Search Results
Results for: 'blood vessels'
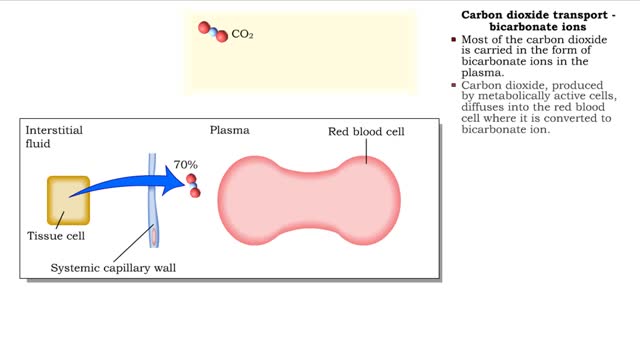
Methods of carbon dioxide transport - carbaminohemoglobin and bicarbonate ions
By: HWC, Views: 11053
• Carbon dioxide is transported three ways: • As bicarbonate ions in the plasma. • Bound to hemoglobin. • As a dissolved gas in the plasma. • A small percent of carbon dioxide is transported as a dissolved gas. • Some of the carbon dioxide is bound to hemoglobin, in the fo...
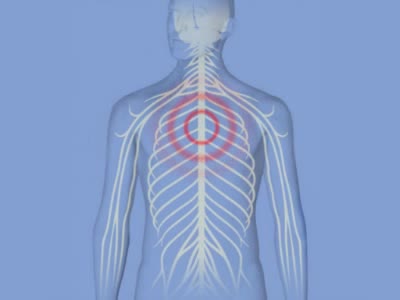
Autonomic Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14261
Parasympathetic Division Works to conserve energy and innervate the digestive system. When activated, it: stimulates the salivary and digestive glands. decreases the metabolic rate. slows the heart rate. reduces blood pressure. promotes the passage of material through the intestines along...
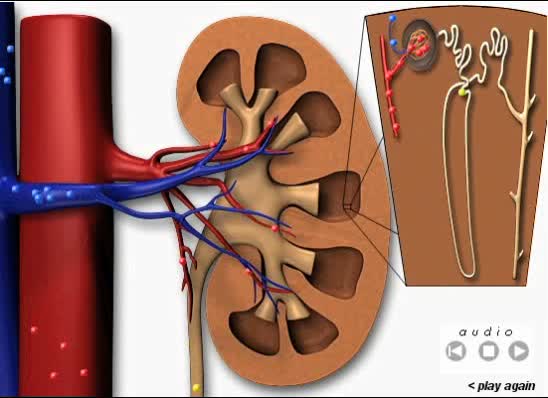
Blood Flow Through the Kidneys
By: Administrator, Views: 13745
Purplish-brown, bean-shaped organs located behind abdominal cavity (retroperitoneal area) on either side of spine, between thoracic vertebrae and lumbar region.
By: Administrator, Views: 13677
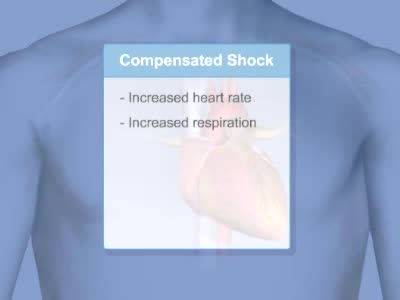
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
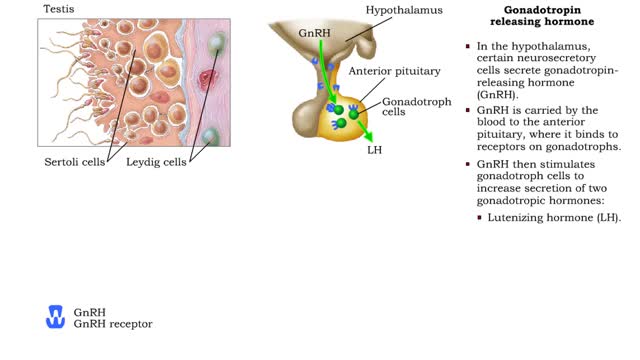
Male Reproductive System - The gonadotropin releasing hormone
By: HWC, Views: 11810
• Hormonal mechanisms that influence male reproductive function involve endocrine tissues contained in the: • Hypothalamus of the brain. • Anterior pituitary. • Testes. • In the hypothalamus, certain neurosecretory cells secrete gonadotropin- releasing hormone (GnRH). • GnRH ...
By: Administrator, Views: 13946
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
By: HWC, Views: 11221
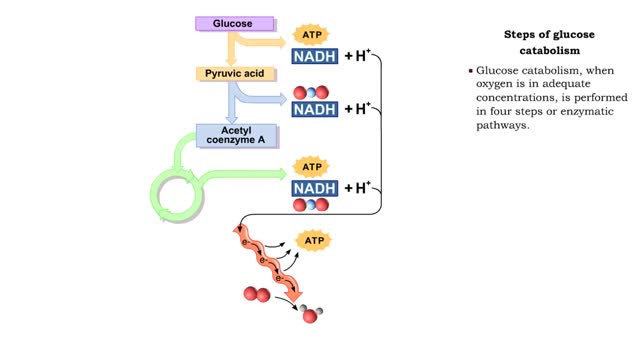
• During digestion, complex carbohydrates are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides, primarily glucose. • The catabolism of glucose is the primary source of energy for cellular production of ATP. • The anabolism of glucose is important in regulating blood glucose levels. • Glucose cat...
A Human Karyotype Preparation Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8327
Blood is collected from the person being analyzed. The blood is added to a growth medium that also contains a chemical that stimulates mitosis. The cells are allowed to grow in this medium for two or three days at body temperature. Colchicine is added to arrest cell division at metaphase. T...
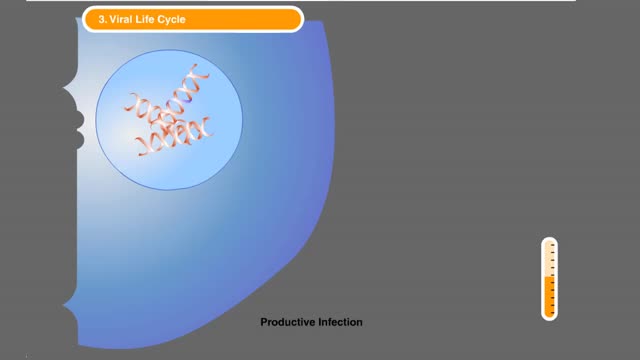
HIV Infection: Viral life cycle
By: HWC, Views: 10414
The series of steps that HIV follows to multiply in the body. The process begins when HIV encounters a CD4 cell. The seven steps in the HIV life cycle are: 1) binding; 2) fusion; 3) reverse transcription; 4) integration; 5) replication; 6) assembly; and 7) budding. Many viruses f...
Advertisement