Search Results
Results for: 'How do proteins work'
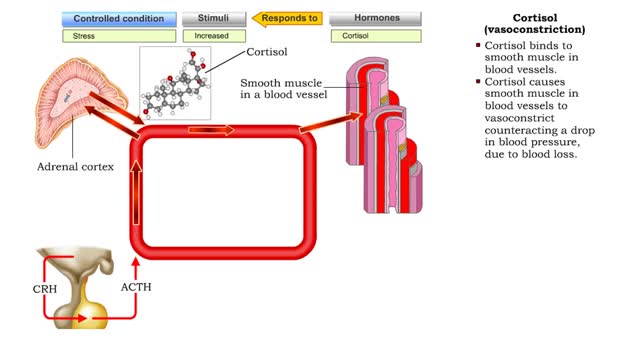
Cortisol (protein catabolism, gluconeogenesis, vasoconstriction & anti-inflammation)
By: HWC, Views: 10742
• Stressors stimulate production of hypothalamic releasing hormones, corticotropin releasing hormone, hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulate. • These hormones promote increased production of 1 cortisol from the zona fasciculata cells of the adrenal cortex. • Cort...
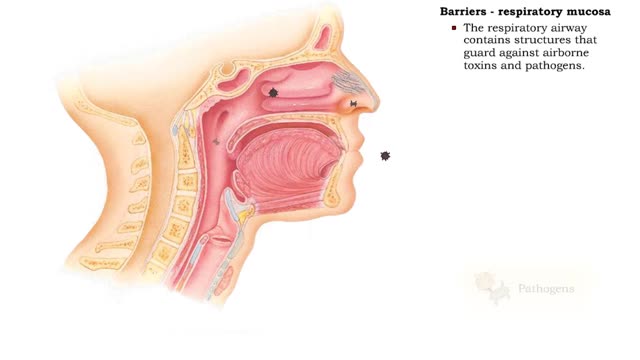
Barriers - eye structures, digestive mucosa, respiratory mucosa & genitourinary mucosa
By: HWC, Views: 11321
• Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and conjunctiva serve to trap microbes preventing their invasion. • Tearing (lacrimation) is a protective mechanism that washes away microbes that attempt to enter the eyes. • Salts, mucus, and lysozymes in tears neutralize substances and bacteria. �...
By: HWC, Views: 11228
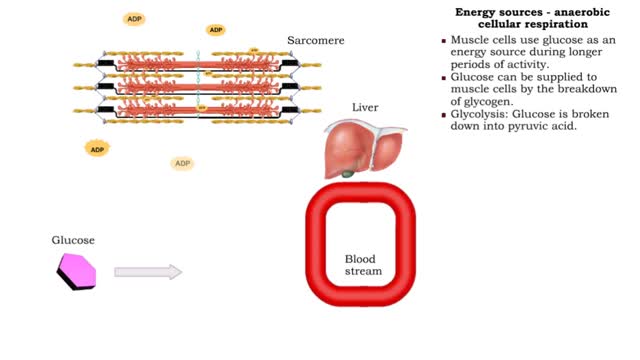
• The amount of ATP stored in a skeletal muscle cell can only provide muscular activity for two to three seconds. • Muscle cells must be able to generate additional molecules of ATP to continue contracting. • Muscle cells can generate ATP from several processes: • Phosphogen syste...
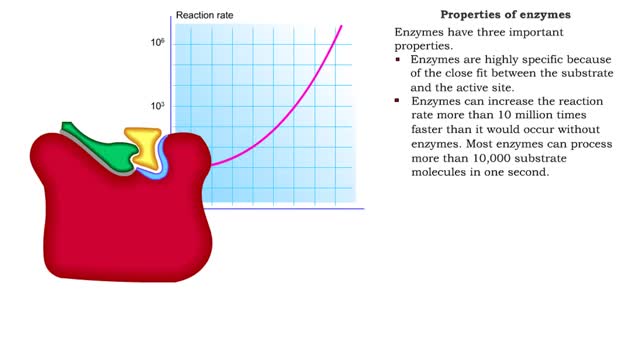
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 10980
■ Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. ■ Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. ■ Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. ■ Coenzymes often come from vitamins. ■ Cofactors affect the shape of...
