Search Results
Results for: 'atmospheric and alveolar pressures'
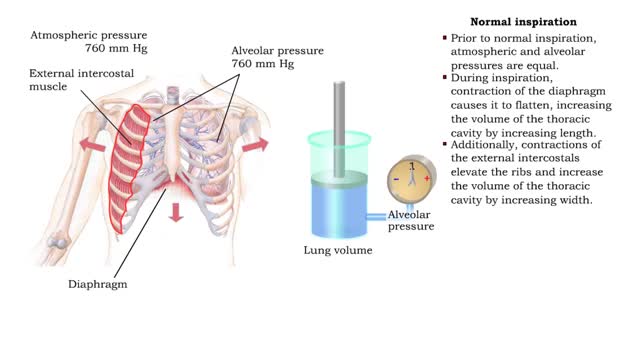
Pressure volume relationships - Normal inspiration and expiration
By: HWC, Views: 10914
• Changing the relative pressure in the compartments can control the direction of airflow between compartments. • In a closed compartment, pressure and volume are inversely related. • Reducing the volume will increase the pressure. • Increasing the volume will decrease the pressure. ...
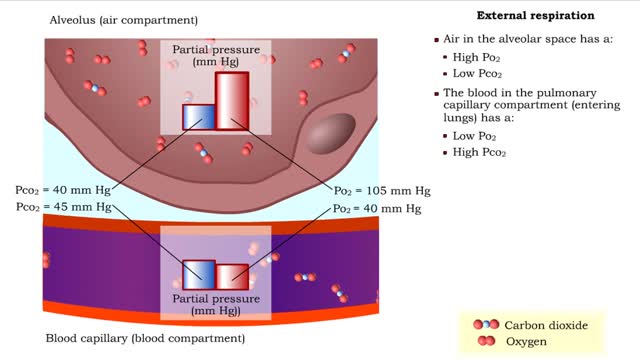
Gas exchange - partial pressure, locations, external and internal respiration
By: HWC, Views: 11225
▪ In a mixture, each individual gas exerts a pressure that is proportional to the concentration of that gas within the mixture. • This part of the total pressure is called a "partial pressure". • A gas moves along the part of the pressure gradient determined by its own concentration. ...
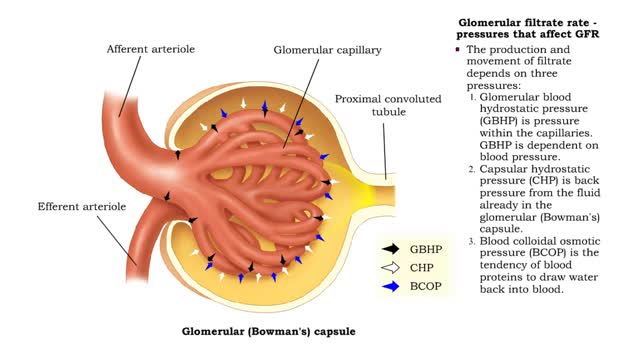
Glomerular filtrate rate: pressures that affect GFR, NFP & GFR and blood composition
By: HWC, Views: 11556
• The glomerular filtration rate is the amount of filtrate formed per minute within the renal corpuscle. • Once the filtrate is formed it moves down the tubule. • The production and movement of filtrate depends on three pressures: I. Glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP) is ...
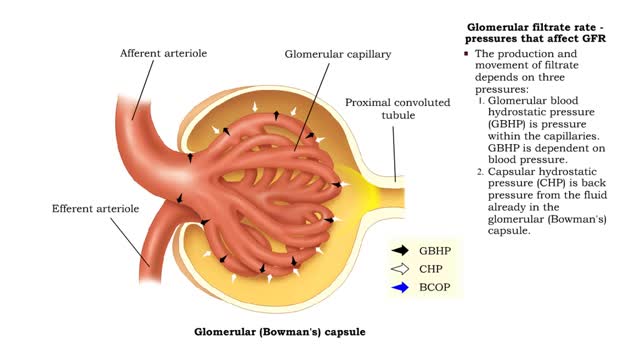
Glomerubular filtrate rate -pressures that affect GFR and net filtration pressure
By: HWC, Views: 11451
• The glomerular filtration rate is the amount of filtrate formed per minute within the renal corpuscle. • Once the filtrate is formed it moves down the tubule. • The production and movement of filtrate depends on three pressures: I. Glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP) is pre...
