Search Results
Results for: 'epithelial cell'
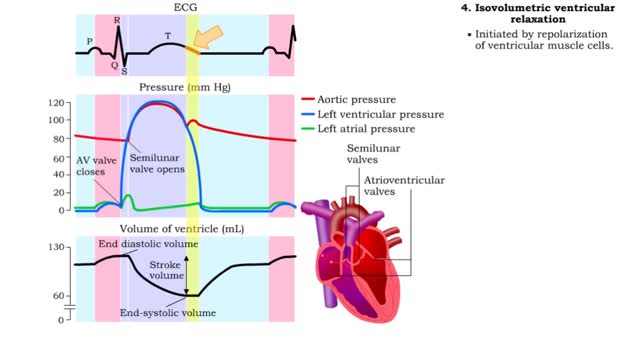
Isovolumetric VC, Ventricular ejection, Isovolumetric & Passive ventricular filling
By: HWC, Views: 10955
• Isovolumetric means that blood volume does not change. • Ventricular blood volume and cell length remain constant. • With valves closed and contraction continuing, ventricular pressure continues to rise. • Ventricular pressure rises above arterial pressure. • Increased ventr...
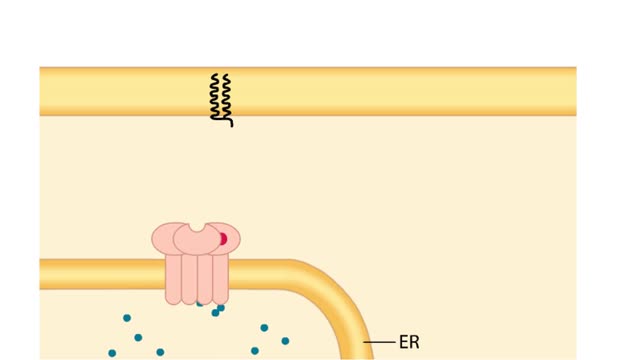
Second Messengers in the Inositol-lipid Signaling Pathway
By: HWC, Views: 10194
Extracellular signals produce specific responses in target cells through the action of intracellular second messengers. Here, we focus on three second messengers, IP3, DAG, and Ca2+, all involved in the inositol-lipid signaling pathway. A hormone-receptor signal on the cell surface leads to the a...
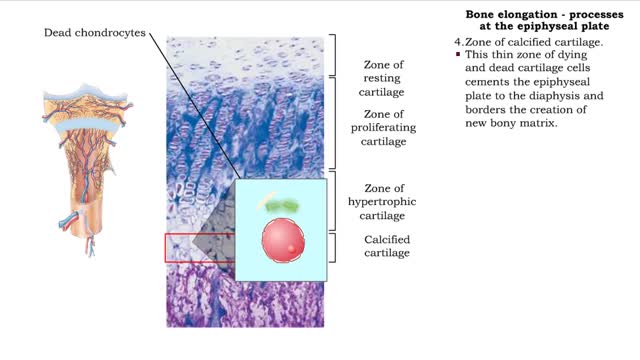
Bone elongation - processes at the epiphyseal plate
By: HWC, Views: 11192
• Interstitial lengthening occurs in only certain bones, primarily those of the appendages. • Such lengthening takes place at the epiphyseal plate, a layer of hyaline cartilage in the metaphysis of a growing bone. 1. Zone of resting cartilage. • Consisting of a hyaline cartilage pa...
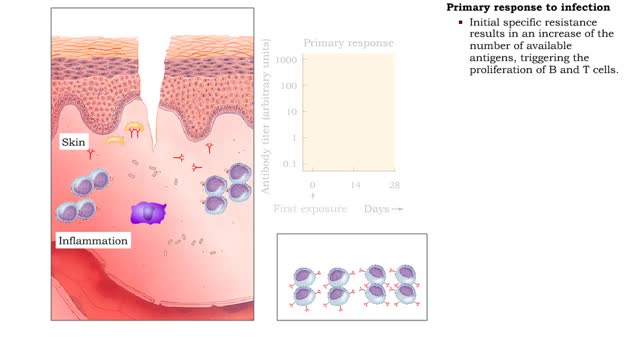
Primary and secondary response to infection
By: HWC, Views: 10904
• Pathogens enter the body by penetrating the non-specific barriers in the skin and mucus membranes. • Pathogens first encounter macrophages and natural killer cells that carry out phagocytosis and cytolysis respectively. • A pathogen's first encounter with the immune system can promo...
