Search Results
Results for: 'bicarbonate ions'
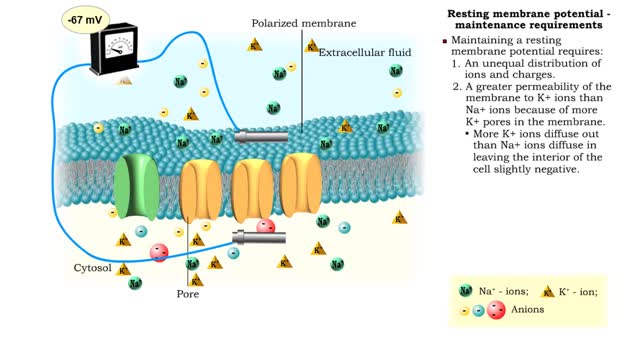
Resting membrane potential - electrical polarity and maintenance requirements
By: HWC, Views: 10867
• A resting membrane potential exists when there is a buildup of: 1. positive ions outside the membrane. 2. negative ions inside the membrane. • Membranes with opposing charges are said to be polarized. • The difference in charge applies only to the small distance across the membran...
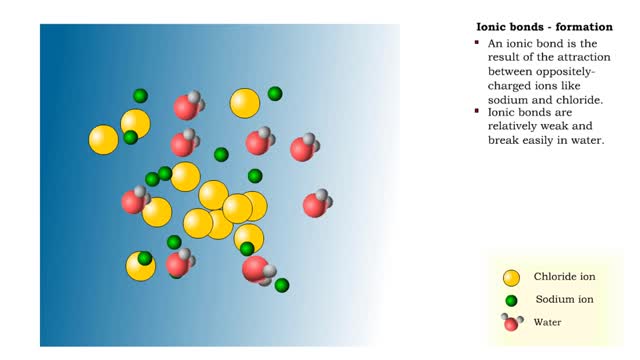
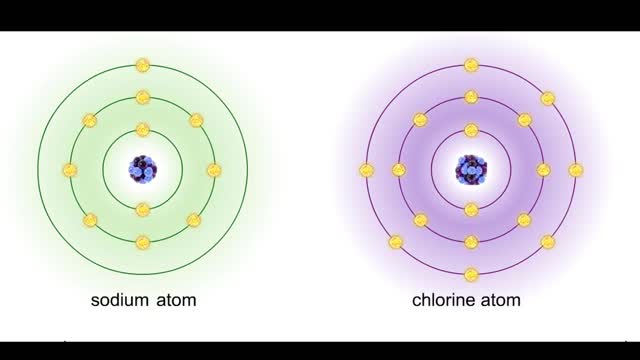
Ionic bonds - role of ions in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11498
Ions • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Atoms now bear a charge and are called ions. • Sodium ion, losing an electron, has a +1 charge. • Chlorine ion, gaining an electron, has a -1 charge. Formation • An ionic bond is t...
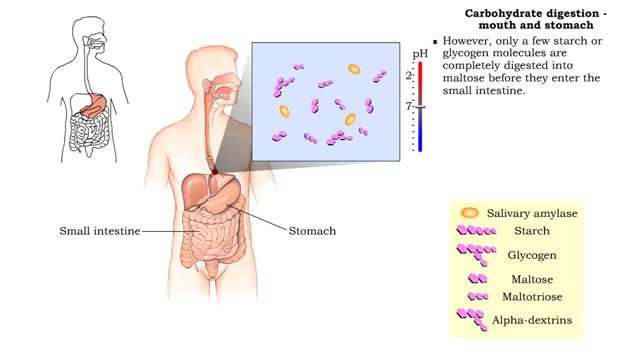
Carbohydrate digestion - mouth and stomach & pancreas and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11056
• Digestion of complex carbohydrates (starches and glycogen) involves: • Amylases produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. • Brush-border enzymes in small intestine. • In the mouth, amylase from the parotid and submandibular salivary glands begins carbohydrate digestion. �...
