Search Results
Results for: 'lymphatic capillaries'
By: Administrator, Views: 578
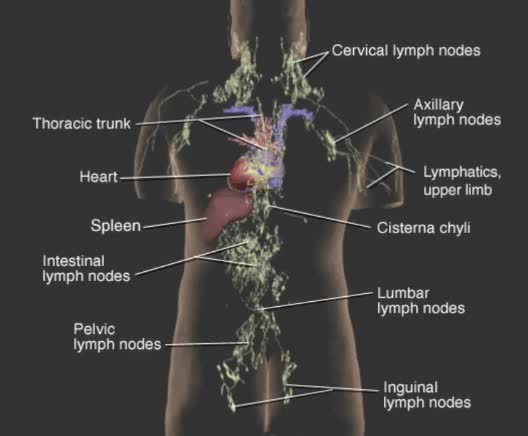
Blood and lymph are two of the body's main fluids and are circulated through two separate but interconnected vessel systems. Blood is circulated by the action of the heart, through the circulatory system consisting largely of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Lymph does not actually circulate. ...
Bulk flow - Factors that influence bulk flow
By: HWC, Views: 11334
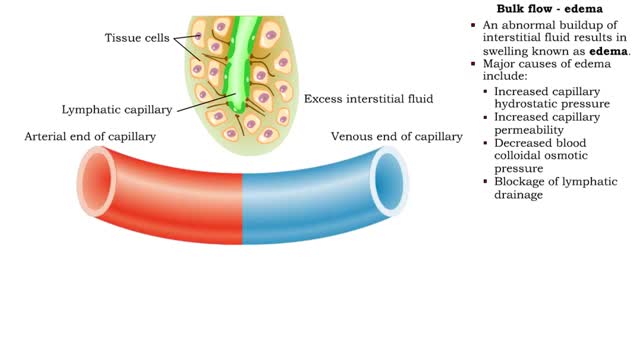
• Bulk flow helps regulate the relative volumes of blood and interstitial fluid. • Flow from blood to interstitium is called filtration. ■ Flow from interstitium to blood is called reabsorption. ■ Four factors determine the net direction of capillary exchange. ■ These factors in...
Net filtration pressure and lymph formation, edema & blood velocity
By: HWC, Views: 10969
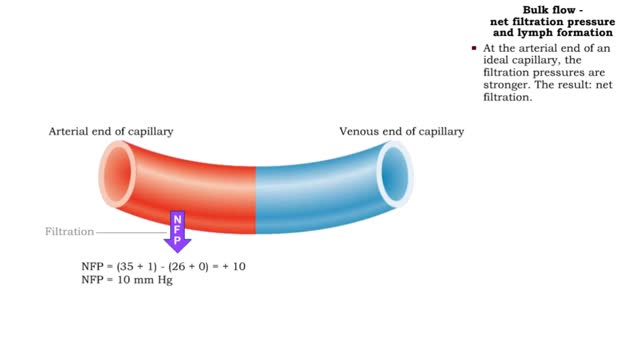
Bulk flow -net filtration pressure and lymph formation • The net filtration pressure (NFP) is the force promoting filtration minus the force promoting reabsorption. • At the arterial end of an ideal capillary, the filtration pressures are stronger. The result: net filtration. • At t...
Barriers - eye structures, digestive mucosa, respiratory mucosa & genitourinary mucosa
By: HWC, Views: 11405
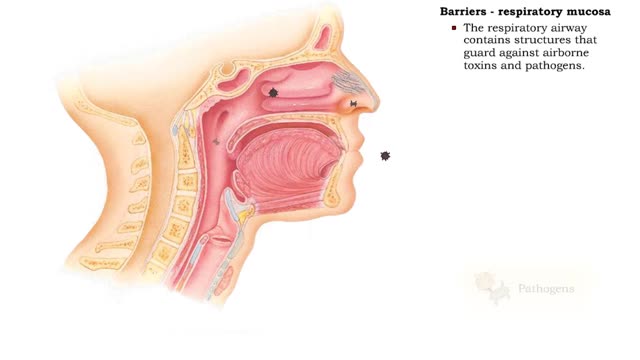
• Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and conjunctiva serve to trap microbes preventing their invasion. • Tearing (lacrimation) is a protective mechanism that washes away microbes that attempt to enter the eyes. • Salts, mucus, and lysozymes in tears neutralize substances and bacteria. �...
