Search Results
Results for: 'blood vessels'
Hormonal feedback loop components & Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10802
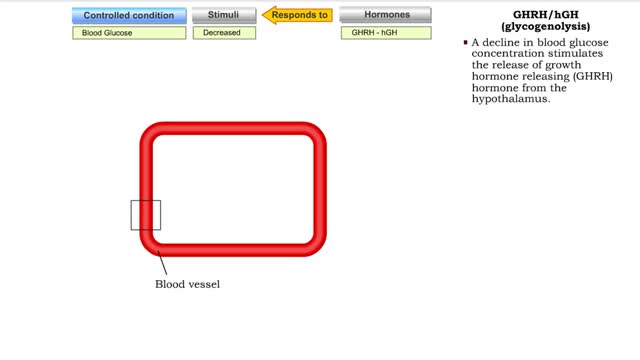
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after ...
Rh blood type and complications during pregnancy & Fertilization
By: HWC, Views: 8489
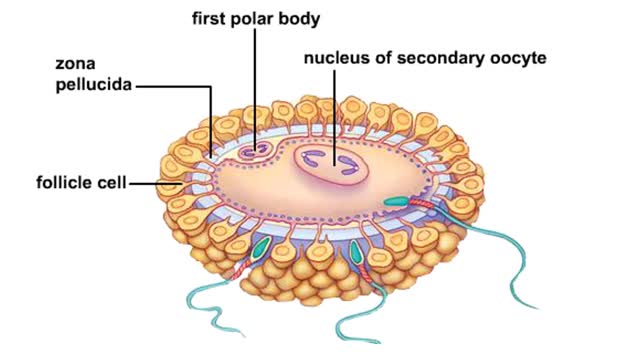
Complications can arise if an Rh- woman is impregnated by an Rh+ man. The fetus maybe Rh+. During childbirth, some of the fetal Rh+ cells may leak into the maternal bloodstream. The woman's immune system views the Rh+ as foreign and makes antibodies against it. If the woman becomes pr...
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11062
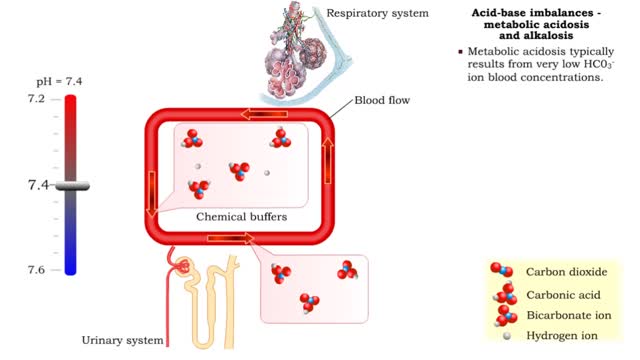
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
By: HWC, Views: 11120
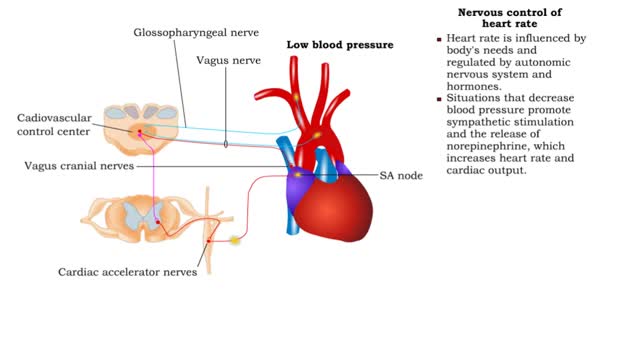
• Heart rate is determined by the rate of depolarizations of the sinoatrial (SA) node. • Cardiac output is directly proportional to heart rate, the greater the heart rate the greater the cardiac output. • Changes in heart rate are associated with exercise, stress or injury. Nervous ...
