Search Results
Results for: 'adenine base'
By: HWC, Views: 11974
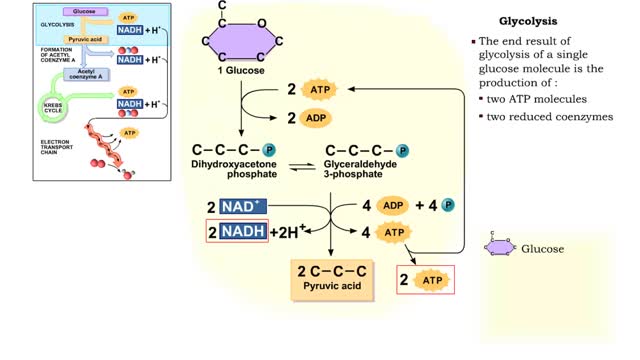
The first reactions involve a single 6-carbon glucose sugar undergoing phosphorylation using two ATP molecules and resulting in two 3-carbon compounds. • The rest of this pathway involves an oxidation reduction reaction, forming two reduced coenzymes, and generation of four ATP molecules. ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14721
Appendectomy. The appendix and cecum are brought through the incision to the surface of the abdomen. The base of the appendix is clamped and ligated, and the appendix is then removed. McBurney’s point is the common location of pain in children and adolescents with appendicitis.
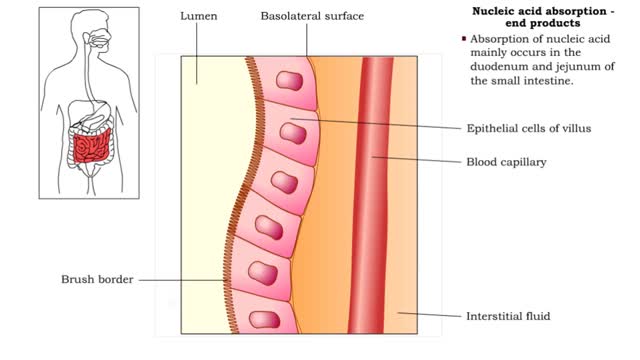
Nucleic acid digestion - brush border enzymes, end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 11533
• Further digestion occurs at the microvilli (brush border) of the epithelial cells of the villi in the small intestine. • Two brush border enzymes complete nucleic acid digestion: • Phosphatases, which catalyze the cleavage of a phosphate to form a nucleoside (nitrogenous base and pent...
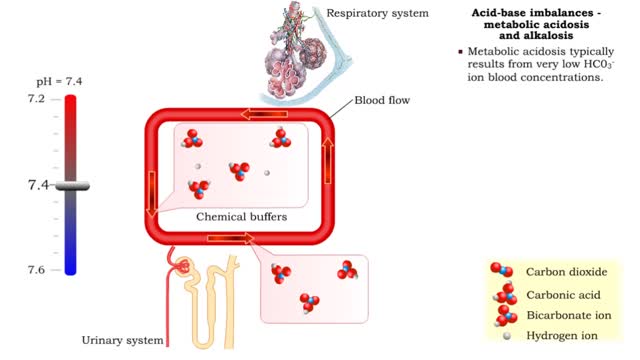
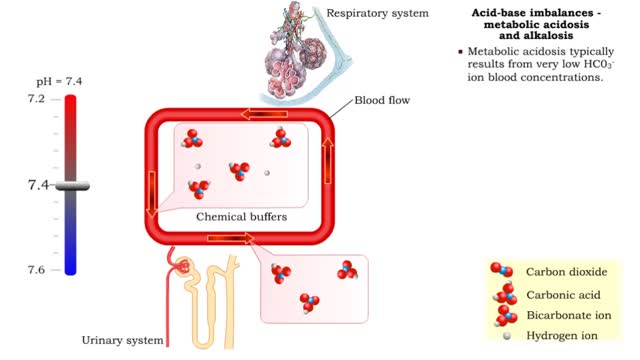
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11849
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
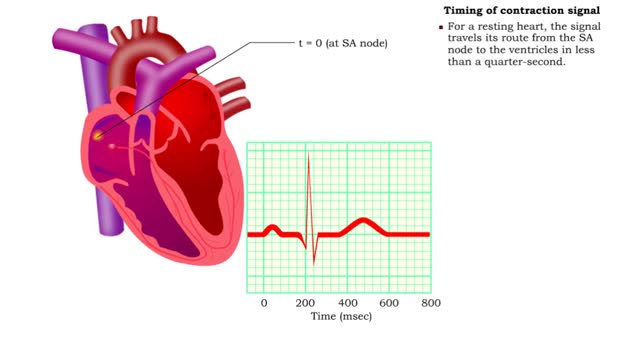
Coaductile pathway, Timing of contraction signal & Conduction system and ECG
By: HWC, Views: 11882
• When the system is healthy, the signal to contract the entire conduction system originates in the SA node - known as the heart's pacemaker. • The SA node triggers contraction because it depolarizes at a faster rate than other parts of the conduction system. • The wave of excitation fr...
