Search Results
Results for: 'Respiratory mucosa'
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 10262
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 11112
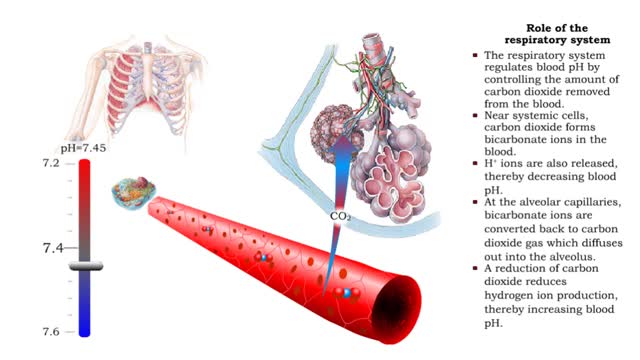
• The respiratory system regulates blood pH by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide removed from the blood. • Near systemic cells, carbon dioxide forms bicarbonate ions in the blood. H+ ions are also released, thereby decreasing blood pH. • At the alveolar capillaries, bicarbonate io...
Effect of blood chemistry - stimuli, hyperventilation response and hypoventilation response
By: HWC, Views: 10196
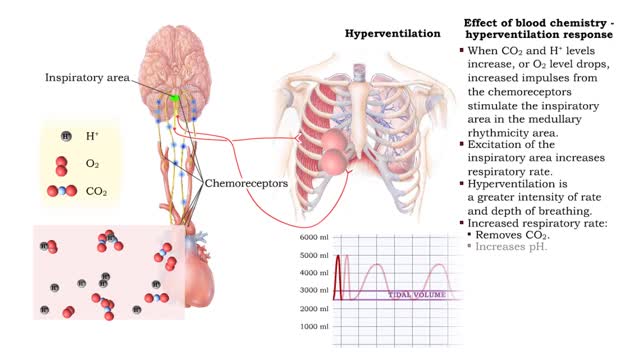
• Respiratory rate is effected by changes in: • Blood pH. • Blood Pco2. • Blood P02. • Chemoreceptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems closely monitor the Fr, CO2 and 02 levels in blood. • Changes in frequency of impulses from Chemoreceptors affect respiratory r...
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 10375
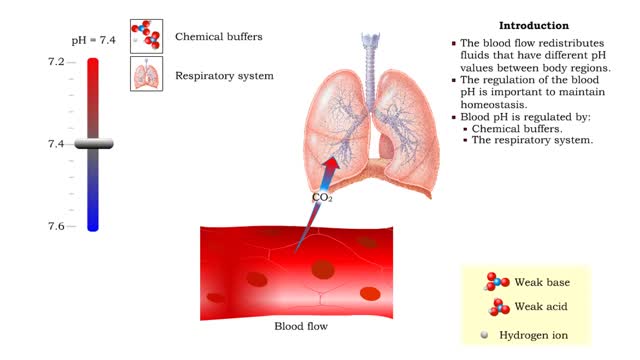
• Dissociation of the chemical substances in the body fluids can result in the production of free hydrogen ions. • The pH scale is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. • Normal blood pH values vary around 7.4. • When hydrogen ion concentration increases, t...
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 10720
• When one pH balancing system is affected then the other balancing system attempts to correct, or compensate for, the pH imbalance. - Respiratory acidosis: • Excessive CO2 is present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased secretion of H+ into urine and reabsorption ...
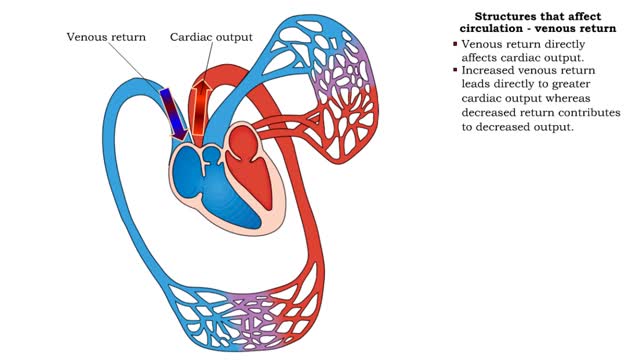
Structures that affect circulation - venous return
By: HWC, Views: 10420
• Venous return directly affects cardiac output. • Increased venous return leads directly to greater cardiac output whereas decreased return contributes to decreased output. • Venous return depends on: • Blood volume regulation by the kidneys. • Venous tone. • Skeletal muscl...
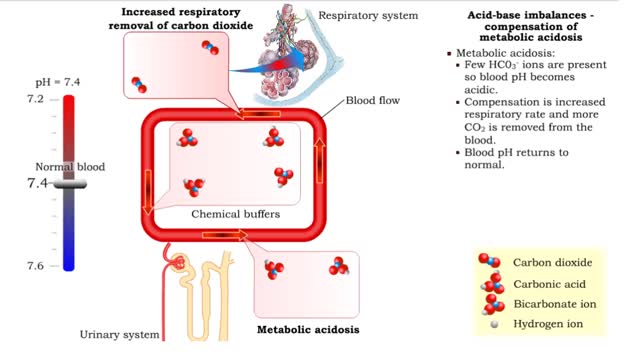
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 10738
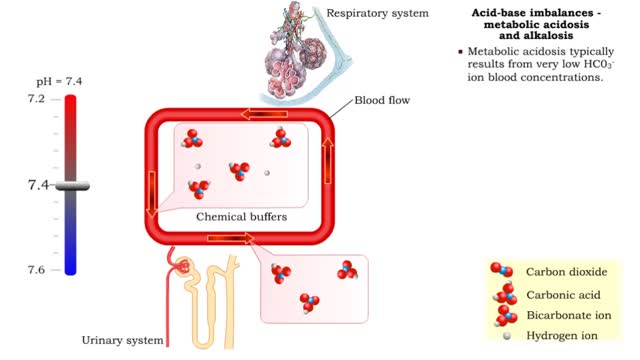
1. Metabolic acidosis: • Few HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased respiratory rate and more CO2 is removed from the blood. • Blood pH returns to normal. 2. Metabolic alkalosis: • Many HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes alkaline...
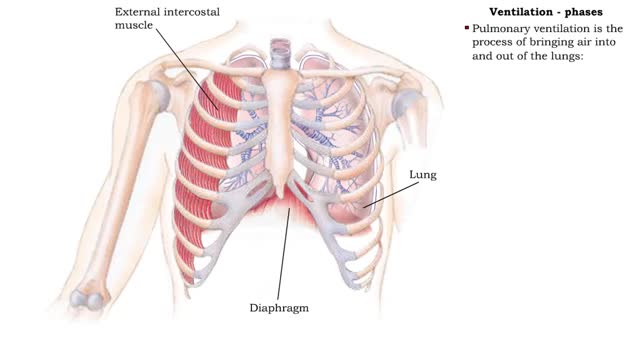
Ventilation - phases and driving forces
By: HWC, Views: 10662
Respiration is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells The combination of 3 processes is required for respiration to occur Ventilation (breathing) External (pulmonary) respiration Internal (tissue) respiration The cardiovascular system assists the respiratory system b...
By: Administrator, Views: 13678
Acute exacerbations of asthma can require management in the emergency department. The child is placed in a semisitting position to facilitate respiratory effort.
Advertisement