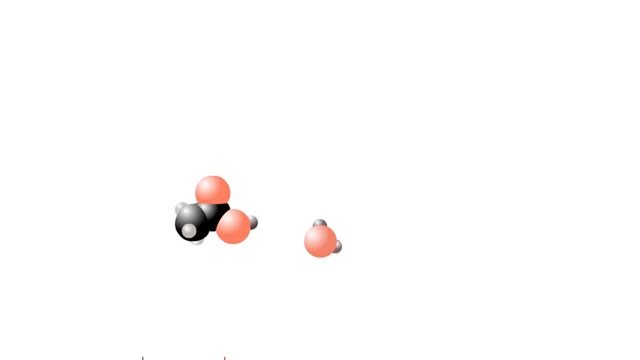
What are Strong & Weak Acids and How they're different?
By: HWC, Views: 9974
Let's consider the changes that take place when hydrogen chloride, HCI, is added to water. You will need to recognize space-filling models of HCI molecules, hydronium ions (H30+), chloride ions (C11, and water molecules (H20). They are shown at the right. When HC1 molecules dissolve in water, ...
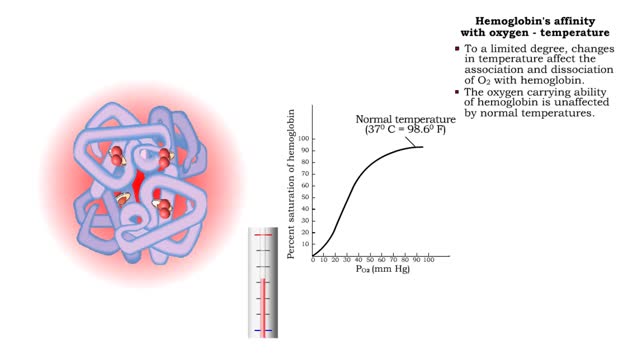
Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - carbon dioxide, temperature and bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
By: HWC, Views: 11171
• The carbon dioxide gas is temporarily converted to carbonic acid in red blood cells by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, and then further converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. • The result of increased carbon dioxide is decreased pH causing the Bohr effect. • Elevated carbon dioxid...
By: HWC, Views: 10004
The slight positive charge of a hydrogen atom in a water molecule can attract an atom with a slight negative charge, such as the nitrogen in a molecule of ammonia. This forms a hydrogen bond between the two atoms. Hydrogen bonds join the two strands of a DNA molecule. Although hydrogen bo...
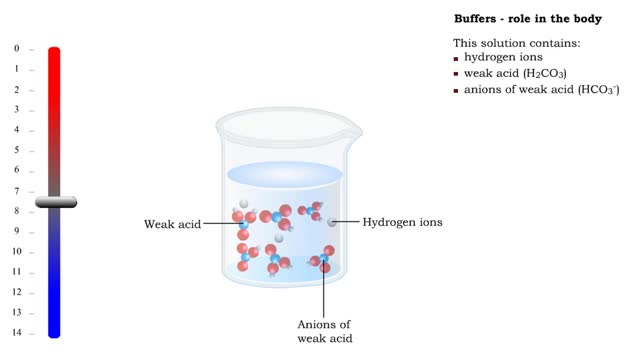
Buffers definition and the role of buffer in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11246
■ Too many H+ break hydrogen bonds and a protein comes apart. ■ Buffers react with excess H+ to protect proteins from breaking down. ■ Buffers consist of weak acid plus anions of that weak acid. This solution contains: • hydrogen ions • weak acid (H2CO3) • anions of we...
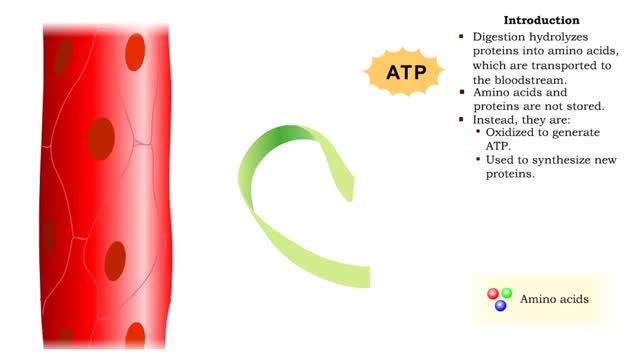
Protein catabolism - deamination
By: HWC, Views: 11397
• Digestion hydrolyzes proteins into amino acids, which are transported to the bloodstream. • Amino acids and proteins are not stored. • Instead, they are: • Oxidized to generate ATP. • Used to synthesize new proteins. • Converted to carbohydrates or lipids for storage (if e...
Advertisement