Search Results
Results for: 'Men'
By: Administrator, Views: 15121
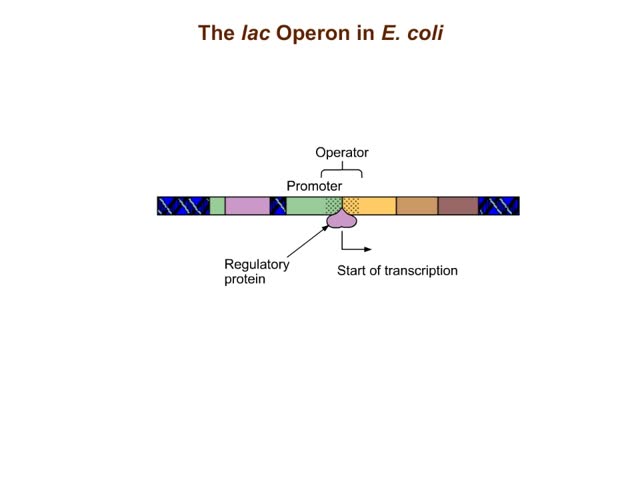
The lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is no...
Embryonic development - Week 4
By: HWC, Views: 11130
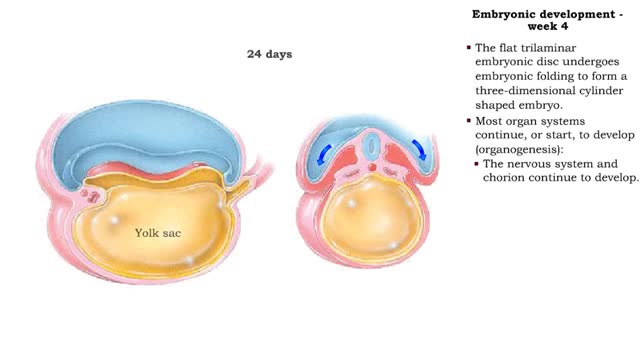
• The flat trilaminar embryonic disc undergoes embryonic folding to form a three-dimensional cylinder shaped embryo. • Most organ systems continue, or start, to develop (organogenesis): • The nervous system and chorion continue to develop. • The heart and the rest of the cardiovas...
Embryonic development - Weeks 5 to 8
By: HWC, Views: 11195
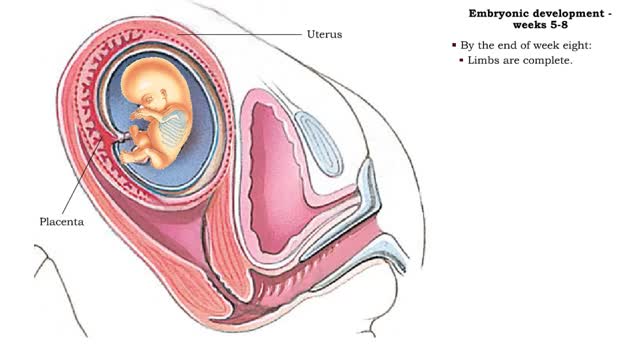
• The second month of development is characterized by rapid development of the head and limbs as well as continued organogenesis. • During the fifth and sixth weeks growth of the brain, and therefore head, is rapid. • Hands and feets begin to form. • During week seven, even more deve...
Fetal development - Weeks 9 to 38
By: HWC, Views: 11186
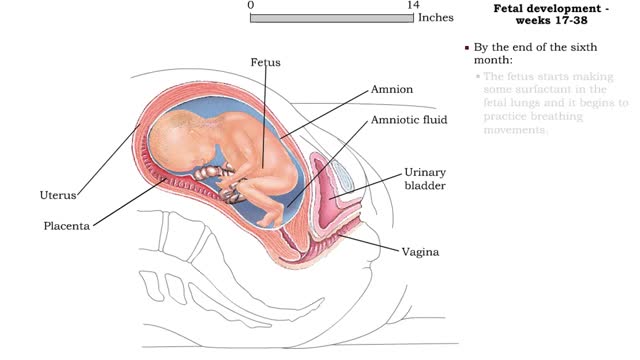
Weeks 9-12 • Fetal development during the third month includes: • A large head, about 1/2 the length of the fetus. • Visible eyes and ears. • A detectable heartbeat. • Kidneys that form urine. • Gender identification. • Weak, undetectable body movements. • By the e...
