. Some of these covalent bonds are nonpolar. Others are polar, either because one atom in the group "hogs" electrons away from other atoms in the group, or...
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Proteins
By: HWC, Views: 10832
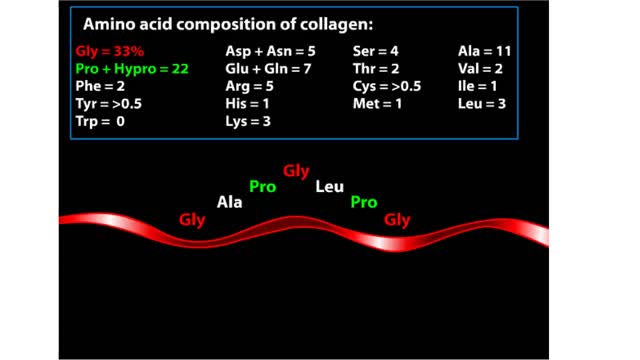
Proteins are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. The 20 different amino acids used to make all proteins differ only in their side chains, and the properties of these side chains account for the great diversity of protein structure and function. Collagen is an example of how a prote...
Proteins Defined, Hierarchy & Composition of Cells
By: HWC, Views: 10829
Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Together with the other three biological macromolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—proteins are the building blocks of cells. Proteins are the most complex and abundant biological macromolecules in cel...
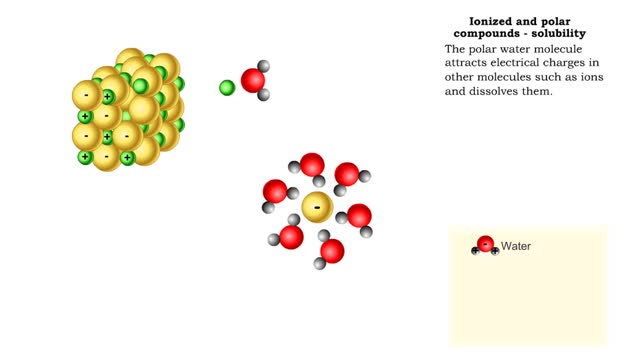
Properties of water -structure of water and polarity (Ionized and polar compounds)
By: HWC, Views: 11481
■ Water transports most of the molecules in the body. ■ The structure of a water molecule allows it to dissolve other molecules. ■ Shared electrons spend more time near the oxygen atom. ■ Oxygen end has a partial negative charge. ■ Hydrogen ends have a partial positive charge....
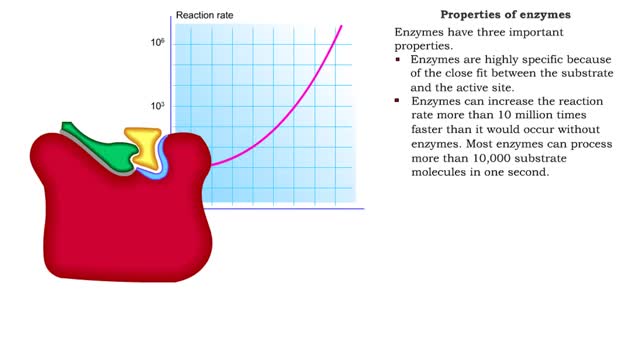
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11285
■ Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. ■ Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. ■ Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. ■ Coenzymes often come from vitamins. ■ Cofactors affect the shape of...
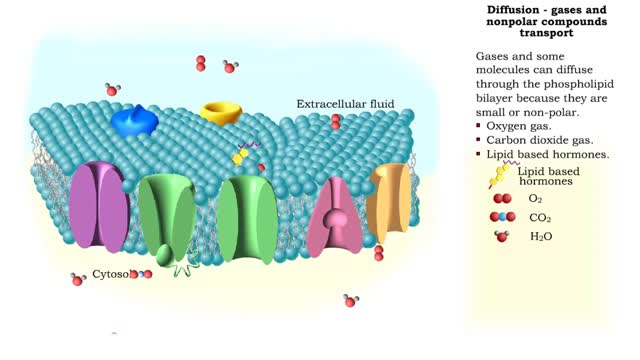
Simple Diffusion - gases and nonpolar compounds transport
By: HWC, Views: 11854
Gases and some molecules can diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer because they are small or non-polar. Oxygen gas. Carbon dioxide gas. Lipid based hormones. Plasma membranes are selectively permeable: The lipid bilayer is always permeable to small, nonpolar, uncharged molecules ...
By: HWC, Views: 10668
Observe the burning logs of wood. The logs burn to emit heat, light and carbon dioxide. What is left behind is ash. This residue is a new substance with a different molecular structure than the original wood. Similarly when baking the dough into bread, it becomes fluffy and light. There is a ch...
Cognitive development by Piaget (Preoperational stage or intelligence)
By: HWC, Views: 10448
The next stage of cognitive development proposed by Piaget, is the preoperational stage, roughly between the ages of 2 and 7. At this stage Piaget asserted that a child has what he called preoperational intelligence. hey can mentally representing objects, but do not have a system for organising...
Advertisement