Search Results
Results for: 'gastric acid'
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Lipids
By: HWC, Views: 11092
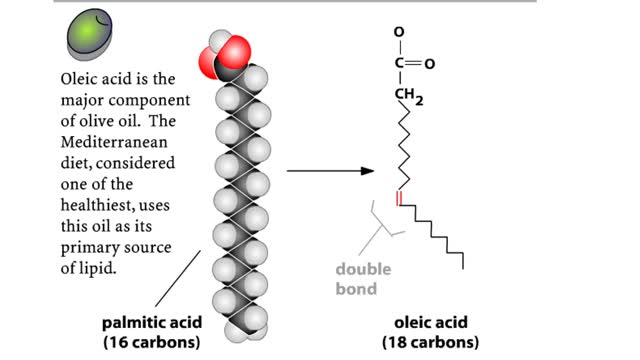
A triglyceride (also called triacylglycerol) is composed of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. The fatty acids attach to the glycerol molecule by a covalent ester bond. The long hydrocarbon chain of each fatty acid makes the triglyceride molecule nonpolar and hydrophobic. Pa...
Buffers definition and the role of buffer in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11732
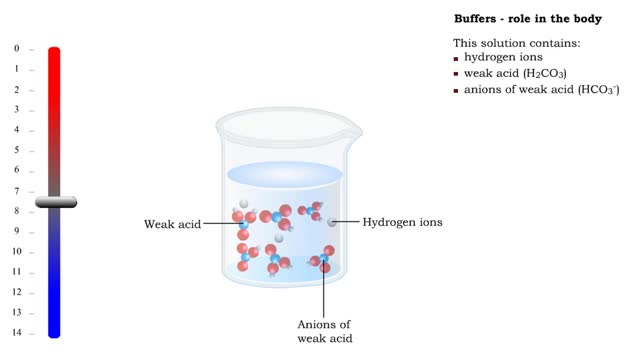
■ Too many H+ break hydrogen bonds and a protein comes apart. ■ Buffers react with excess H+ to protect proteins from breaking down. ■ Buffers consist of weak acid plus anions of that weak acid. This solution contains: • hydrogen ions • weak acid (H2CO3) • anions of we...
By: HWC, Views: 11973
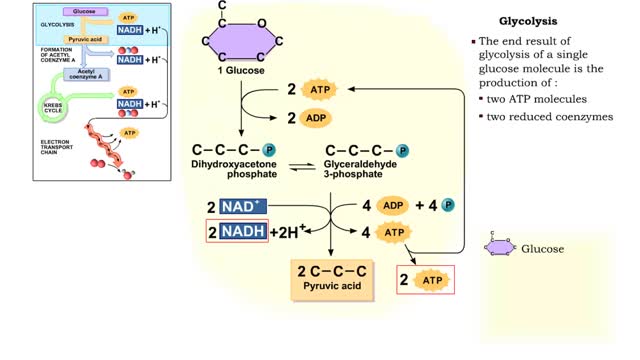
The first reactions involve a single 6-carbon glucose sugar undergoing phosphorylation using two ATP molecules and resulting in two 3-carbon compounds. • The rest of this pathway involves an oxidation reduction reaction, forming two reduced coenzymes, and generation of four ATP molecules. ...
Carbohydrate digestion - mouth and stomach & pancreas and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11566
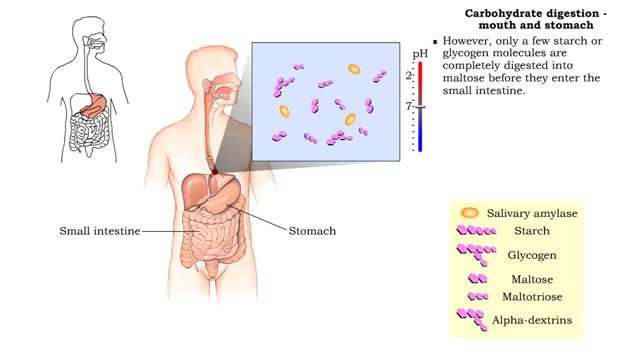
• Digestion of complex carbohydrates (starches and glycogen) involves: • Amylases produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. • Brush-border enzymes in small intestine. • In the mouth, amylase from the parotid and submandibular salivary glands begins carbohydrate digestion. �...
