Search Results
Results for: 'ENS'
By: HWC, Views: 12160
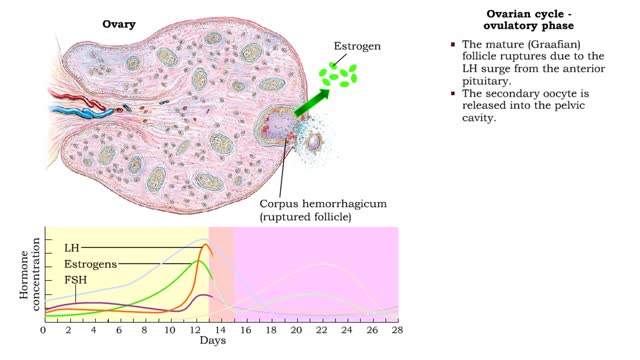
• The ovarian cycle is a monthly sequence of events, consisting of three phases: • Preovulatory • Ovulatory • Post ovulatory Preovulatory phase • prior to ovulation: Primary follicles develop into secondary follicles. • Follicular cells surrounding the primary oocyte In...
Uterine (menstrual) cycle - phases
By: HWC, Views: 11633
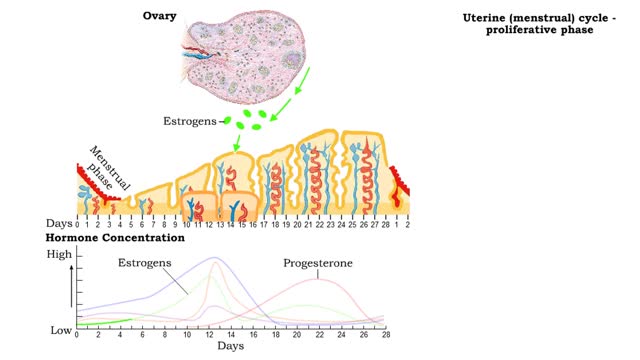
• The uterus goes through a cyclical developmental pattern to be ready for implantation and support of an embryo. • The uterine, or menstrual, cycle is under the control of ovarian horrnones. • The uterine cycle also has three phases: • Menstrual phase • Proliferative phase �...
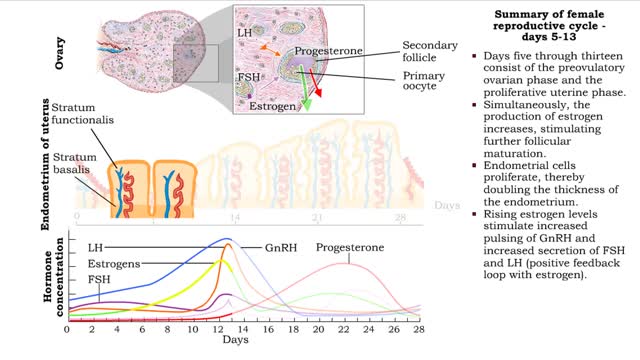
Summary of female reproductive cycle days 1-28
By: HWC, Views: 12177
■ The first five days of the cycle include the menstrual phase. ■ Progesterone and estrogen levels are low. ■ Menses occurs. ■ GnRH pulses more frequently promoting FSH and LH levels to rise. ■ Primary follicles are stimulated to develop. ■ Days five through thirteen consist o...
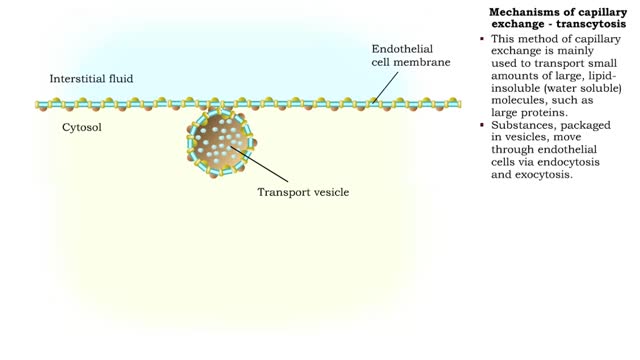
Mechanisms of capillary exchange
By: HWC, Views: 11902
■ The primary role of capillaries is to permit the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells (via interstitial fluid). ■ Oxygen and nutrients move from the blood to the cells. ■ Carbon dioxide and other wastes move from the cells to the blood. The three ba...
