Search Results
Results for: 'adenine base'
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Nucleic acids
By: HWC, Views: 11595
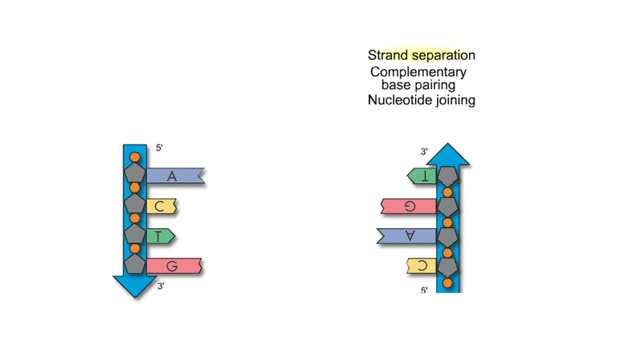
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids (polymers of nucleotides). Two polymers with complementary nucleotide sequences can pair with each other. This pairing endows nucleic acids with the ability to store, transmit, and retrieve genetic information. Two strands of DNA pair by hydrogen bonding. A compon...
Subunits of DNA And Semi Conservative Replication
By: HWC, Views: 8024
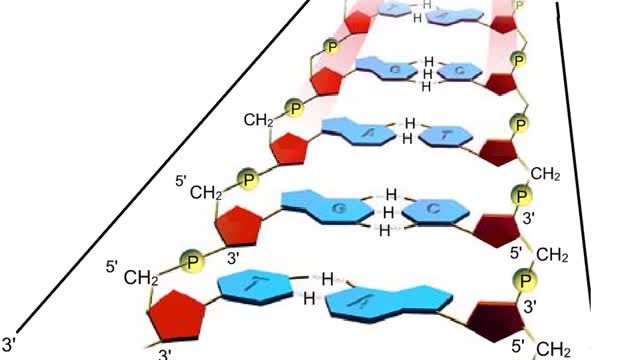
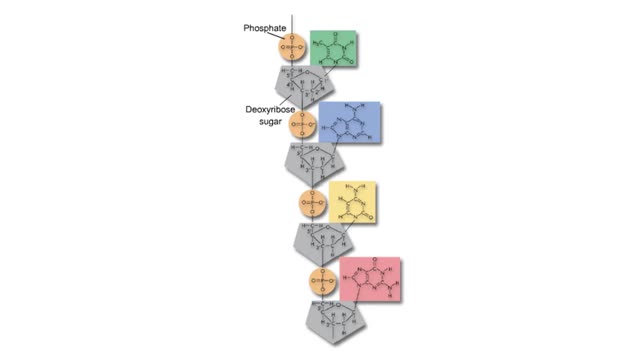
Adenine is a purine with a double-ring structure. In double-stranded DNA, adenine base-pairs with thymine. Guanine is a purine with a double-ring structure. In double-stranded DNA, guanine base-pairs with cytosine. Thymine is a pyrimidine with a single-ring structure. In double-stranded DNA, th...
By: HWC, Views: 5613
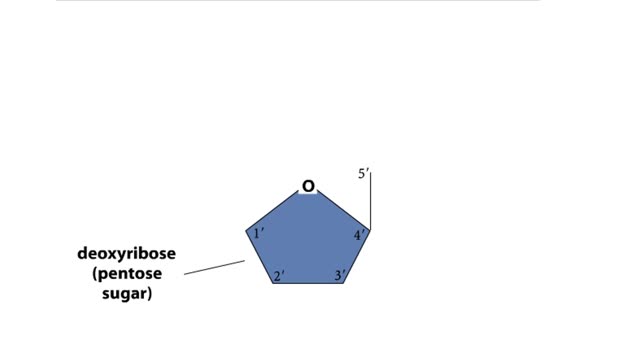
A section from a DNA double helix The backbone of each DNA strand consists of alternating deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups. The two strands run in opposite directions. One runs from the 5' to 3' direction, the other in the 3' to 5' direction. Think of the deoxyribose units o...
