Search Results
Results for: 'Ear'
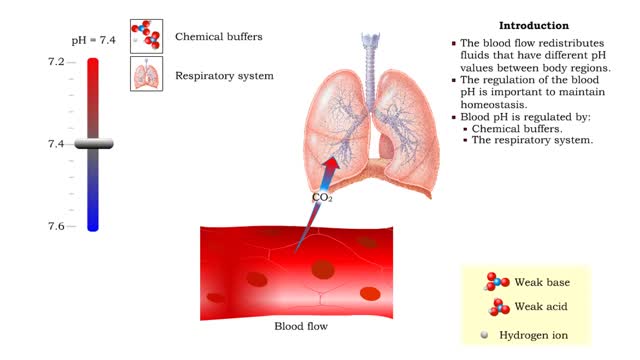
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 10756
• Dissociation of the chemical substances in the body fluids can result in the production of free hydrogen ions. • The pH scale is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. • Normal blood pH values vary around 7.4. • When hydrogen ion concentration increases, t...
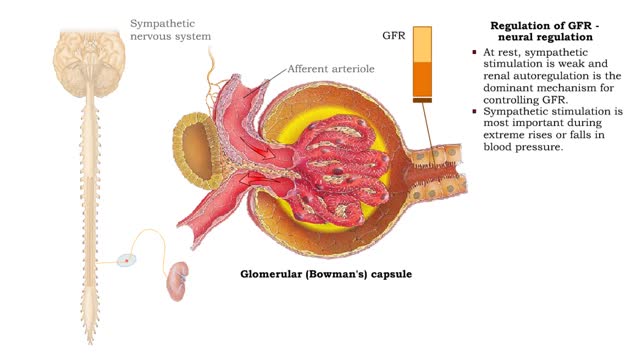
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 11964
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
By: HWC, Views: 11672
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
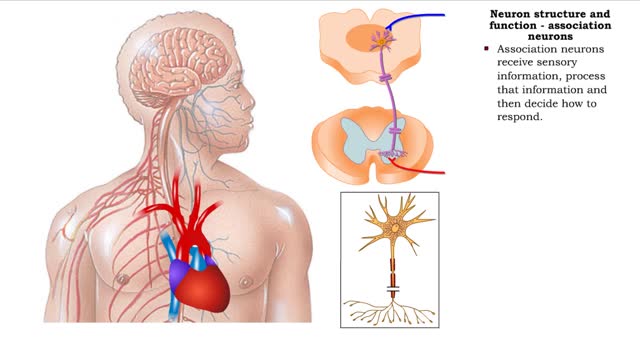
Neuron structure and function - sensory neurons, association neurons & motor neurons
By: HWC, Views: 10876
• The primary function of the nervous system is to provide rapid communication within the body to maintain homeostasis. • This function underlies behaviors, thinking and control of organ functions. • The basic functions of the nervous system are provided by: • Sensory neurons • ...
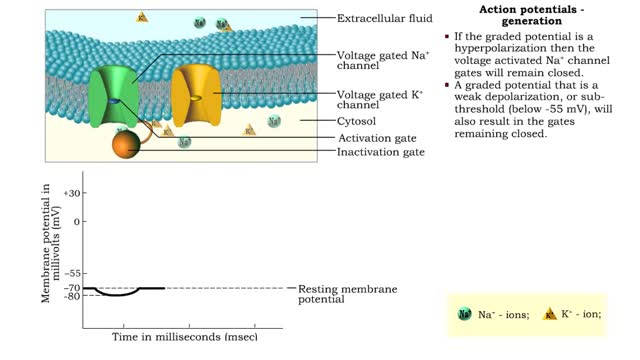
Action potentials - electrical characteristics and generation
By: HWC, Views: 10732
• An action potential is the nervous impulse or signal for long distance communication. Each action potential is generated at the cell's trigger zone. • Action potentials are considered an all-or-nothing phenomena because they are either generated or not. • The generation of an action...
