Search Results
Results for: 'Nucleic acid digestion'
The pH scale - Strong acids and Weak acids
By: HWC, Views: 11855
The pH scale • Expresses concentration of H+. • range: 0-14. • 7 is neutral. • Less 7 is acid. • greater 7 is basic (alkaline). Strong acids - role in the body ■ In strong acids all molecules dissociate. ■ HC1 is highly acidic and found only in the stomach. • H...
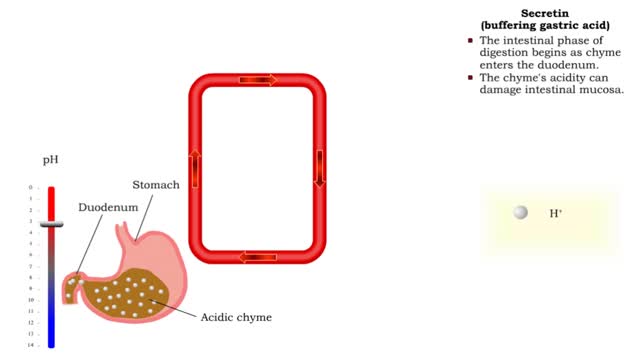
Gastrin (gastric emptying) & Secretin (buffering gastric acid)
By: HWC, Views: 11258
• Gastrin also binds to the smooth muscle cells in the stomach causing: • Increased gastric motility. • Opening of pyloric sphincter. • Increased gastric emptying. • The intestinal phase of digestion begins as chyme enters the duodenum. • The chyme's acidity can damage int...
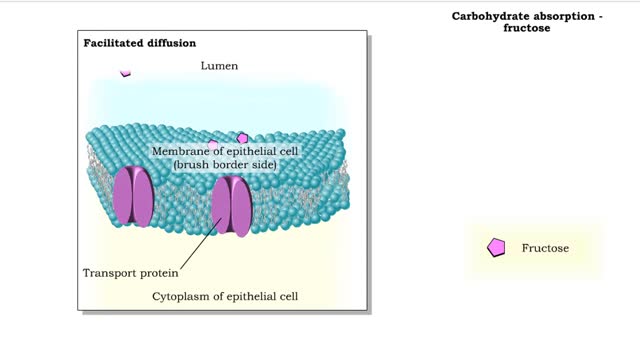
Carbohydrate digestion (brush border enzymes, end products) & Carb absorption (fructose, galactose)
By: HWC, Views: 11647
• Carbohydrate digestion concludes in microvilli of the small intestine, in brush border epithelial cells. Carbohydrate digestion -brush border enzymes • Four brush-border enzymes are involved: • Alpha-dextrinase breaks down alpha-dextrin chains by removing glucose units. • Sucras...
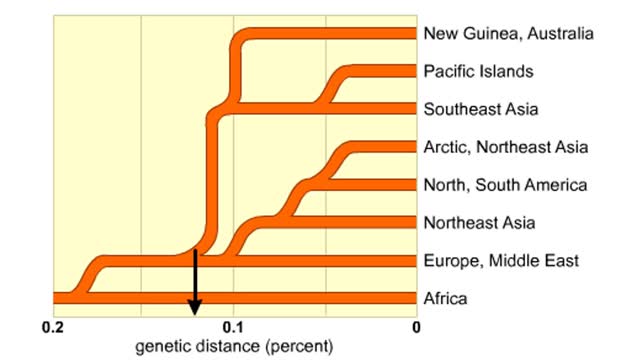
Genetic distance between human groups
By: HWC, Views: 8606
One proposed family tree for modern humans. This family tree is based on nucleic-add hybridization studies of many genes and immuno-logical comparisons. Branch points show presumed genetic divergences. This data indicates that the greatest genetic distance separates humans native to Afri...
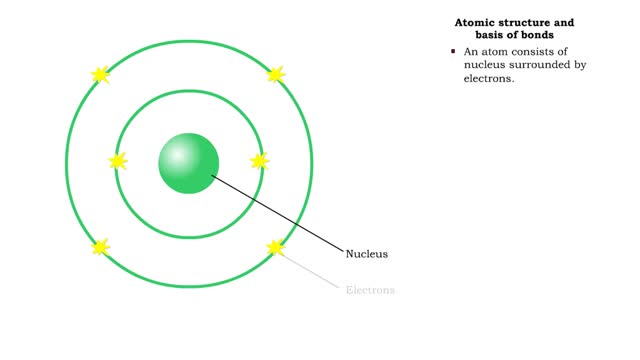
Bond types - Atomic structure and basis of bonds
By: HWC, Views: 12122
• Chemical bonds are fundamental to the structure and function of many types of molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, gases, salts and water. ■ These molecules are composed of atoms that are held together by three different types of bonds. • The three types ...
