Search Results
Results for: 'contraction of the diaphragm'
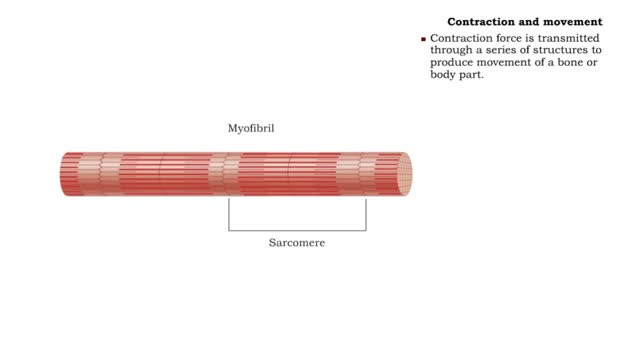
Contraction cycle of a sarcomere
By: HWC, Views: 11503
• A single nervous signal releases Ca2+ ions into the sarcoplasm and initiates the contraction cycle. step 1. ATP hydrolysis • ATP provides the to move myosin molecules back into the energized configuration necessary to perform the power stroke. Step 2. Crossbridge attachment • Myosin...
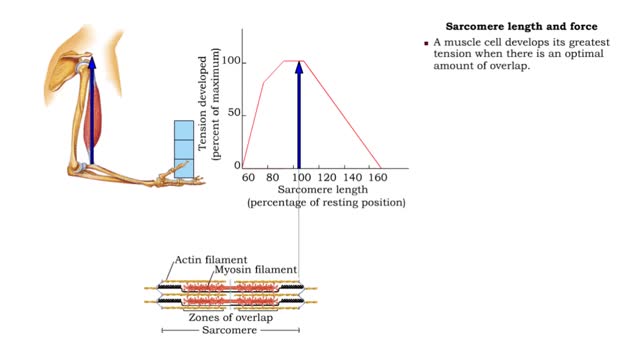
Factors that influence muscle tension - Sarcomere length and force, understretched and overstretched
By: HWC, Views: 11130
• Muscle tension generated through the contraction of muscle cells provides the force necessary for the muscular system to function. • The amount of tension produced depends on several factors: • Sarcomere length Frequency of stimulation • Motor unit size • Recruitment of moto...
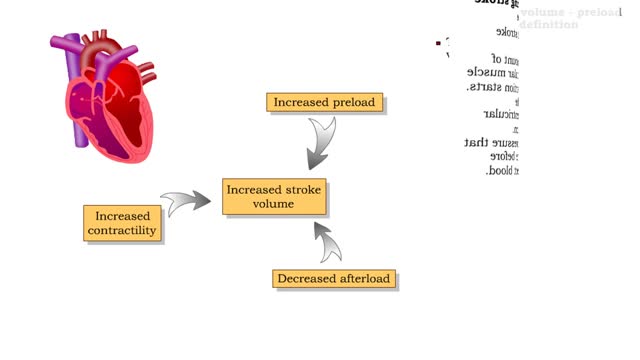
Definitions of stroke volume, preload definition & Factors influencing stroke volume
By: HWC, Views: 10818
• Stroke volume is directly correlated with cardiac output-the greater the stroke volume the greater the cardiac output. • Stroke volume represents the difference in the amount of blood between: • the volume in the ventricles at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume EDV); • the ...
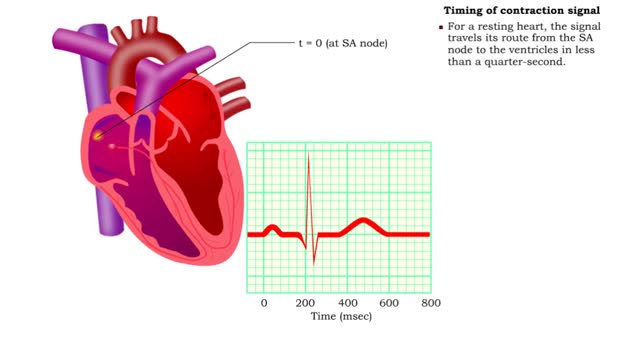
Coaductile pathway, Timing of contraction signal & Conduction system and ECG
By: HWC, Views: 11262
• When the system is healthy, the signal to contract the entire conduction system originates in the SA node - known as the heart's pacemaker. • The SA node triggers contraction because it depolarizes at a faster rate than other parts of the conduction system. • The wave of excitation fr...
