Search Results
Results for: 'Neural regulation of blood pressure'
By: Administrator, Views: 14272
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
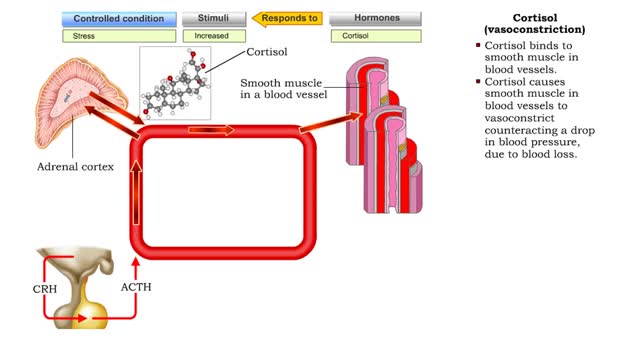
Cortisol (protein catabolism, gluconeogenesis, vasoconstriction & anti-inflammation)
By: HWC, Views: 11057
• Stressors stimulate production of hypothalamic releasing hormones, corticotropin releasing hormone, hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulate. • These hormones promote increased production of 1 cortisol from the zona fasciculata cells of the adrenal cortex. • Cort...
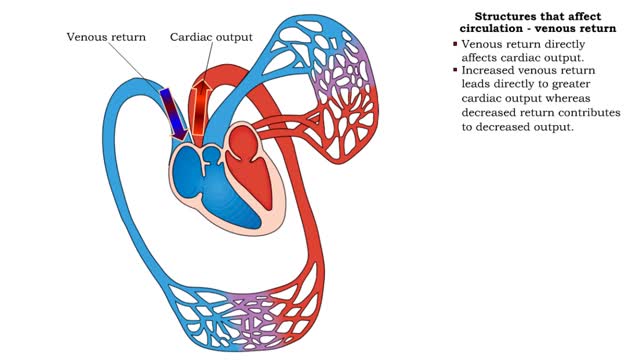
Structures that affect circulation - venous return
By: HWC, Views: 11237
• Venous return directly affects cardiac output. • Increased venous return leads directly to greater cardiac output whereas decreased return contributes to decreased output. • Venous return depends on: • Blood volume regulation by the kidneys. • Venous tone. • Skeletal muscl...
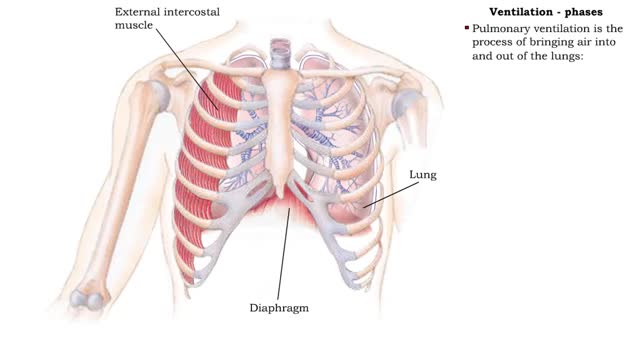
Ventilation - phases and driving forces
By: HWC, Views: 11452
Respiration is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells The combination of 3 processes is required for respiration to occur Ventilation (breathing) External (pulmonary) respiration Internal (tissue) respiration The cardiovascular system assists the respiratory system b...
Double Vacuum Process (Illustration No Audio)
By: HWC, Views: 10408
In this so-called low-pressure process, the wood is first subjected to a short and relatively weak initial vacuum, after which the treatment vessel is flooded with preservative solution and reduced to normal pressure The double vacuum container is loaded with timber. A partial vacuum is draw...
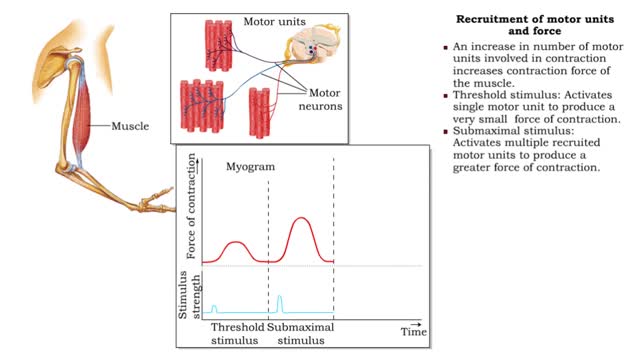
Frequency of stimulation and force (Recruitment of motor units and force)
By: HWC, Views: 11643
• Muscle tension depends on the frequency of stimulation. • Muscle twitch: First stimulus. • Wave summation: When a second stimulus excites a partially relaxed muscle, producing a stronger contraction. • Unfused tetanus: Successive stimulations at the same frequency, producing a se...
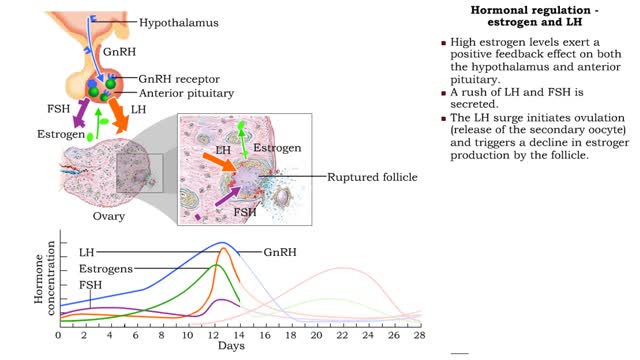
Phases of the Female Reproductive Cycle - Hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 11791
FSH, LH and estrogen • FSH travels through the bloodstream from the anterior pituitary to the ovaries. • FSH promotes follicular growth. Increased follicular growth promotes estrogen production. • Small increases in blood estrogen levels inhibit the release of FSH and LH into the bl...
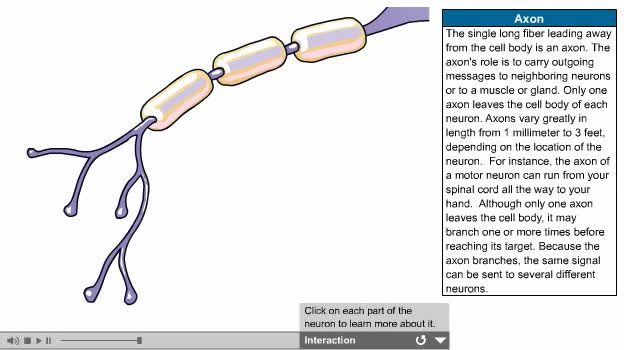
By: Administrator, Views: 14932
There are several types of neurons, three of which are: Motor neurons, Sensory neurons, Interneurons. The nervous system is usually described as having two interconnected divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS: Includes the brain and spinal...
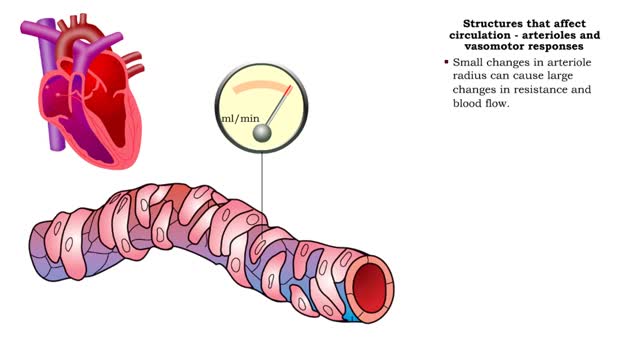
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses
By: HWC, Views: 11008
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. ■ Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. ■ Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
Advertisement