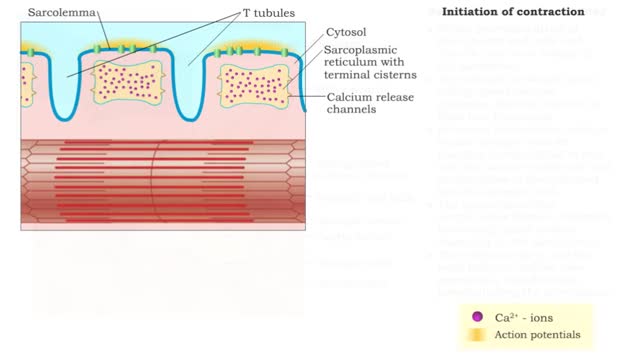
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 11518
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
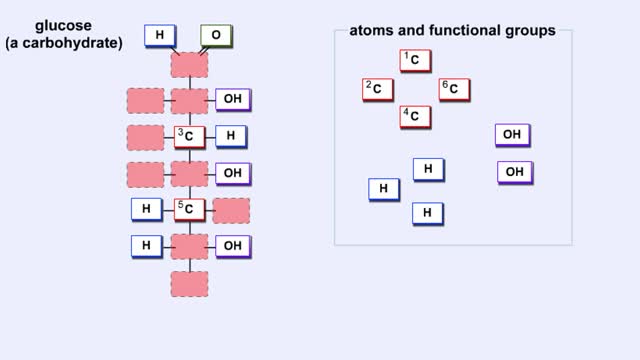
What Are Carbohydrates? Importance of Carbs & High Carb Food
By: HWC, Views: 11184
We hear a lot about carbohydrates in the news. Everybody seems to be on a low-carb diet. The news media often has stories on this diet fad, and companies are busy producing products with reduced carbohydrates. What's this fascination with carbohydrates? In a word: "Diet." The fact is that carb...
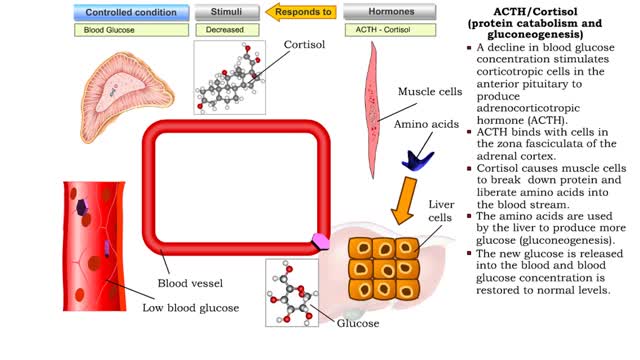
ACTH/Cortisol (glycogenolysis, protein catabolism, lipolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10906
• A decline in blood glucose concentration stimulates corticotropic cells in the anterior pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). • ACTH binds with cells in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. • Increased ACTH promotes the production of cortisol, the major gluco...
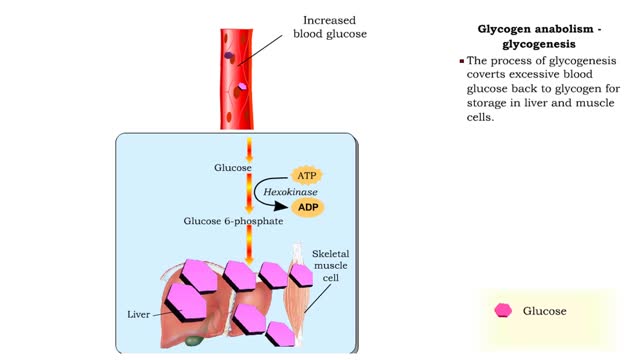
Glucose anabolism reactions: Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 11391
• Glucose not needed immediately is stored as glycogen. The process that creates it is glycogenesis. • When ATP is needed for body activities, stored glycogen is broken down by a process called glycogenolysis. • Glucose can be formed through two different anabolic reactions: • Glycog...
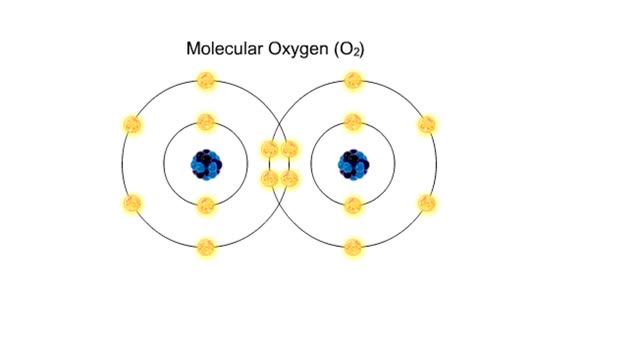
Bond in biological molecules (Ionic, Covalent and Hydrogen bonds)/ How atoms bond?
By: HWC, Views: 8343
Sodium atoms and chloride atoms have unfilled orbitals in their outer shells. The lone electron in the outermost shell of a sodium atom can be pulled or knocked out. This ionizes the atom. It is now a positively charged sodium ion. A chlorine atom has an electron vacancy in its outer shell and...
Advertisement