Search Results
Results for: 'filtrate formation and composition'
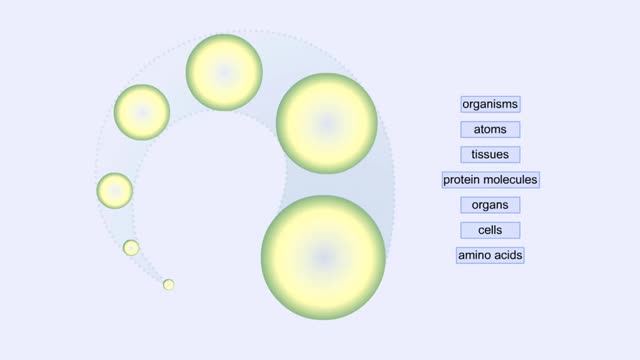
Proteins Defined, Hierarchy & Composition of Cells
By: HWC, Views: 11287
Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Together with the other three biological macromolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—proteins are the building blocks of cells. Proteins are the most complex and abundant biological macromolecules in cel...
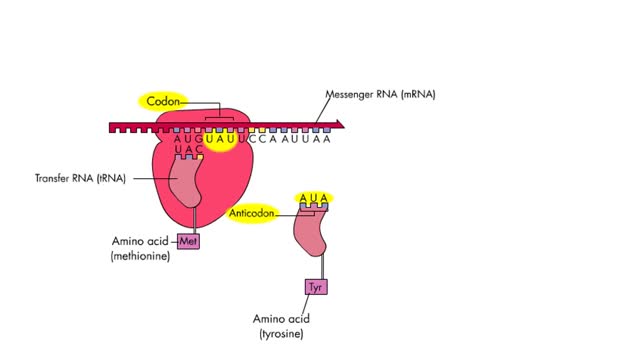
The 4 steps of translation Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7618
Translation is the process of formation of a polypeptide chain according to codon present in mRNA. The four steps of translation are: Activation or charging of tRNA Initiation – recognition of start codon, binding of ribosomal subunits to mRNA and formation of initiation complex with Met-tR...
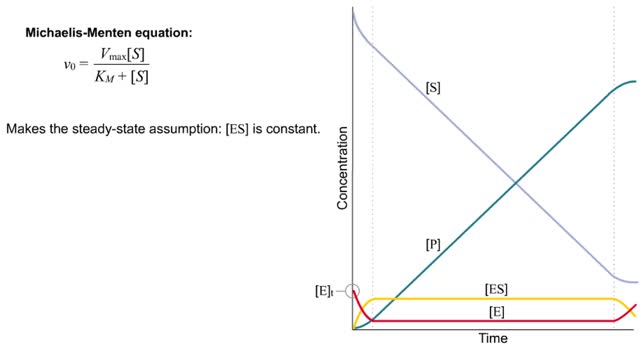
Michaelis–Menten equation & Kinetic parameters
By: HWC, Views: 11536
The Michaelis–Menten equation is the rate equation for a one-substrate enzyme-catalyzed reaction. This equation relates the initial reaction rate (v0), the maximum reaction rate (Vmax), and the initial substrate concentration [S] through the Michaelis constant KM—a measure of the substrat...
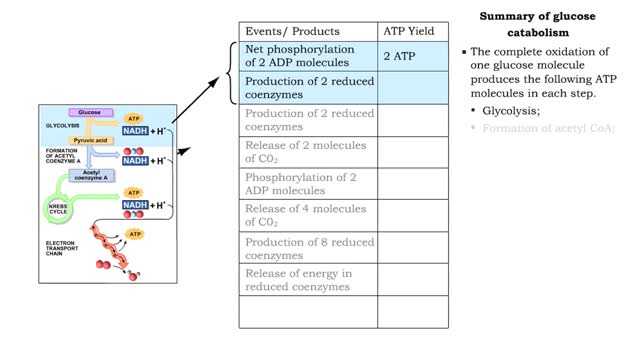
By: HWC, Views: 11967
■ The complete oxidation of one glucose molecule produces the following ATP molecules in each step. • Glycolysis; • Formation of acetyl CoA; • Krebs cycle; • Electron transport chain. ■ In addition, glucose catabolism produces six CO2 molecules and water.
