Search Results
Results for: 'Neural regulation of blood pressure'
By: HWC, Views: 11034
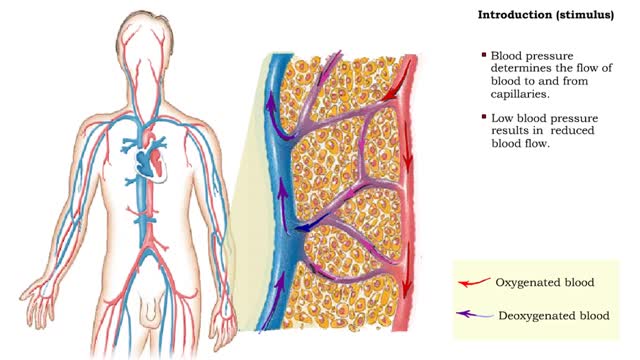
• Blood pressure determines the flow of blood to and from capillaries. • Low blood pressure results in reduced blood flow. • High blood pressure can cause blood vessels to break. In humans, sensitivity is due to portions of the nervous system called receptors. Receptors are typicall...
Stroke volume - afterload definition & hypertension
By: HWC, Views: 10705
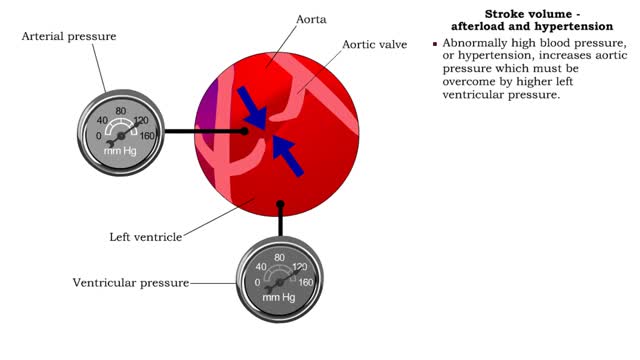
• Pressure (or other resisting force) that ventricles must overcome to push open semilunar valves and eject blood. ▪ Normally, the left ventricle blood pressure must overcome arterial pressure in the aorta. ▪ Abnormally high blood pressure, or hypertension, increases aortic pressure w...
Glomerular filtrate rate: pressures that affect GFR, NFP & GFR and blood composition
By: HWC, Views: 11844
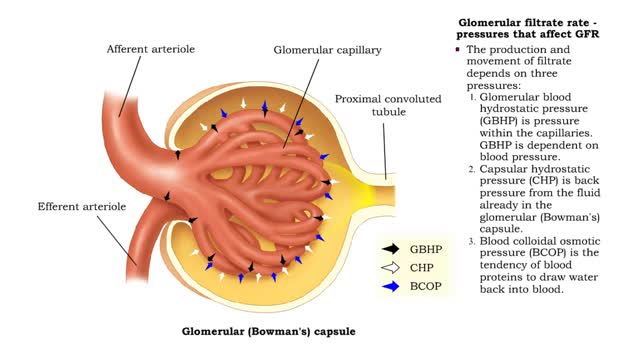
• The glomerular filtration rate is the amount of filtrate formed per minute within the renal corpuscle. • Once the filtrate is formed it moves down the tubule. • The production and movement of filtrate depends on three pressures: I. Glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP) is ...
Glomerubular filtrate rate -pressures that affect GFR and net filtration pressure
By: HWC, Views: 11708
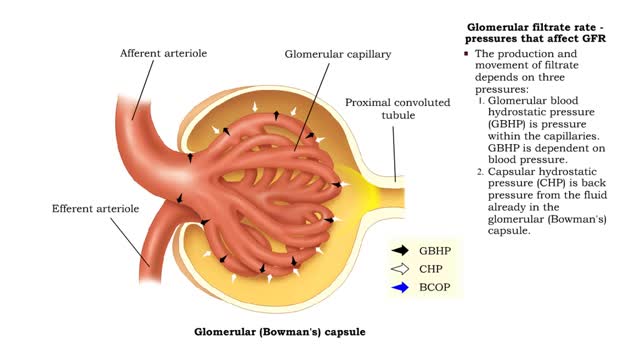
• The glomerular filtration rate is the amount of filtrate formed per minute within the renal corpuscle. • Once the filtrate is formed it moves down the tubule. • The production and movement of filtrate depends on three pressures: I. Glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP) is pre...