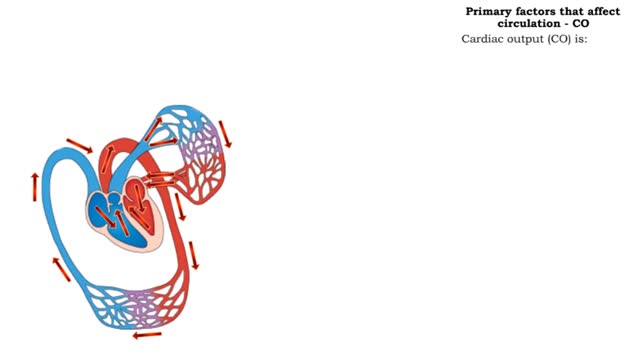
The primary factors that affect circulation - MABP, CO and SVR
By: HWC, Views: 12104
Introduction Blood flow is determined by the relative intensities of factors that drive and resist moving blood. • Cardiac output (CO) equals the mean arterial blood pressure (MABP, a driving force) divided by systemic vascular resistance (SVR, a resisting force). • Hormones and the cen...
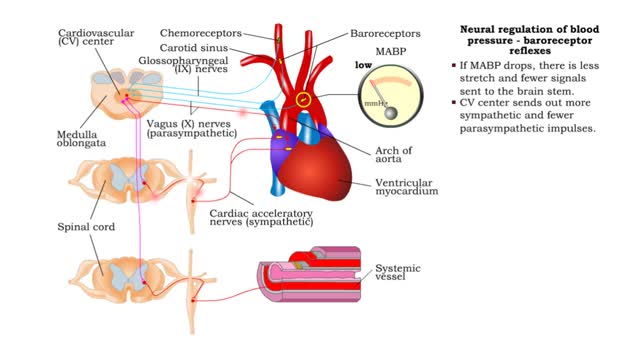
Neural regulation of blood pressure - baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes
By: HWC, Views: 12084
• The nervous system regulates blood pressure with two reflex arcs: baroreceptor and chemoreceptor. ■ Baroreceptors (pressure) and chemoreceptors (chemical) are located in the carotid sinus and aortic arch. • Carotid sinus reflex helps maintain normal blood pressure in brain. • Ba...
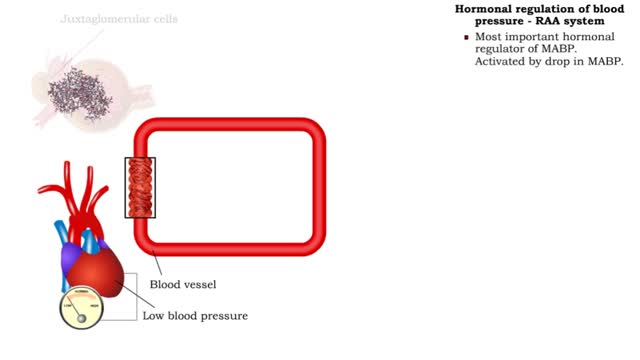
Hormonal regulation of blood pressure - RAA system
By: HWC, Views: 12224
■ Long-term regulation of MABP is under hormonal control. • Hormones that affect blood pressure and volume: the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) system, antidiuretic hormone (ADM), and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP). ■ Most important hormonal regulator of MABP. Activated by drop in...
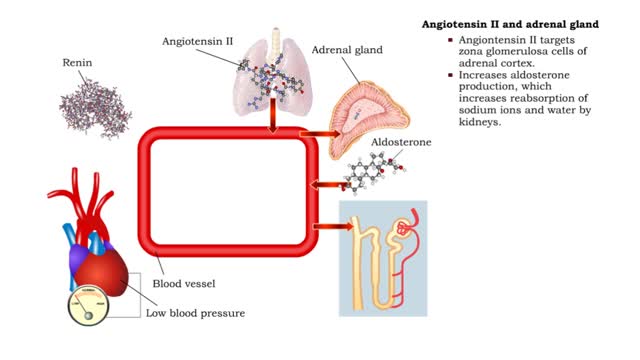
Angiotensin II - kidneys, adrenal glands and dehydration
By: HWC, Views: 11797
• Angiontensin II targets cells in the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. ■ The reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- ions sets up an osmotic gradient favoring the retention of water. • Decreases urine production and increases blood volume and pressure. • Angiontensin II targets zon...
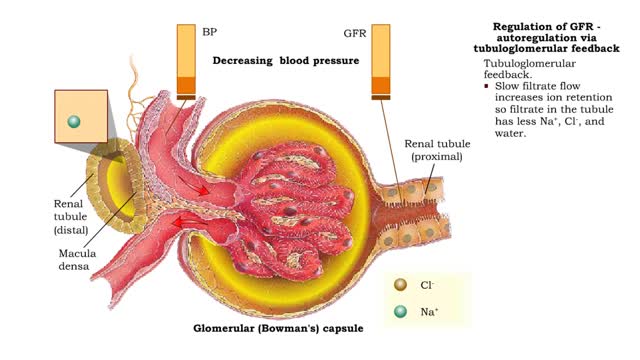
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via myogenic mechanism Myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 13278
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Renal autoregulation occurs when...
Advertisement