Search Results
Results for: 'molecule of ammonia'
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 11452
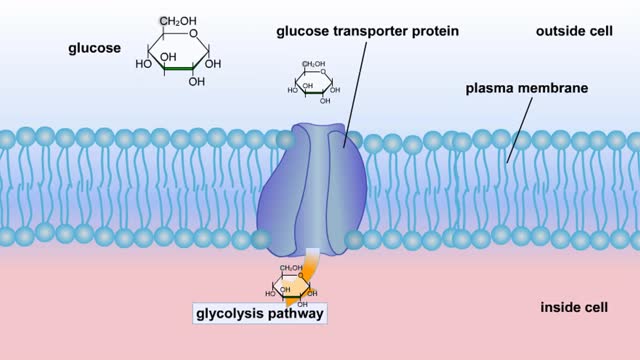
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
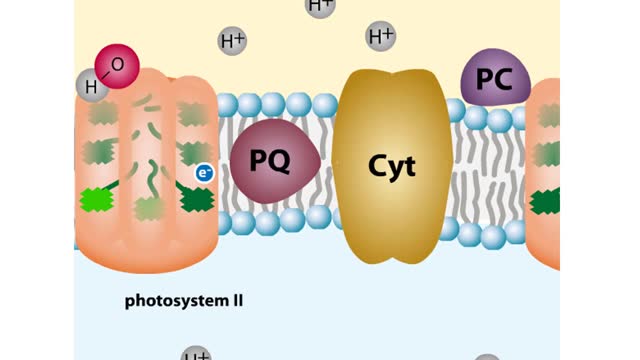
ETC Protein Complexes & Chemiosmosis (Total ATP Production and ATP Synthase)
By: HWC, Views: 11435
You will notice that FADH2 donates two electrons further downstream than NADH. This results in only two protons being pumped across the inner membrane. The final electron acceptor for these transported electrons is oxygen. Oxygen receives these electrons, plus protons from the aqueous matrix. ...
What are Strong & Weak Acids and How they're different?
By: HWC, Views: 10483
Let's consider the changes that take place when hydrogen chloride, HCI, is added to water. You will need to recognize space-filling models of HCI molecules, hydronium ions (H30+), chloride ions (C11, and water molecules (H20). They are shown at the right. When HC1 molecules dissolve in water, ...
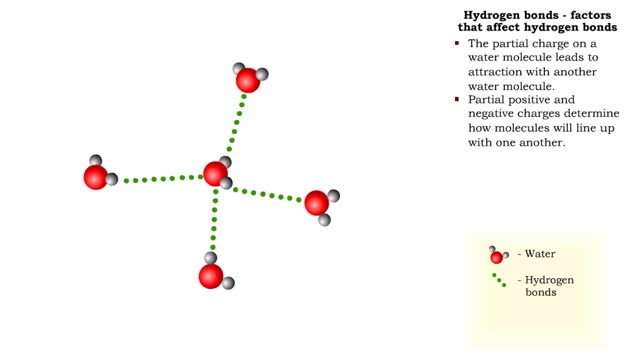
Hydrogen bonds - role in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11995
A hydrogen bond is the electromagnetic attraction between polar molecules in which hydrogen is bound to a larger atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen. This is not a sharing of electrons, as in a covalent bond. Instead, this is an attraction between the positive and negative poles of charged atoms. ...
What are the Parts of a Plant Cell?
By: HWC, Views: 10764
Every chloroplast in a plant cell is packed with stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll, as well as most of the other components required for the light reactions of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll-containing structures within the membranes are c...
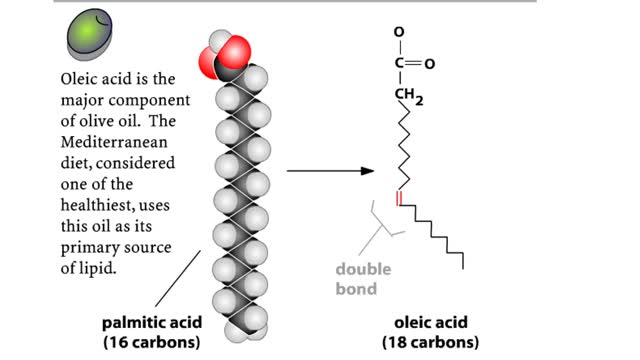
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Lipids
By: HWC, Views: 11114
A triglyceride (also called triacylglycerol) is composed of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. The fatty acids attach to the glycerol molecule by a covalent ester bond. The long hydrocarbon chain of each fatty acid makes the triglyceride molecule nonpolar and hydrophobic. Pa...
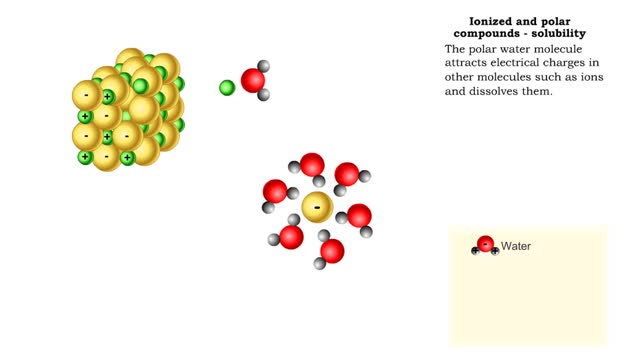
Properties of water -structure of water and polarity (Ionized and polar compounds)
By: HWC, Views: 11863
■ Water transports most of the molecules in the body. ■ The structure of a water molecule allows it to dissolve other molecules. ■ Shared electrons spend more time near the oxygen atom. ■ Oxygen end has a partial negative charge. ■ Hydrogen ends have a partial positive charge....
Sister chromatids of a metaphase chromosome animation
By: HWC, Views: 9909
At metaphase, the chromosomes are duplicated and are at their most condensed. In each chromosome. two identical sister chromatids are held together at a constricted region called the centromere. When a chromosome is condensed, interactions among chromosomal proteins keep loops of DNA tightly ...
Advertisement