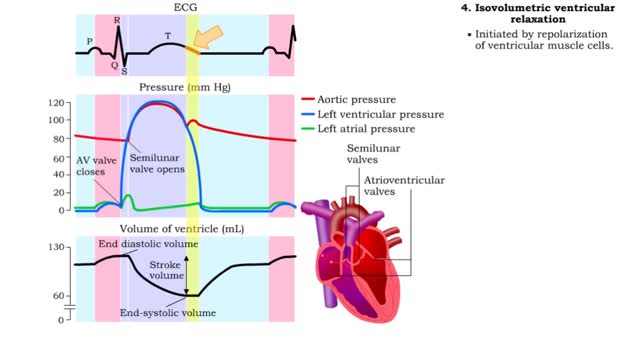
Isovolumetric VC, Ventricular ejection, Isovolumetric & Passive ventricular filling
By: HWC, Views: 11251
• Isovolumetric means that blood volume does not change. • Ventricular blood volume and cell length remain constant. • With valves closed and contraction continuing, ventricular pressure continues to rise. • Ventricular pressure rises above arterial pressure. • Increased ventr...
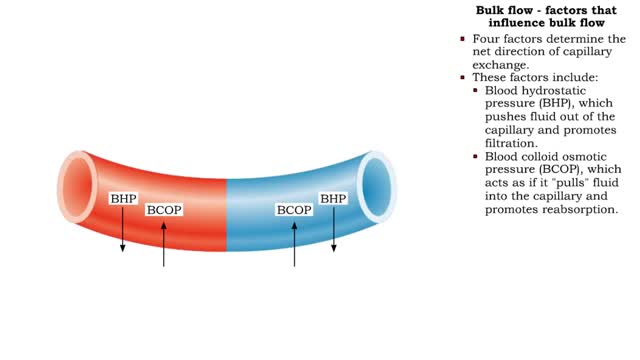
Bulk flow - factors that influence bulk flow
By: HWC, Views: 10896
• Bulk flow helps regulate the relative volumes of blood and interstitial fluid. • Flow from blood to interstitium is called filtration. • Flow from interstitium to blood is called reabsorption. • Four factors determine the net direction of capillary exchange. • These factors in...
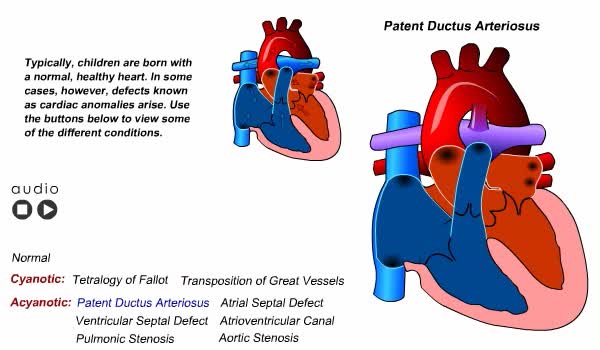
Congenital Heart Defects Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14445
Pulse, blood pressure, and respiration vary according to the child’s age. A newborn’s pulse rate is irregular and rapid, varying from 120 to 140 beats per minute. Blood pressure is low and can vary with the size of the cuff used. Average blood pressure at birth is 80/46. Respirations are ...
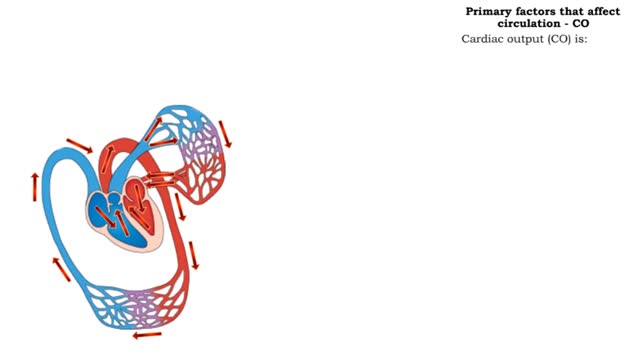
The primary factors that affect circulation - MABP, CO and SVR
By: HWC, Views: 11733
Introduction Blood flow is determined by the relative intensities of factors that drive and resist moving blood. • Cardiac output (CO) equals the mean arterial blood pressure (MABP, a driving force) divided by systemic vascular resistance (SVR, a resisting force). • Hormones and the cen...
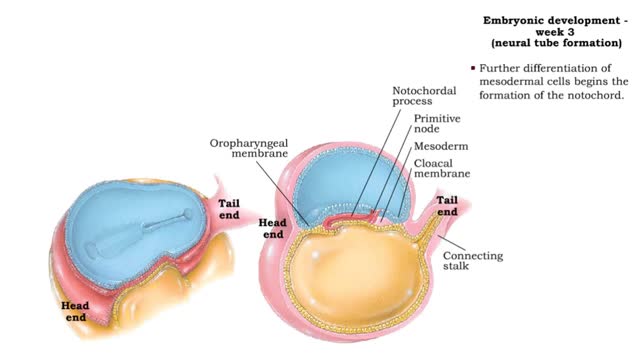
Embryonic development - Week 3
By: HWC, Views: 11393
Week 3 (gastrulation) • Three primary germ layers are formed which provide cells for organ formation in the following months. • These germ cell layers are formed by a process known as gastrulation, which involves rearranging epiblast cells. • As cells from the epiblast migrate, a fain...
Advertisement