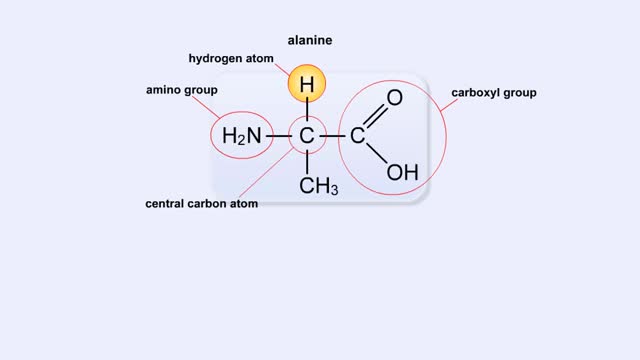
Structure of Amino Acid, Peptide Bonds & Polypeptides
By: HWC, Views: 11289
Here are the molecular formulas of three different amino acids. All amino acids share this backbone. The main difference between every amino acid is the side groups seen here, and these side groups give each of the amino acids their different characteristics. But before we get into that, let's ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14960
Digestive system contains both primary and accessory organs for the conversion of food and fluids into a semiliquid that can be absorbed for the body to use. Three main functions: - Digestion - Absorption - Elimination With aging: - Digestive system becomes less motile. - Glandular sec...
What are Strong & Weak Acids and How they're different?
By: HWC, Views: 10464
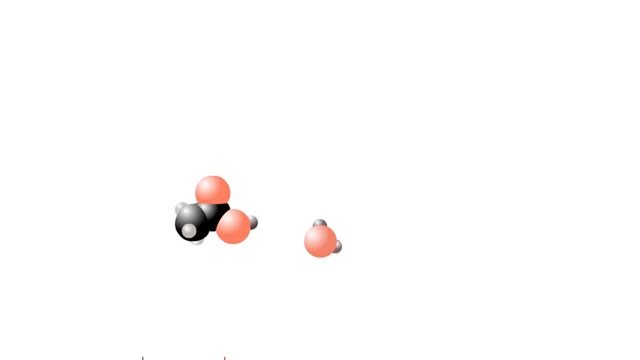
Let's consider the changes that take place when hydrogen chloride, HCI, is added to water. You will need to recognize space-filling models of HCI molecules, hydronium ions (H30+), chloride ions (C11, and water molecules (H20). They are shown at the right. When HC1 molecules dissolve in water, ...
By: HWC, Views: 11583
Acids and bases are found all around your house. For example, if you open your pantry or refrigerator, you might see a lot of acids. Fruit juice, soda pop, vinegar, and milk are all examples of acids. The word acid actually comes from a Latin term meaning ''sour.'' Many materials, like sugar for ...
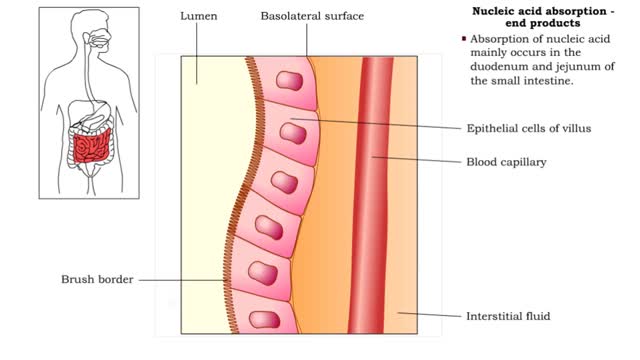
Nucleic acid digestion - brush border enzymes, end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 11530
• Further digestion occurs at the microvilli (brush border) of the epithelial cells of the villi in the small intestine. • Two brush border enzymes complete nucleic acid digestion: • Phosphatases, which catalyze the cleavage of a phosphate to form a nucleoside (nitrogenous base and pent...
Advertisement