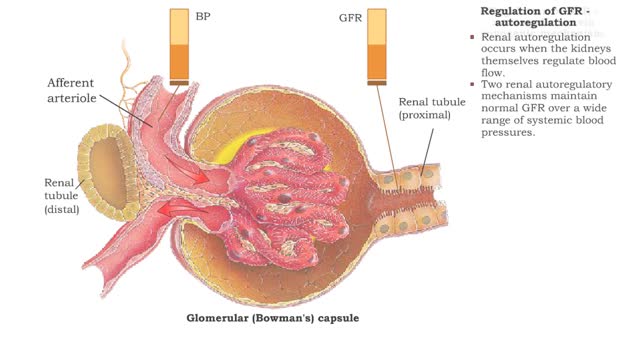
Regulation of GFR: three methods, autoregulation & autoregulation via myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 11652
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Hormonal regulation. • Ren...
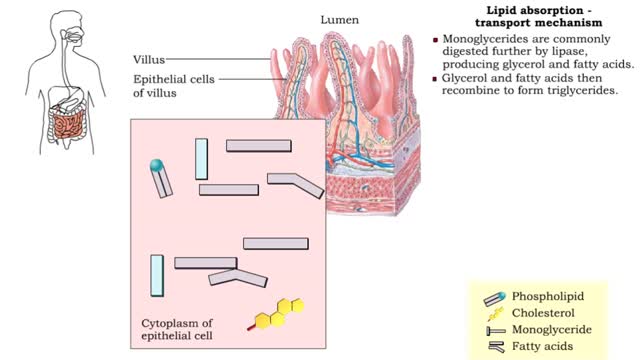
Lipid absorption - end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 10725
• The end products, fatty acids and monoglycerides, depend on bile salts for absorption. • Bile salts form micelles (tiny spheres), which ferry fatty acids and monoglycerides to epithelial cells. • Free fatty acids, monoglycerides, and some phospholipids and cholesterol molecules, dif...
By: Administrator, Views: 488
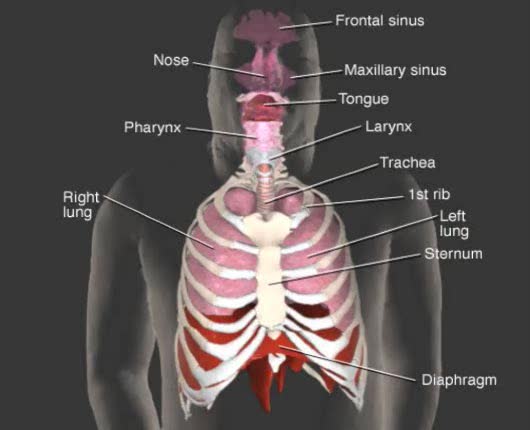
Respiratory system: nose pharynx larynx trachea bronchi lungs Respiratory system’s primary function: Furnish oxygen (O2) for use by individual tissue cells and take away their gaseous waste product, carbon dioxide (CO2), through act of respiration. External respiration Lungs are vent...
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via myogenic mechanism Myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 12685
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Renal autoregulation occurs when...
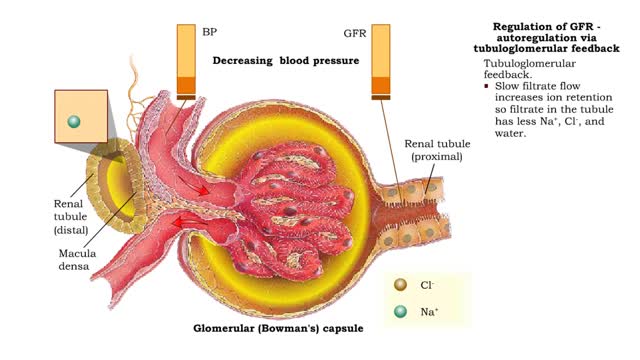
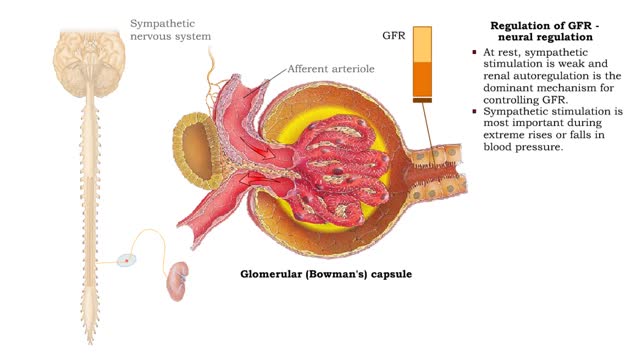
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 12195
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
Advertisement