By: HWC, Views: 8165
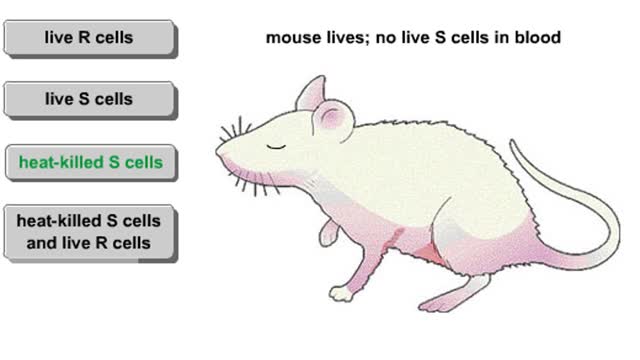
In the late 1920s, Fred Griffith was attempting to develop a vaccine against a bacterium that causes pneumonia. To find out why two strains of the bacteria differed in their deadliness, he injected mice with four different mixtures. Mice injected with R cells remained healthy. When Griffith ex...
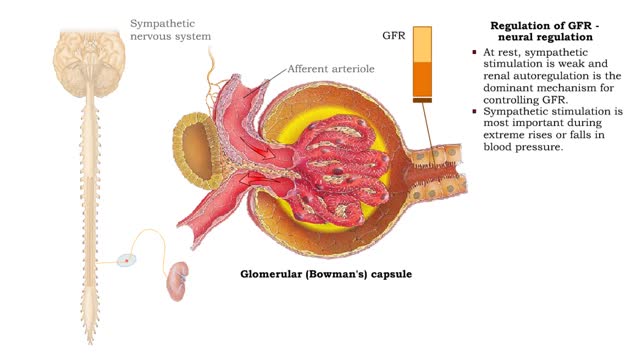
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 12065
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
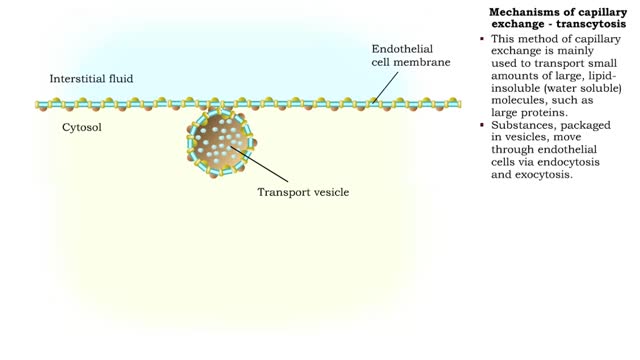
Mechanisms of capillary exchange
By: HWC, Views: 11188
■ The primary role of capillaries is to permit the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells (via interstitial fluid). ■ Oxygen and nutrients move from the blood to the cells. ■ Carbon dioxide and other wastes move from the cells to the blood. The three ba...
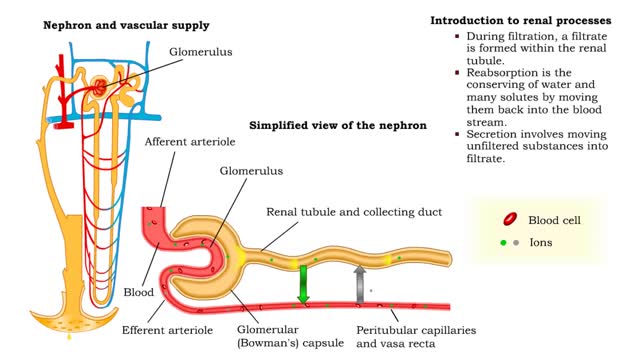
Introduction to filtration - filtrate formation and composition
By: HWC, Views: 11146
• At the nephron, the three process responsible for the formation of urine include: • Glomerular filtration. • Tubular reabsorption. • Tubular secretion. • During filtration, a filtrate is formed within the renal tubule. • Reabsorption is the conserving of water and many s...
By: Administrator, Views: 15254
The islets of Langerhans are composed of three major types of cells: Alpha cells secrete glucagon, elevating blood sugar. Beta cells secrete insulin, maintaining normal blood sugar. Delta cells secrete somatostatin, which suppresses release of glucagon and insulin. Hyposecretion or inadequa...
Advertisement