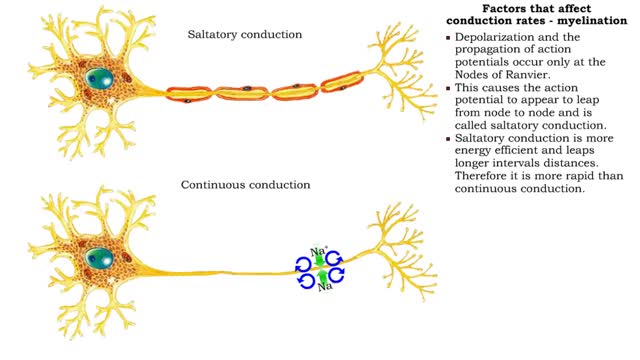
Factors that affect conduction rates (myelination, axon diameter & temperature)
By: HWC, Views: 11063
• Several factors determine the rate of conduction of action potentials: • Myelination • Axon diameter • Temperature • The step-by-step depolarization of an axon is called continuous conduction and occurs along unmyelinated axons. • Neurons in the PNS have many axons that ...
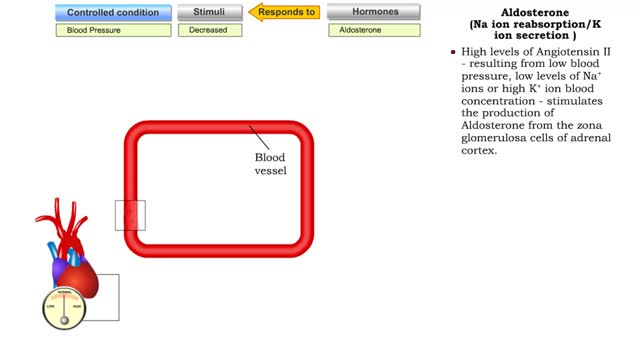
Atrial natriuretic peptide (vasodilation) & Aldosterone
By: HWC, Views: 10619
• Certain situations will cause the body's stress level to rise. • increased blood pressure will stretch the atria of the heart, stimulating the secretion of atria natriuretic peptide (MP). • ANP causes muscle cells in blood vessels to relax. • Blood pressure is lowered as a result ...
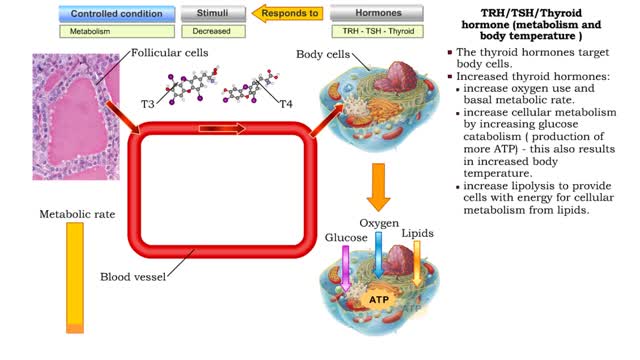
By: HWC, Views: 10500
Thyroid hormone production • A decline in metabolic rate caused by increased metabolic need or physical exertion stimulates the production of thyrotropin hormone releasing (TRH) hormone from the cells of the hypothalamus. • Thyrotropin hormone releasing hormone targets the thyrotrophic ce...
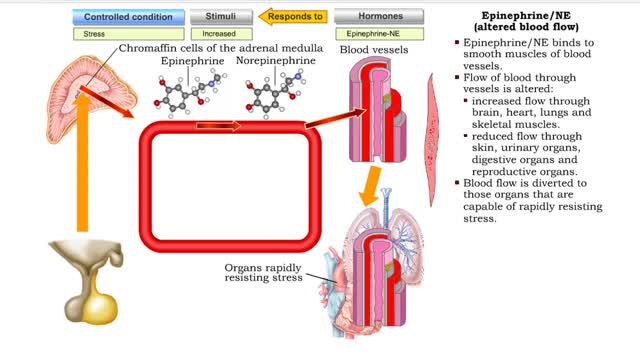
Epinephrine/NE (heart rate, altered blood flow, glycogenolysis & bronchodilation)
By: HWC, Views: 10760
• Stressors trigger increased sympathetic stimulation from the hypothalamus to the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla. • This causes the immediate release of epinephrine and norepinephrine (NE). • Epinephrine/NE binds to the cardiac muscles of the heart. • Cardiac muscle cells ...
Advertisement