By: HWC, Views: 11467
An ecosystem is a community of organisms and their environment. The community forms the living component of the ecosystem. These are called the 'biotic' factors, which means all of the living things in the ecosystem. The environment forms the nonliving component of the ecosystem, such as ...
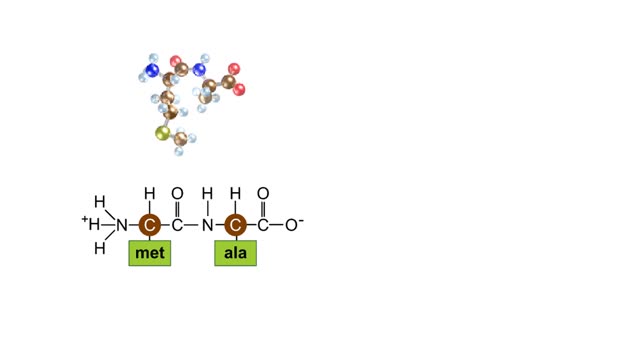
Peptide Bond Formation Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5557
During protein synthesis, peptide bonds link amino acids together in the order specified by DNA instructions. In this case, the first two amino acids in the protein are methionine and alanine. Here are ball-and-stick models of these amino acids. Peptide bond formation is a type of condensatio...
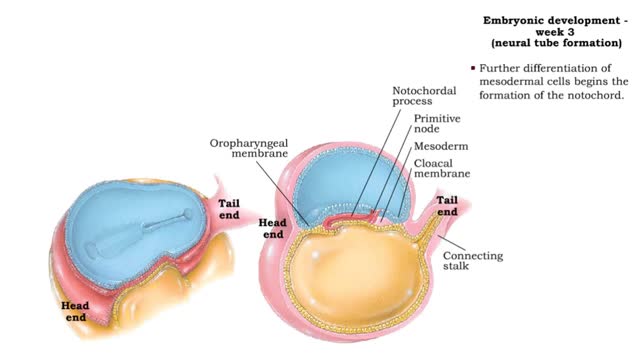
Embryonic development - Week 3
By: HWC, Views: 11785
Week 3 (gastrulation) • Three primary germ layers are formed which provide cells for organ formation in the following months. • These germ cell layers are formed by a process known as gastrulation, which involves rearranging epiblast cells. • As cells from the epiblast migrate, a fain...
By: HWC, Views: 9893
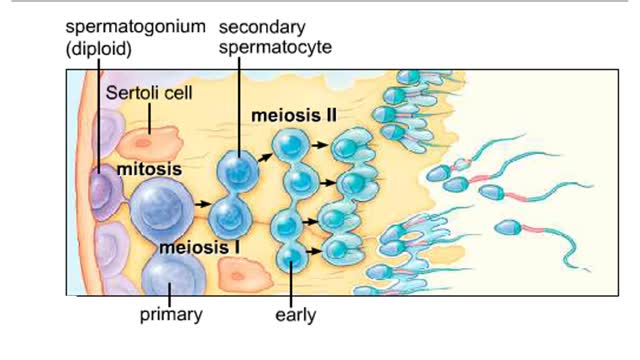
Spermatogenesis takes place inside the seminiferous tubules. Diploid spermatogonia located near the outer edge of the tubule divide mitotically to form primary spermatocytes. The first meiotic division produces secondary spermatocytes with a haploid number of duplicated chromosomes. T...
By: HWC, Views: 8224
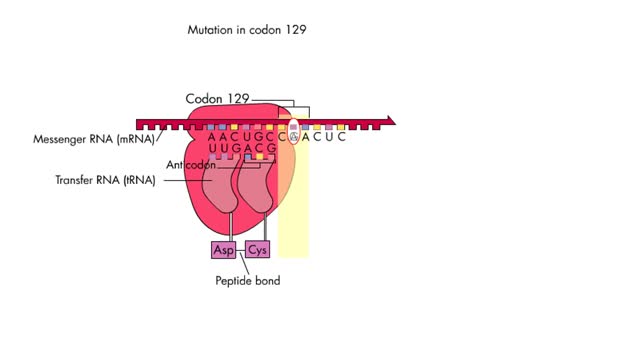
A mutation, which may arise during replication and/or recombination, is a permanent change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. Damaged DNA can be mutated either by substitution, deletion or insertion of base pairs. Mutations, for the most part, are harmless except when they lead to cell death or t...
Advertisement