Search Results
Results for: 'second and third levels of protein structure'
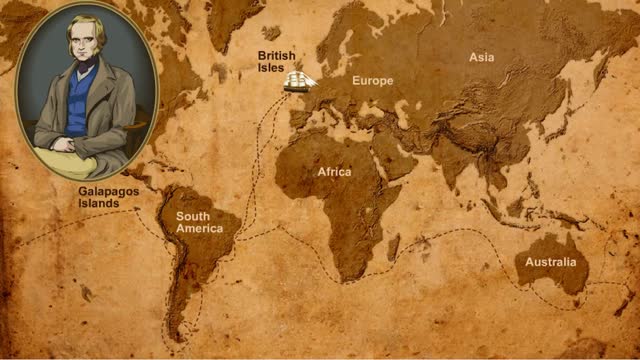
Diversity of Living Creatures - Charles Darwin & the Beagle's Voyage
By: HWC, Views: 11286
As we look around at the living creatures on Earth, we see a great amount of diversity. In some cases, the differences are quite noticeable, like the differences between plants and animals. Some differences are not as easy to see, like the differences between two species of lizard. How did all...
By: HWC, Views: 10873
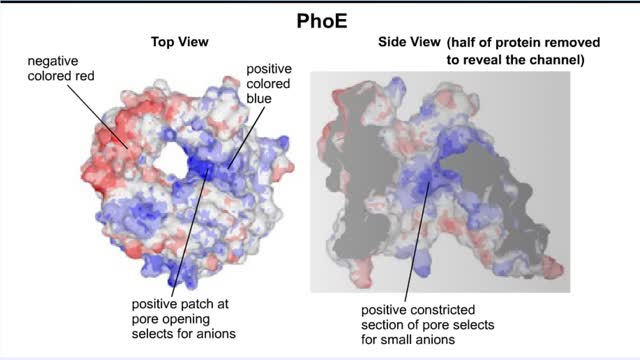
Transmembrane channels, also called membrane channels, are pores within a lipid bilayer. The channels can be formed by protein complexes that run across the membrane or by peptides. They may cross the cell membrane, connecting the cytosol, or cytoplasm, to the extracellular matrix. Membrane po...
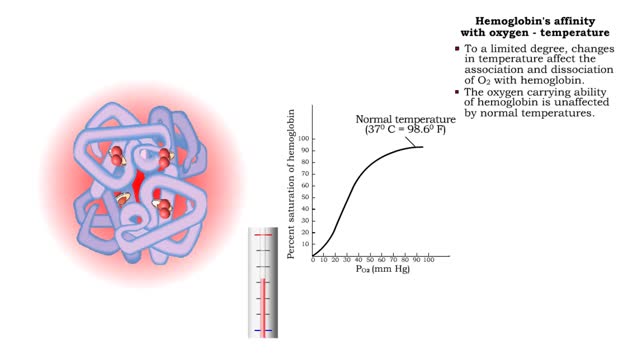
Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - carbon dioxide, temperature and bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
By: HWC, Views: 11681
• The carbon dioxide gas is temporarily converted to carbonic acid in red blood cells by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, and then further converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. • The result of increased carbon dioxide is decreased pH causing the Bohr effect. • Elevated carbon dioxid...
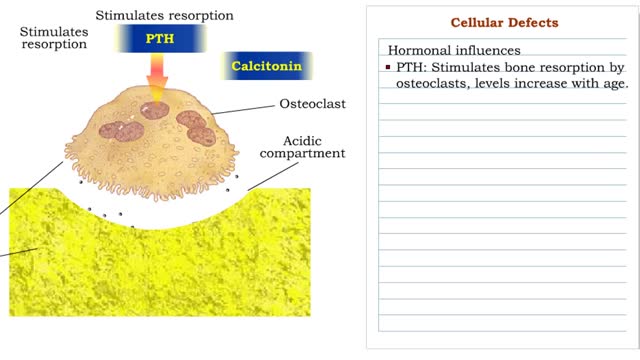
Cellular Defects - Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts and Osteocytes
By: HWC, Views: 11336
■ Metabolically active bone-building cells that secrete astroid. ■ Cover surfaces of newly formed bone and respond to growth stimuli ■ Less responsive to growth factors as the body ages. ■ Contribute to hone loss once their reproductive and biosynthetic potential lessens....
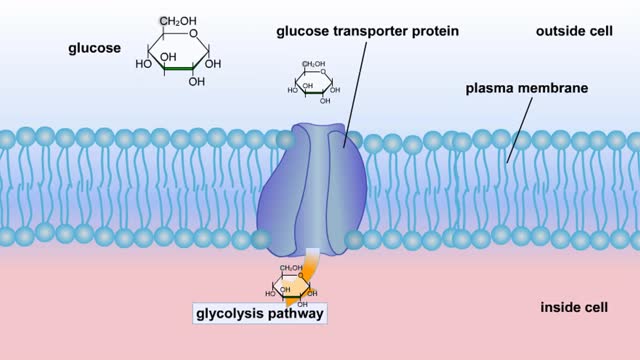
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 11436
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
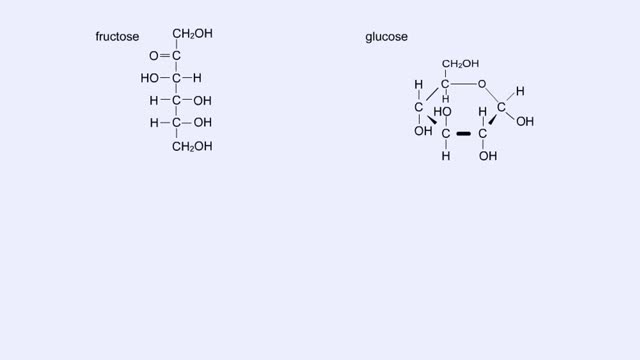
By: HWC, Views: 11459
Here are the molecular structures of three simple sugars: glucose, ribose, and fructose. Look at these simple sugars and identify what characteristics they all share. As you can see, all of the carbohydrates have carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1 and there is always a double bo...
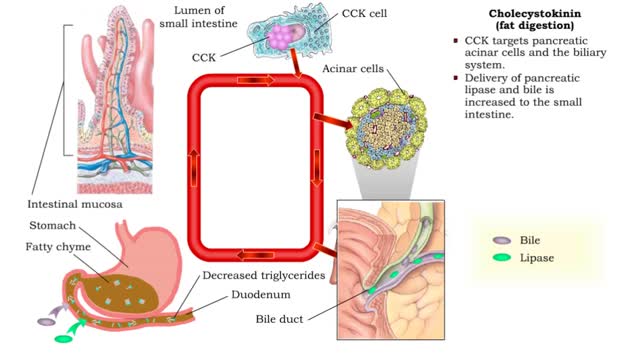
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 11560
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
Chronology of leptin research (A history of leptin research)
By: HWC, Views: 8727
In 1950. researchers at Jackson Laboratories noticed that one of their mice had become extremely obese—it had an insatiable appetite. Intrigued, they bred a strain of mice showing this characteristic. In the late 1960s, researchers surgically connected the bloodstreams of a normal mouse and a...
Studying the Left and Right Brain Independently
By: Administrator, Views: 14962
A seizure, technically known as an epileptic seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with loss of consciousness (tonic-clonic seizure), to shakin...
Advertisement