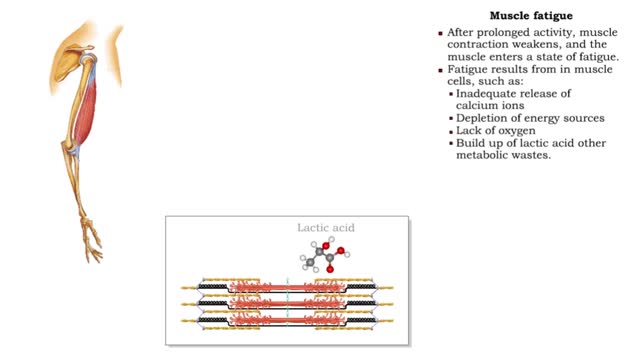
By: HWC, Views: 11445
• After prolonged activity, muscle contraction weakens, and the muscle enters a state of fatigue. • Fatigue results from in muscle cells, such as: • Inadequate release of calcium ions • Depletion of energy sources • Lack of oxygen • Build up of lactic acid other metabolic w...
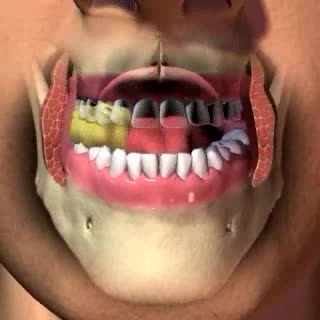
By: Administrator, Views: 15432
The mouth or oral cavity is formed by: - The hard and soft palates at the top or roof - the cheeks - the tongue - the lips Contains the teeth and salivary glands. The gingivae (gums) surround the necks of the teeth. The lingual frenulum is a thin fold of mucous membrane that connects...
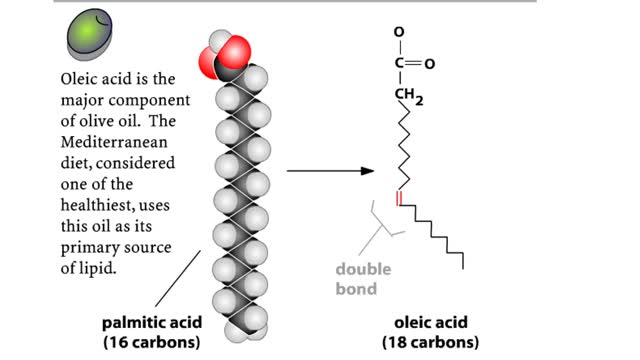
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Lipids
By: HWC, Views: 11114
A triglyceride (also called triacylglycerol) is composed of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. The fatty acids attach to the glycerol molecule by a covalent ester bond. The long hydrocarbon chain of each fatty acid makes the triglyceride molecule nonpolar and hydrophobic. Pa...
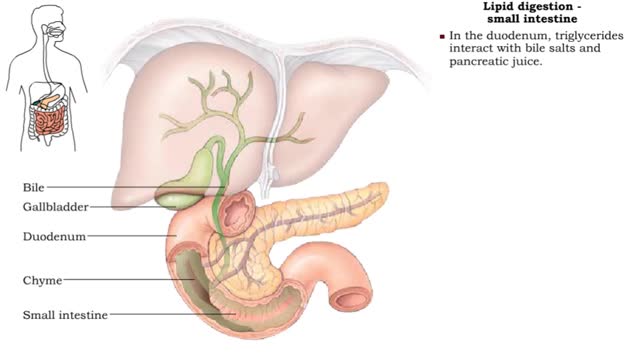
Lipid digestion - mouth, stomach and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11884
• Lipid digestion takes place primarily in the small intestine; some occurs in the mouth and stomach. • Lipases are enzymes that break down triglycerides and phospholipids. • Lingual and gastric lipases hydrolyze a small amount of triglycerides. • End products are fatty acids and...
Advertisement