Glycolysis - Introduction to ATP and the burning of sugar
By: HWC, Views: 11948
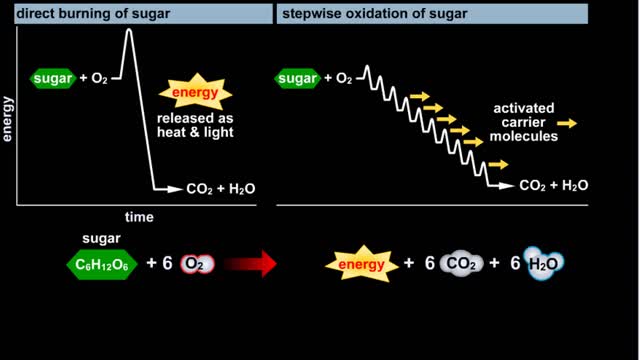
Do you use sugar with your coffee or tea? Or do you occasionally drink a sport or soft drink? As millions of people do each day, they obtain energy from the sugar added or contained in these drinks. How can we understand this concept of energy within a sugar molecule? Let's take a tablespoon ...
By: HWC, Views: 8197
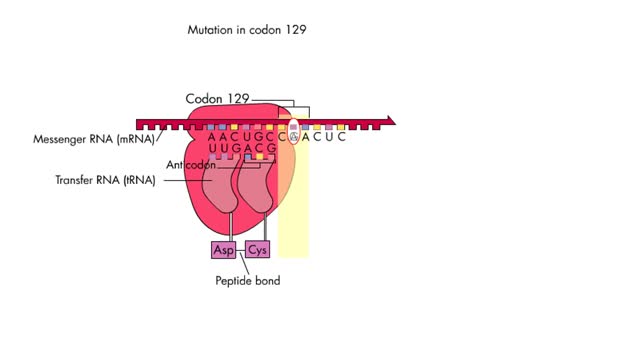
A mutation, which may arise during replication and/or recombination, is a permanent change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. Damaged DNA can be mutated either by substitution, deletion or insertion of base pairs. Mutations, for the most part, are harmless except when they lead to cell death or t...
Polymerase chain reaction PCR - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5624
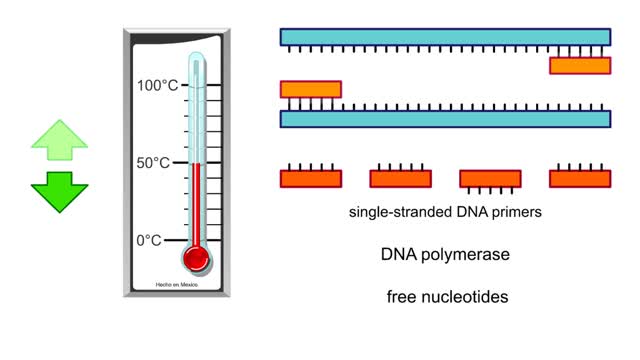
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method that amplifies fragments of DNA. The purpose of PCR is to create copies of a specific region of DNA. To use this technique, researchers must know the base sequences at either end of the region of interest. They use this information to create...
By: HWC, Views: 11582
Acids and bases are found all around your house. For example, if you open your pantry or refrigerator, you might see a lot of acids. Fruit juice, soda pop, vinegar, and milk are all examples of acids. The word acid actually comes from a Latin term meaning ''sour.'' Many materials, like sugar for ...
Splitting of Sugar, Oxidation/ Reduction & ATP Generation
By: HWC, Views: 11403
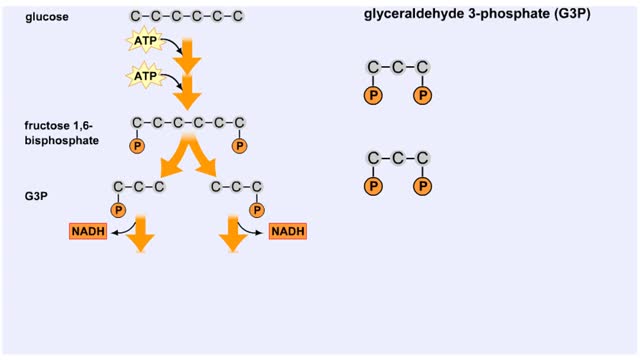
The next reaction shows us the meaning of "glycolysis" or the splitting of glucose. The fructose bisphosphate molecule is split into two molecules each containing 3 carbons as the backbone. FBP is split into two 3-carbon molecules called G3P, or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. Notice that the phos...
Advertisement