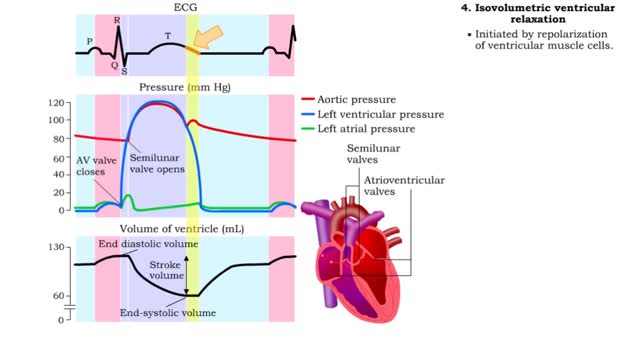
Isovolumetric VC, Ventricular ejection, Isovolumetric & Passive ventricular filling
By: HWC, Views: 10946
• Isovolumetric means that blood volume does not change. • Ventricular blood volume and cell length remain constant. • With valves closed and contraction continuing, ventricular pressure continues to rise. • Ventricular pressure rises above arterial pressure. • Increased ventr...
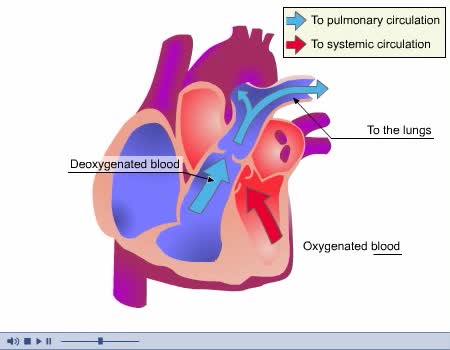
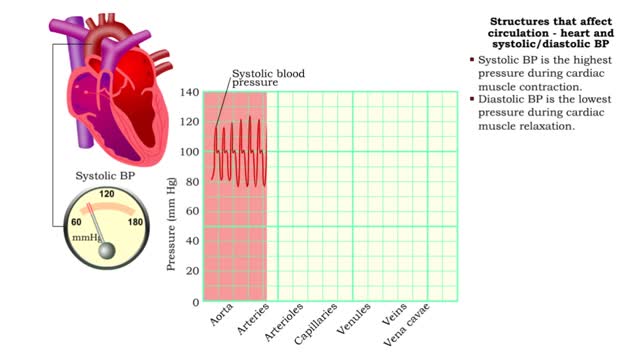
Structures that affect circulation - heart and systolic/diastolic BP
By: HWC, Views: 10998
• Heart generates blood pressure. • Arterioles produce resistance thereby regulating blood flow to tissues. • Veins store blood; kidneys regulate blood volume; both affect venous return and cardiac output. ■ Contractions of the ventricles determine blood pressure, which drives th...
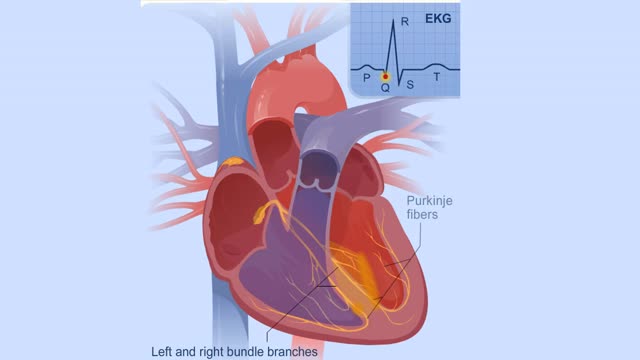
Electrical Conduction System of the Heart
By: HWC, Views: 10104
Your heart is a muscle that works continuously, much like a pump. Each beat of your heart is set in motion by an electrical signal from within your heart muscle. The electrical activity is recorded by an electrocardiogram. known as an EKG or ECG. Each beat of your heart begins with an electric...
By: HWC, Views: 10972
Preload definition • Preload is the degree of stretch of cardiac muscles cells prior to contraction. • The amount of stretch is related to the end-diastolic volume[EDV]. • Increased return blood flow from the veins increases end-diastolic volume. Cardiac muscle sarcomeres stretch and ...
Advertisement