Search Results
Results for: 'blood and systemic cell compartments'
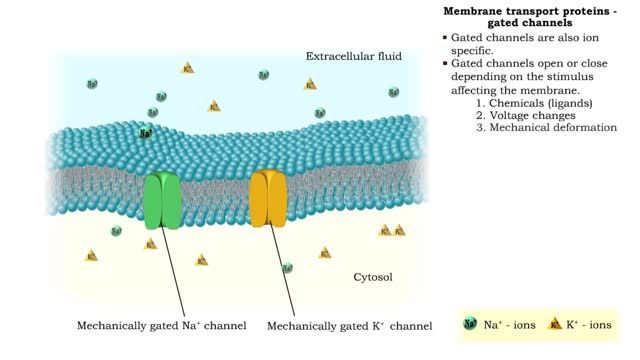
Membrane transport proteins - pores, gated channels and pumps
By: HWC, Views: 11054
• a Three different types of membrane ion transport proteins are required to produce and carry electrical signals: • Pores • Gated channels • Na+/ K+ pump • Pores are always open and allow the diffusion of Na+ and K+ ions across the membrane, down their concentration gradients...
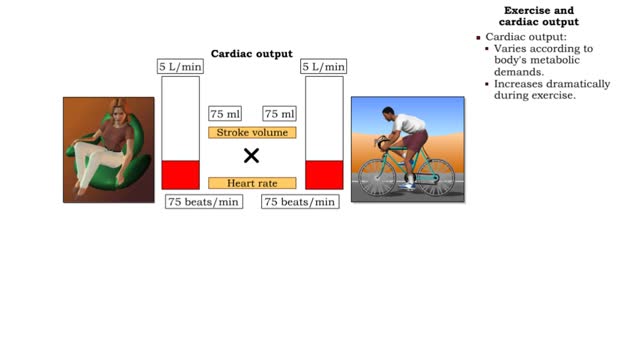
Exercise and cardiac output & Definition of stroke volume
By: HWC, Views: 10878
▪ Cardiac output: • Maintains blood flow throughout the body. • Measure of blood volume ejected from the heart over a given time. • Determined by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume (CO = SV x HR). • Heart rate: Number of beats/min. • Stroke volume: Amount of blood eject...
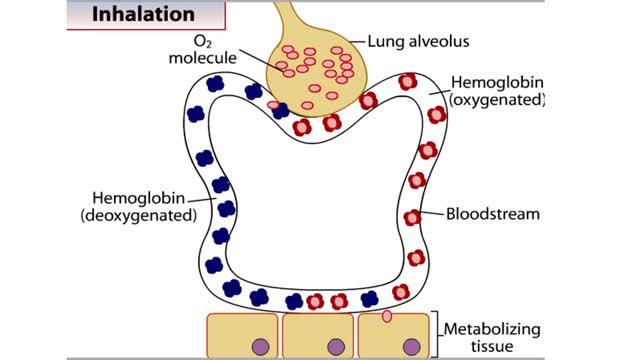
How Hemoglobin Picks Up and Delivers Oxygen
By: HWC, Views: 10283
All of the cells in our bodies require oxygen (02) for survival and must release carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste product. The respiratory and circulatory systems work together as delivery systems for these gases. The lungs exchange these gases between the environment and the bloodstream. The bloo...
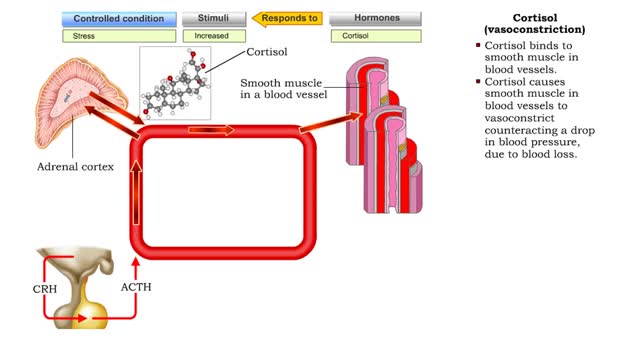
Cortisol (protein catabolism, gluconeogenesis, vasoconstriction & anti-inflammation)
By: HWC, Views: 10634
• Stressors stimulate production of hypothalamic releasing hormones, corticotropin releasing hormone, hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulate. • These hormones promote increased production of 1 cortisol from the zona fasciculata cells of the adrenal cortex. • Cort...