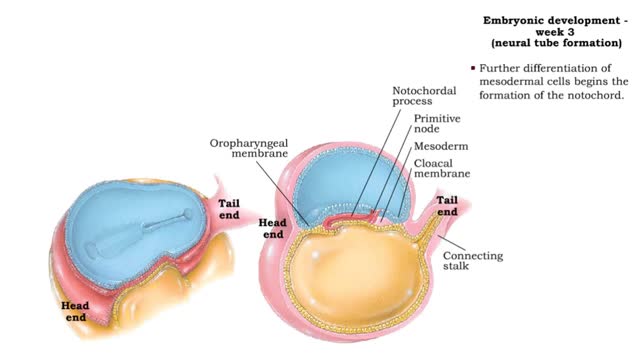
Embryonic development - Week 3
By: HWC, Views: 11069
Week 3 (gastrulation) • Three primary germ layers are formed which provide cells for organ formation in the following months. • These germ cell layers are formed by a process known as gastrulation, which involves rearranging epiblast cells. • As cells from the epiblast migrate, a fain...
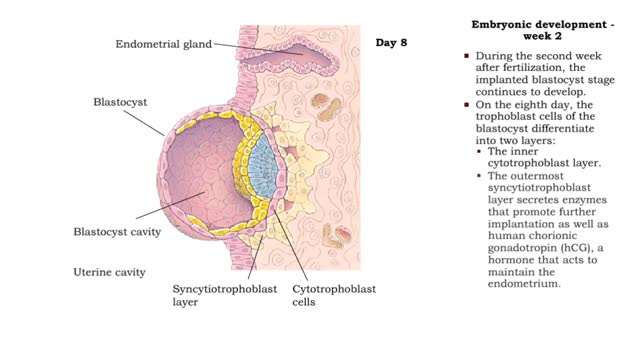
Embryonic development - week 1 and 2
By: HWC, Views: 11026
The first through eighth weeks after fertilization are called the embryonic. Week 1 • Within a day, the zygote begins mitotic cell division (cleavage) forming blastomeres. By the 4th day, the blastomeres have formed a solid ball called a morula. • The morula enters uterine cavity ar...
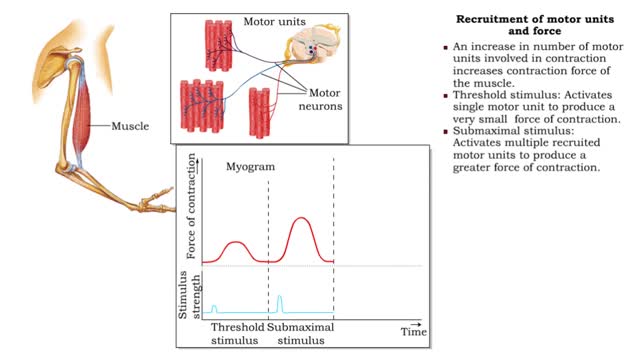
Frequency of stimulation and force (Recruitment of motor units and force)
By: HWC, Views: 11305
• Muscle tension depends on the frequency of stimulation. • Muscle twitch: First stimulus. • Wave summation: When a second stimulus excites a partially relaxed muscle, producing a stronger contraction. • Unfused tetanus: Successive stimulations at the same frequency, producing a se...
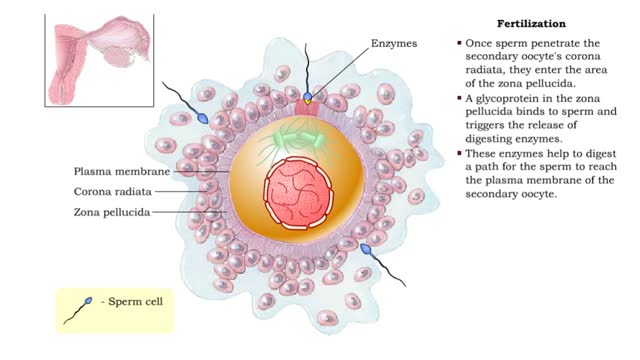
By: HWC, Views: 11419
• Fertilization is the process by which the two gametes from the parents fuse their genetic material to form a new individual (zygote). • Fertilization requires that sperm cells swimming through the uterine tube contact a secondary oocyte. • Once sperm penetrate the secondary oocyte's ...
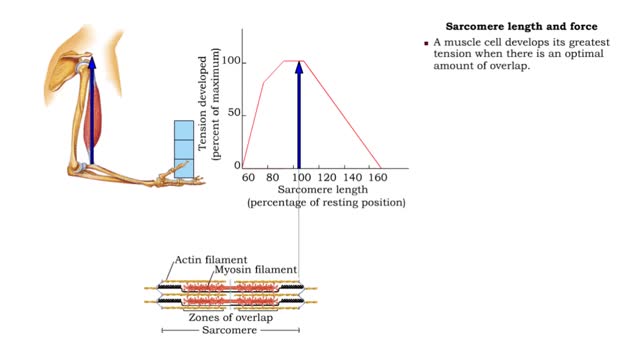
Factors that influence muscle tension - Sarcomere length and force, understretched and overstretched
By: HWC, Views: 11095
• Muscle tension generated through the contraction of muscle cells provides the force necessary for the muscular system to function. • The amount of tension produced depends on several factors: • Sarcomere length Frequency of stimulation • Motor unit size • Recruitment of moto...
Advertisement