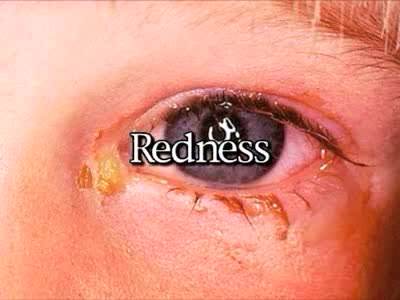
By: Administrator, Views: 14221
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is inflammation of the outermost layer of the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid. It makes the eye appear pink or reddish. Pain, burning, scratchiness, or itchiness may occur. The affected eye may have increased tears or be "stuck shu...
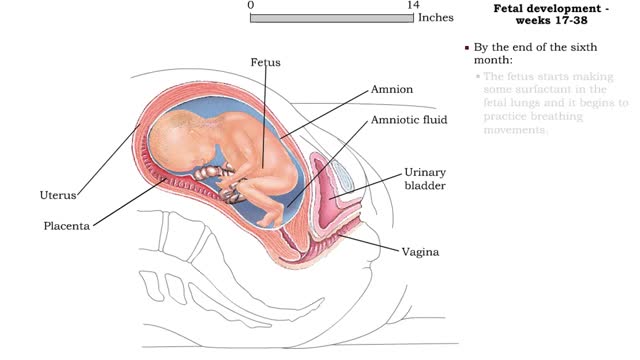
Fetal development - Weeks 9 to 38
By: HWC, Views: 11244
Weeks 9-12 • Fetal development during the third month includes: • A large head, about 1/2 the length of the fetus. • Visible eyes and ears. • A detectable heartbeat. • Kidneys that form urine. • Gender identification. • Weak, undetectable body movements. • By the e...
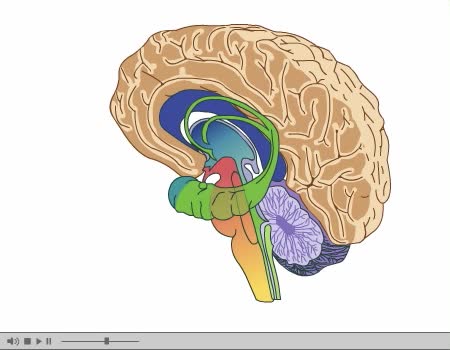
Brain Anatomy Animation (Part 2 of 2)
By: Administrator, Views: 15379
Its nervous tissue consists of millions of nerve cells and fibers. It is the largest mass of nervous tissue in the body. The brain is enclosed by three membranes known collectively as the meninges: dura mater arachnoid pia mater The major structures are the: cerebrum cerebellum dienc...
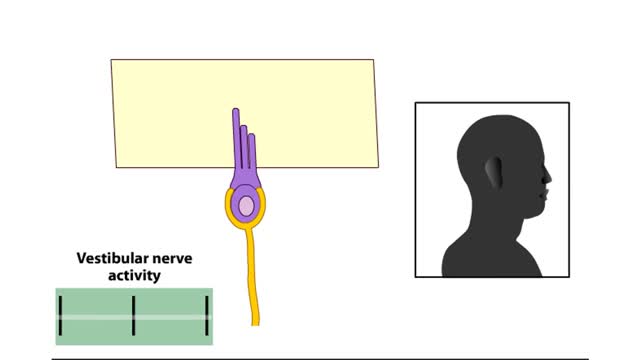
By: HWC, Views: 10067
The vestibular system has important sensory and motor functions, contributing to the perception of self-motion, head position, and spatial orientation relative to gravity. The function of the vestibular system can be simplified by remembering some basic terminology of classical mechanics. All ...
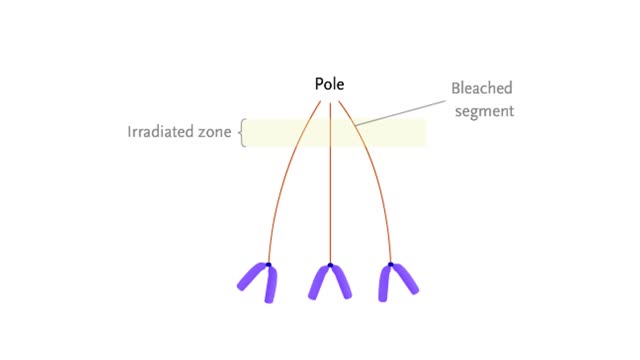
Mechanisms for chromosome movement Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8174
At mitotic metaphase, the fully-formed spindle is composed of many microtubules that extend from the poles. Some of these, the kinetochore microtubules, are attached to the kinetochores of each chromosome. Kinetochores are located at the centromeres. At anaphase, sister chromatids separate and...
Advertisement