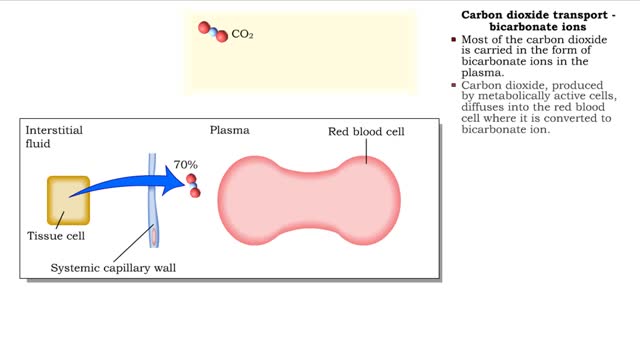
Methods of carbon dioxide transport - carbaminohemoglobin and bicarbonate ions
By: HWC, Views: 11104
• Carbon dioxide is transported three ways: • As bicarbonate ions in the plasma. • Bound to hemoglobin. • As a dissolved gas in the plasma. • A small percent of carbon dioxide is transported as a dissolved gas. • Some of the carbon dioxide is bound to hemoglobin, in the fo...
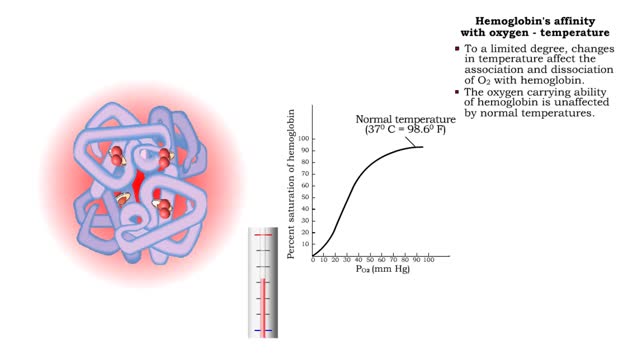
Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - carbon dioxide, temperature and bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
By: HWC, Views: 11022
• The carbon dioxide gas is temporarily converted to carbonic acid in red blood cells by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, and then further converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. • The result of increased carbon dioxide is decreased pH causing the Bohr effect. • Elevated carbon dioxid...
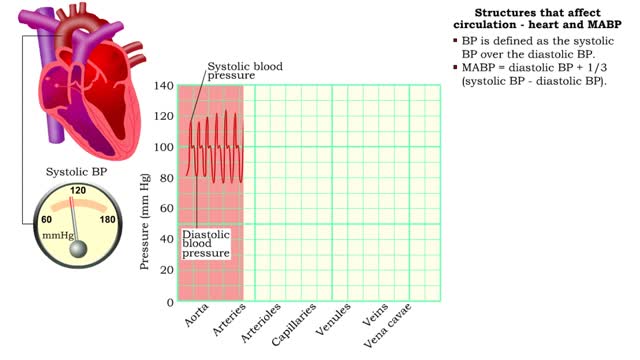
Structures that affect circulation - heart and MABP
By: HWC, Views: 10582
â– BP is defined as the systolic BP over the diastolic BP. â– MABP = diastolic BP + 1/3 (systolic BP - diastolic BP). â– MABP accounts for diastole lasting longer than systole; mean is not equidistant between the two pressures.
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 10925
• Dissociation of the chemical substances in the body fluids can result in the production of free hydrogen ions. • The pH scale is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. • Normal blood pH values vary around 7.4. • When hydrogen ion concentration increases, t...
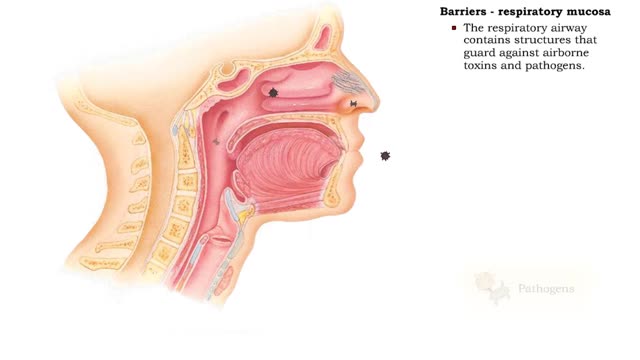
Barriers - eye structures, digestive mucosa, respiratory mucosa & genitourinary mucosa
By: HWC, Views: 11336
• Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and conjunctiva serve to trap microbes preventing their invasion. • Tearing (lacrimation) is a protective mechanism that washes away microbes that attempt to enter the eyes. • Salts, mucus, and lysozymes in tears neutralize substances and bacteria. â€...
Advertisement