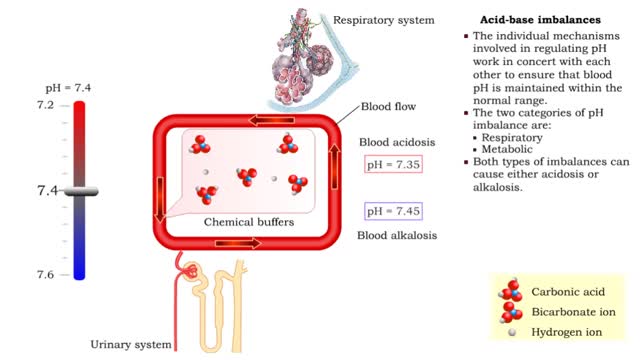
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 12041
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
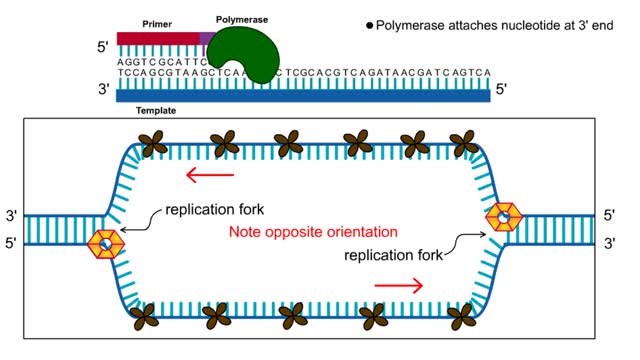
By: HWC, Views: 11080
First step: strands are separated • Helicase unwinds the DNA double helix at the replication fork • SSBs coat the single strands to prevent reannealing • Polymerase attaches nucleotide at 3' end • Synthesis is in 5' to 3' direction DNA Polymerase: • Only extends nucleic ac...
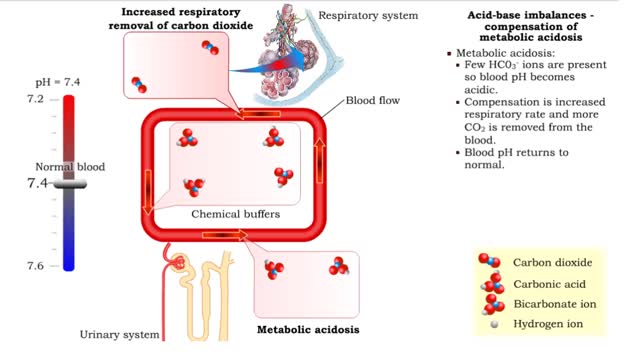
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11848
1. Metabolic acidosis: • Few HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased respiratory rate and more CO2 is removed from the blood. • Blood pH returns to normal. 2. Metabolic alkalosis: • Many HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes alkaline...
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11939
• When one pH balancing system is affected then the other balancing system attempts to correct, or compensate for, the pH imbalance. - Respiratory acidosis: • Excessive CO2 is present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased secretion of H+ into urine and reabsorption ...
Advertisement