By: Administrator, Views: 13923
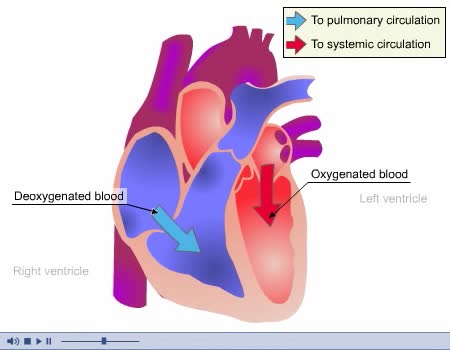
Prior to atrial systole, blood has been flowing passively from the atrium into the ventricle through the open AV valve. During atrial systole the atrium contracts and tops off the volume in the ventricle with only a small amount of blood. Atrial contraction is complete before the ventricle begins...
Epinephrine/NE (heart rate, altered blood flow, glycogenolysis & bronchodilation)
By: HWC, Views: 10763
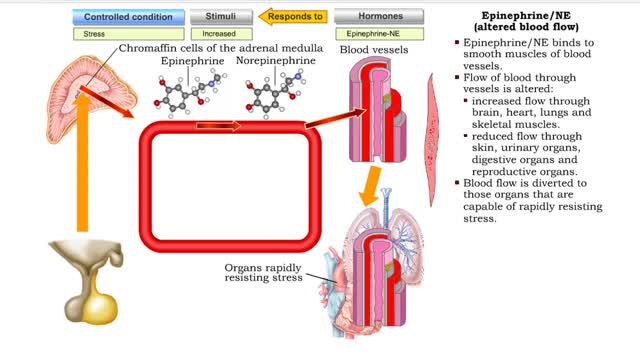
• Stressors trigger increased sympathetic stimulation from the hypothalamus to the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla. • This causes the immediate release of epinephrine and norepinephrine (NE). • Epinephrine/NE binds to the cardiac muscles of the heart. • Cardiac muscle cells ...
Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - carbon dioxide, temperature and bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
By: HWC, Views: 10880
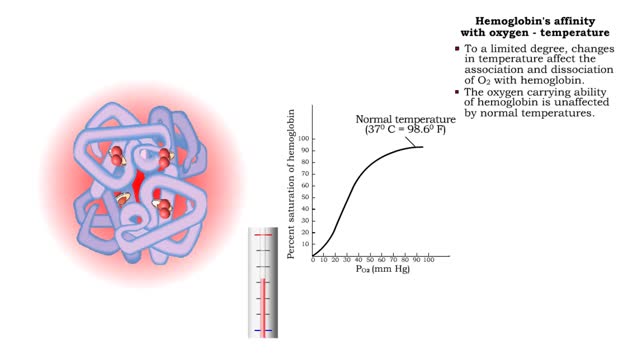
• The carbon dioxide gas is temporarily converted to carbonic acid in red blood cells by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, and then further converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. • The result of increased carbon dioxide is decreased pH causing the Bohr effect. • Elevated carbon dioxid...
ACTH/Cortisol (glycogenolysis, protein catabolism, lipolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10778
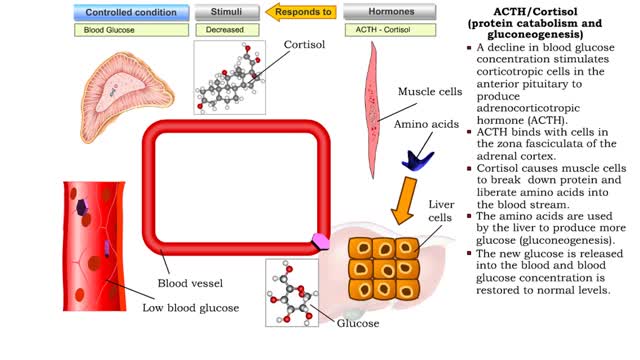
• A decline in blood glucose concentration stimulates corticotropic cells in the anterior pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). • ACTH binds with cells in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. • Increased ACTH promotes the production of cortisol, the major gluco...
X chromosome inactivation in calico cats
By: HWC, Views: 7864
X chromosome inactivation causes a mosaic tissue effect in calico cats. what makes this female calico cat "calico." Like all mammals, this cat began her life as a single cell. That cell had two X chromosomes, one from each parent. One of the chromosomes carried a dominant allele for the ...
Advertisement